Suspension plays a critical role in vehicle performance, impacting ride comfort, handling, and safety by absorbing shocks from road irregularities. Modern suspension systems are designed using advanced materials and technologies to optimize stability and control, enhancing your driving experience. Explore the rest of this article to understand the different types of suspension systems and how they affect your vehicle.
Table of Comparison
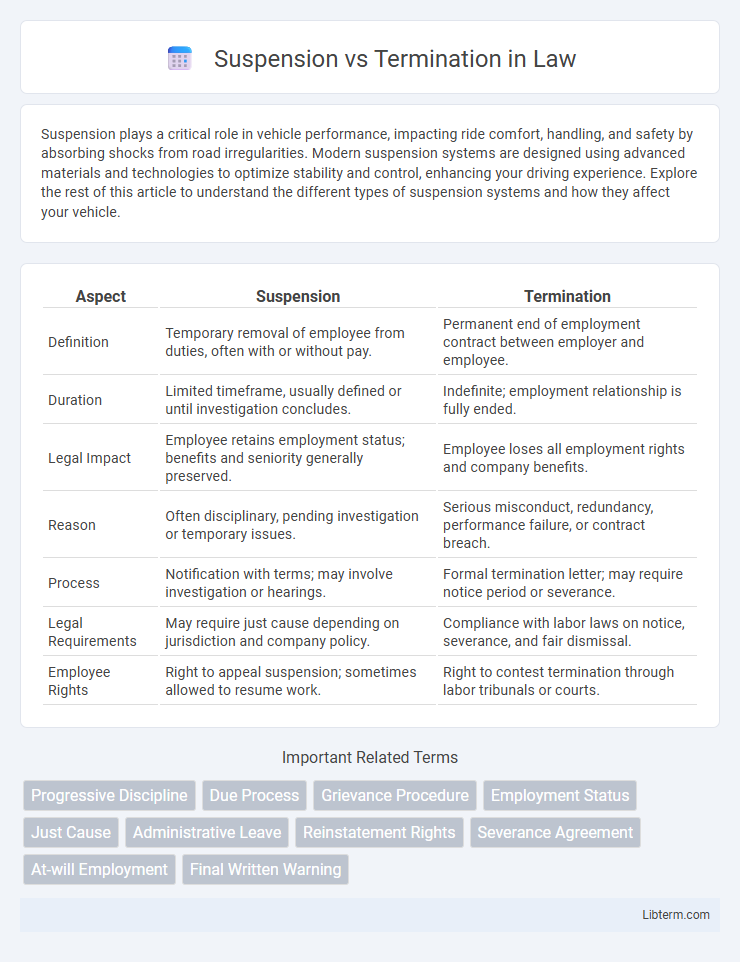
| Aspect | Suspension | Termination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary removal of employee from duties, often with or without pay. | Permanent end of employment contract between employer and employee. |
| Duration | Limited timeframe, usually defined or until investigation concludes. | Indefinite; employment relationship is fully ended. |
| Legal Impact | Employee retains employment status; benefits and seniority generally preserved. | Employee loses all employment rights and company benefits. |
| Reason | Often disciplinary, pending investigation or temporary issues. | Serious misconduct, redundancy, performance failure, or contract breach. |
| Process | Notification with terms; may involve investigation or hearings. | Formal termination letter; may require notice period or severance. |
| Legal Requirements | May require just cause depending on jurisdiction and company policy. | Compliance with labor laws on notice, severance, and fair dismissal. |
| Employee Rights | Right to appeal suspension; sometimes allowed to resume work. | Right to contest termination through labor tribunals or courts. |
Understanding Suspension and Termination
Suspension temporarily halts an employee's work duties or access to company resources, often as a disciplinary measure or pending investigation, while termination permanently ends the employment relationship. Understanding suspension involves recognizing it as a reversible action aimed at addressing specific issues without severing ties, whereas termination signifies a final decision due to performance, conduct, or organizational needs. Both actions impact employee status and require clear documentation to ensure compliance with employment laws and company policies.
Key Differences Between Suspension and Termination
Suspension temporarily halts an employee's work duties without ending employment, often used as a disciplinary measure or during investigations, while termination permanently ends the employment relationship. Suspension preserves the employee's status and benefits, whereas termination results in loss of all employee privileges and separation from the company. The key differences lie in duration, intent, and impact on employee rights and company obligations.
Legal Implications of Suspension vs Termination
Suspension temporarily halts an employee's duties without severing the employment contract, allowing for investigation or disciplinary review, while termination permanently ends the employment relationship and triggers legal obligations such as final paycheck, severance, and potential claims of wrongful dismissal. Legal implications of suspension often involve ensuring due process and adherence to labor laws to avoid allegations of unfair treatment, whereas termination requires strict compliance with statutory requirements, including notice periods and valid grounds to minimize litigation risk. Employers must document all actions meticulously to defend against disputes, as both suspension and termination carry significant legal consequences affecting employee rights and organizational liabilities.
Common Reasons for Employee Suspension
Employee suspension commonly occurs due to violations of workplace policies, such as misconduct, insubordination, or breaches of safety protocols. Employers also suspend employees pending investigations into allegations like harassment, theft, or fraud to maintain workplace integrity. Frequent causes include repeated absenteeism, poor performance, or failure to comply with company regulations, distinguishing suspension from termination, which usually follows unresolved or severe infractions.
Typical Grounds for Employee Termination
Typical grounds for employee termination include poor performance, violation of company policies, misconduct, and gross negligence. Termination may also result from redundancy due to organizational restructuring or economic downturns. Employers must document these grounds clearly to ensure compliance with labor laws and minimize legal risks.
Suspension Process: Steps and Best Practices
The suspension process involves key steps such as clear documentation of the reasons, delivering a formal notice to the employee, and setting a defined suspension period to provide time for investigation or corrective action. Best practices emphasize maintaining transparent communication, ensuring compliance with company policies and labor laws, and conducting a fair review before reinstatement or termination decisions. Properly managing suspension mitigates legal risks and sustains employee trust during disciplinary proceedings.
Termination Procedures: What Employers Need to Know
Termination procedures require employers to follow legal guidelines, including providing documented reasons for dismissal and adhering to notice period regulations under labor laws. Employers must conduct exit interviews, settle final payments promptly, and ensure compliance with anti-discrimination statutes to avoid wrongful termination claims. Proper documentation and transparent communication during termination minimize legal risks and maintain organizational integrity.
Impact on Employee Benefits: Suspension vs Termination
Suspension temporarily halts an employee's work duties while often maintaining eligibility for certain benefits such as health insurance and retirement contributions, depending on company policy and legal requirements. Termination typically ends all employee benefits immediately or after a short grace period, including health coverage, retirement plans, and accrued paid time off. Employers must clearly communicate the specific benefits status during suspension or after termination to ensure compliance and support for the employee.
How Suspension and Termination Affect Company Culture
Suspension often signals a temporary disciplinary measure that can create uncertainty and tension within company culture, potentially undermining employee trust and morale. Termination conveys a more definitive action that may reinforce accountability but risks fostering fear and decreased loyalty among remaining staff. Both suspension and termination influence workplace atmosphere, shaping perceptions of fairness and management transparency critical to sustained employee engagement.
Best Practices for Employers: Choosing the Right Disciplinary Action
Employers should carefully assess the severity and context of employee misconduct to decide between suspension and termination, ensuring actions align with company policies and legal requirements. Suspension serves as a temporary measure to investigate issues or provide corrective opportunities, while termination is reserved for severe or repeated violations that jeopardize workplace safety or integrity. Documenting the decision-making process, communicating transparently with the employee, and consulting legal counsel help mitigate risks and foster a fair disciplinary environment.
Suspension Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com