Statutory interpretation involves analyzing and applying laws enacted by legislative bodies to specific cases, ensuring that the legislature's intent is honored while addressing the language's literal and contextual meaning. This process often requires examining the text, legislative history, and purpose of the statute to resolve ambiguities and reconcile conflicting provisions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how statutory interpretation shapes legal outcomes and impacts your rights.
Table of Comparison
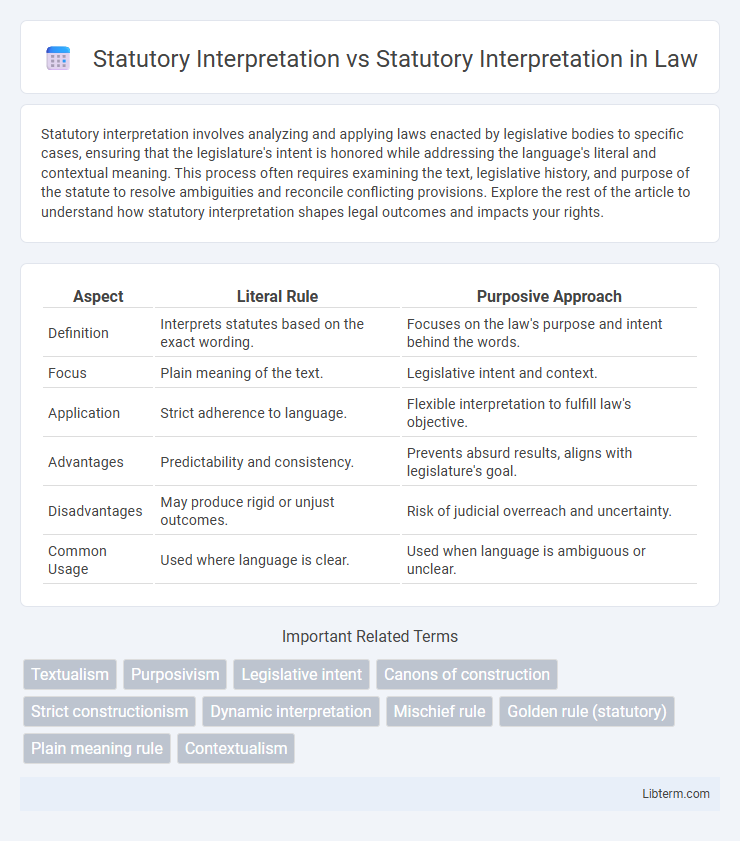
| Aspect | Literal Rule | Purposive Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interprets statutes based on the exact wording. | Focuses on the law's purpose and intent behind the words. |
| Focus | Plain meaning of the text. | Legislative intent and context. |
| Application | Strict adherence to language. | Flexible interpretation to fulfill law's objective. |
| Advantages | Predictability and consistency. | Prevents absurd results, aligns with legislature's goal. |
| Disadvantages | May produce rigid or unjust outcomes. | Risk of judicial overreach and uncertainty. |
| Common Usage | Used where language is clear. | Used when language is ambiguous or unclear. |
Introduction to Statutory Interpretation
Statutory interpretation involves the process by which courts analyze and apply legislation to specific cases, ensuring that the intent of lawmakers is accurately implemented. It requires understanding the literal, purposive, and contextual meanings of statutory language to resolve ambiguities and fill gaps within the law. Effective statutory interpretation balances the plain meaning of the text with legislative intent, judicial precedent, and broader legal principles to achieve just outcomes.
The Importance of Statutory Interpretation in Legal Systems
Statutory interpretation plays a critical role in legal systems by ensuring that laws are applied consistently and fairly according to legislative intent. Courts rely on interpretation principles, such as the literal, purposive, and golden rules, to resolve ambiguities in statutory language and adapt laws to evolving social contexts. Accurate statutory interpretation upholds the rule of law, prevents arbitrary decision-making, and supports judicial accountability within constitutional frameworks.
Key Principles of Statutory Interpretation
Key principles of statutory interpretation include the literal rule, which focuses on the plain and ordinary meaning of the text, the golden rule that allows modification of the literal meaning to avoid absurd results, and the purposive approach emphasizing the legislature's intended purpose behind the statute. Courts also apply the ejusdem generis principle, restricting general words to the same category as specific words preceding them, and the noscitur a sociis rule, interpreting words in context by considering associated terms. These principles collectively guide judicial decisions to ensure clarity, consistency, and alignment with legislative intent in applying statutory law.
Historical Development of Statutory Interpretation
Historical development of statutory interpretation reveals a transition from rigid textualism to purposive approaches, reflecting evolving judicial philosophies and legislative complexities. Early interpretative methods prioritized literal meanings based on common law traditions, while modern frameworks incorporate legislative intent and social context to resolve ambiguities. This evolution enhances legal predictability and aligns statutory application with contemporary societal values, underscoring the dynamic nature of statutory construction.
Methods and Approaches to Statutory Interpretation
Methods and approaches to statutory interpretation primarily include the literal, golden, and purposive approaches, each emphasizing different aspects of legal texts. The literal method focuses on the ordinary meaning of the statute's language, while the golden rule allows modification to avoid absurd outcomes. The purposive approach seeks to fulfill the legislative intent behind the statute, often utilizing external materials such as legislative history and preambles to clarify ambiguous provisions.
Statutory Interpretation in Common Law Systems
Statutory interpretation in common law systems relies heavily on purposive and literal approaches to discern legislative intent, emphasizing the text's ordinary meaning within its legal context. Courts apply established canons of construction, such as the ejusdem generis rule and the mischief rule, to resolve ambiguities and ensure consistency with precedent. This method contrasts with civil law systems, where codified statutes predominate and judicial interpretation tends to be more systematic and less reliant on precedent.
Statutory Interpretation in Civil Law Jurisdictions
Statutory interpretation in civil law jurisdictions primarily relies on the literal meaning of the codified statutes, emphasizing the text within comprehensive legal codes such as the French Civil Code or the German Burgerliches Gesetzbuch. Judges in civil law systems often apply systematic and teleological methods to understand legislative intent, focusing on the purpose and broader context of the statute rather than precedent. This contrasts with common law systems, where judicial decisions and case law play a significant role in shaping statutory interpretation.
Challenges and Controversies in Statutory Interpretation
Challenges in statutory interpretation often arise from ambiguous language in legislation and differing judicial philosophies, leading to multiple plausible readings of the same statute. Controversies typically center on the balance between legislative intent and textualism, with debates over whether courts should prioritize the statute's literal wording or the purpose behind the law. These difficulties complicate consistent application of laws and influence how precedents shape future judicial decisions.
Judicial Precedents Impacting Statutory Interpretation
Judicial precedents significantly influence statutory interpretation by providing authoritative guidance on ambiguous legislative texts, ensuring consistency in legal application across different cases. Courts rely on prior decisions to clarify legislative intent, resolving conflicts arising from vague or broad statutory language. This precedent-based approach fosters stability in the legal system while allowing for adaptive interpretations aligned with evolving societal values.
Future Trends in Statutory Interpretation
Future trends in statutory interpretation emphasize the growing role of digital tools and artificial intelligence in analyzing legislative texts, enhancing precision and reducing human bias. Courts increasingly rely on contextual and purposive approaches, integrating broader social and technological developments to ensure laws remain relevant amid rapid change. Emerging legal frameworks also highlight the importance of transparency and inclusivity, promoting equitable access to justice through adaptive interpretative methods.
Statutory Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com