A Motion for New Trial allows a party to request the court to reconsider and potentially overturn a verdict due to errors that affected the trial's fairness. It is commonly filed when new evidence emerges, procedural mistakes occur, or juror misconduct is evident. Explore the full article to understand how this motion can impact your case and the steps involved in filing it.
Table of Comparison
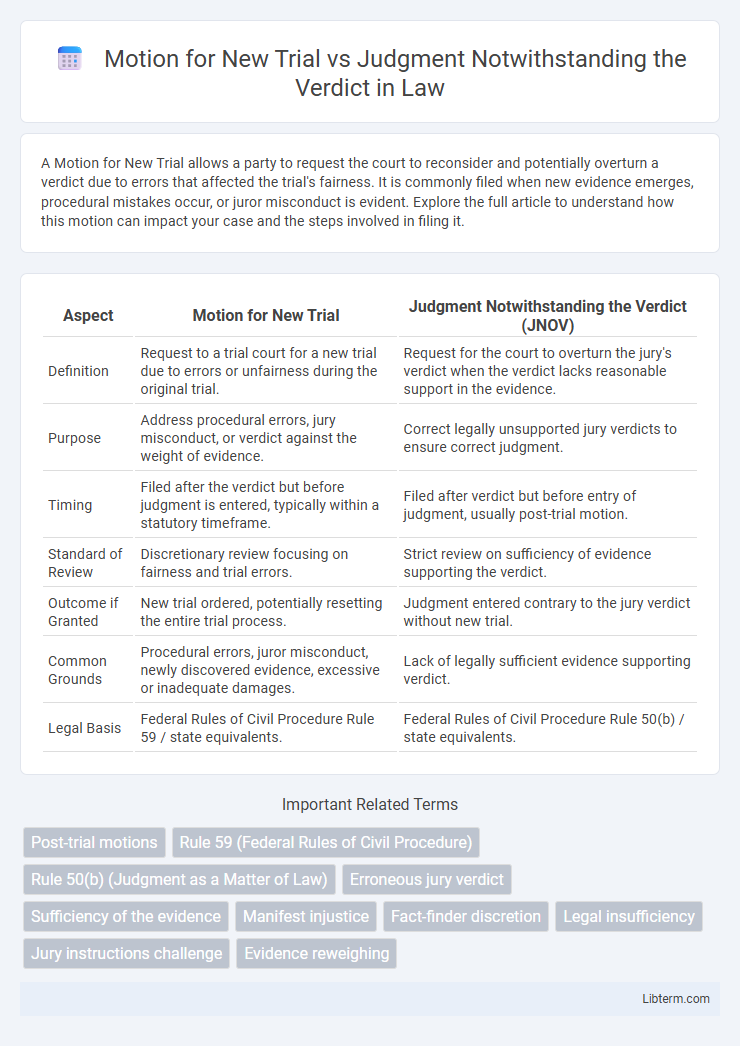
| Aspect | Motion for New Trial | Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Request to a trial court for a new trial due to errors or unfairness during the original trial. | Request for the court to overturn the jury's verdict when the verdict lacks reasonable support in the evidence. |
| Purpose | Address procedural errors, jury misconduct, or verdict against the weight of evidence. | Correct legally unsupported jury verdicts to ensure correct judgment. |
| Timing | Filed after the verdict but before judgment is entered, typically within a statutory timeframe. | Filed after verdict but before entry of judgment, usually post-trial motion. |
| Standard of Review | Discretionary review focusing on fairness and trial errors. | Strict review on sufficiency of evidence supporting the verdict. |
| Outcome if Granted | New trial ordered, potentially resetting the entire trial process. | Judgment entered contrary to the jury verdict without new trial. |
| Common Grounds | Procedural errors, juror misconduct, newly discovered evidence, excessive or inadequate damages. | Lack of legally sufficient evidence supporting verdict. |
| Legal Basis | Federal Rules of Civil Procedure Rule 59 / state equivalents. | Federal Rules of Civil Procedure Rule 50(b) / state equivalents. |
Introduction to Post-Trial Motions
Post-trial motions serve as critical tools for parties seeking to challenge or alter a jury's verdict, with a Motion for New Trial typically requesting a do-over due to errors affecting trial fairness or significant jury misconduct. In contrast, a Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) asks the court to overturn the jury's decision when the evidence overwhelmingly supports the opposing party, arguing that no reasonable jury could have reached the given verdict. Both motions must comply with strict procedural rules and deadlines, emphasizing the strategic importance of understanding their differing legal standards and practical applications in post-trial litigation.
Defining Motion for New Trial
A Motion for New Trial is a legal request filed by a party seeking to nullify a jury's verdict due to errors during the trial, such as procedural mistakes, newly discovered evidence, or prejudicial conduct affecting the outcome. Unlike a Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV), which asks the court to override the jury's decision based on insufficient evidence or legal errors, a Motion for New Trial aims to have the entire trial redone to ensure a fair proceeding. Courts grant a Motion for New Trial when they determine that substantial issues compromised the integrity of the original trial.
Understanding Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV)
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) is a post-trial motion filed by a party requesting the court to overturn the jury's verdict on the grounds that the evidence presented at trial was legally insufficient to support the verdict. JNOV targets errors in the application of law or insufficient factual support, contrasting with a Motion for New Trial, which generally challenges procedural errors or the fairness of the trial process. Courts grant JNOV only when no reasonable jury could have reached the verdict based on the evidence, emphasizing its role in correcting legal mistakes rather than re-evaluating factual disputes.
Legal Basis for Filing a Motion for New Trial
A Motion for New Trial is filed based on legal grounds such as errors in the trial procedure, newly discovered evidence, or verdicts that are against the weight of the evidence, as outlined in Rule 59 of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. The motion challenges the fairness or accuracy of the original trial, seeking to correct substantial mistakes or injustices. This legal basis contrasts with a Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV), which directly contests the sufficiency of evidence to support the jury's verdict under Rule 50.
Grounds for Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) is granted when the court finds that no reasonable jury could have reached the given verdict based on the evidence presented, indicating a legal error in applying the law to facts. Grounds for JNOV include insufficient evidence to support the jury's decision, contradictions in the jury's findings, or misapplication of legal standards by the jury. This motion challenges the factual basis of the jury verdict, seeking to correct errors that invalidate the outcome without a new trial.
Procedural Differences Between New Trial and JNOV
A Motion for New Trial challenges the trial court to set aside the jury's verdict due to errors affecting the trial's fairness, such as procedural mistakes or newly discovered evidence, requiring the court to weigh whether these errors likely impacted the outcome. In contrast, a Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) seeks to overturn the jury's decision by arguing that no reasonable jury could have reached such a verdict based on the evidence presented, focusing on legal insufficiency rather than procedural issues. Procedurally, a motion for a new trial is granted before the final judgment, allowing a retrial, whereas a JNOV is entered after the verdict and is a judgment as a matter of law, often bypassing further trial proceedings.
Burden of Proof and Judicial Standards
A Motion for New Trial challenges the fairness or correctness of trial proceedings, requiring the movant to prove errors or new evidence that likely affected the verdict. Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) demands a higher burden of proof, where the moving party must show that no reasonable jury could have reached the given verdict based on the evidence presented. Courts apply strict judicial standards in JNOV to overturn jury findings, whereas motions for a new trial allow more judicial discretion to remedy procedural or substantive trial errors.
Timing and Deadlines for Post-Trial Motions
A Motion for New Trial typically must be filed within 28 days after the entry of judgment, allowing parties to request a new trial due to errors or new evidence. Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) generally has a shorter deadline, often within 28 days post-verdict but before final judgment entry, challenging the sufficiency of the evidence supporting the jury's decision. Courts strictly enforce these timing rules to ensure timely resolution and preservation of appellate rights in post-trial motions.
Possible Outcomes and Legal Implications
A Motion for New Trial seeks to overturn a verdict due to errors during the trial or the verdict being against the weight of the evidence, potentially resulting in a completely new trial. Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) allows a judge to reverse the jury's decision if no reasonable jury could have reached that verdict based on the evidence presented. Both motions carry significant legal implications, affecting the finality of judgments and potentially prolonging litigation or altering case outcomes without starting anew.
Strategic Considerations for Litigants
Filing a Motion for New Trial allows litigants to challenge a verdict based on errors during the trial or newly discovered evidence, providing an opportunity to rectify factual or procedural mistakes without overturning the entire judgment. A Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) targets the legal sufficiency of the evidence, requesting the court to overturn the jury's decision when no reasonable jury could have reached that verdict. Strategic considerations include assessing the strength of evidence versus procedural errors, the likelihood of success, and potential impacts on settlement negotiations and appellate review.
Motion for New Trial Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com