A witness plays a crucial role in providing firsthand testimony that can influence the outcome of legal proceedings or investigations. Their observations and accounts help establish facts and verify events, ensuring justice and truth are upheld. Discover how witness testimonies impact cases and what you need to know about their role in the following article.
Table of Comparison
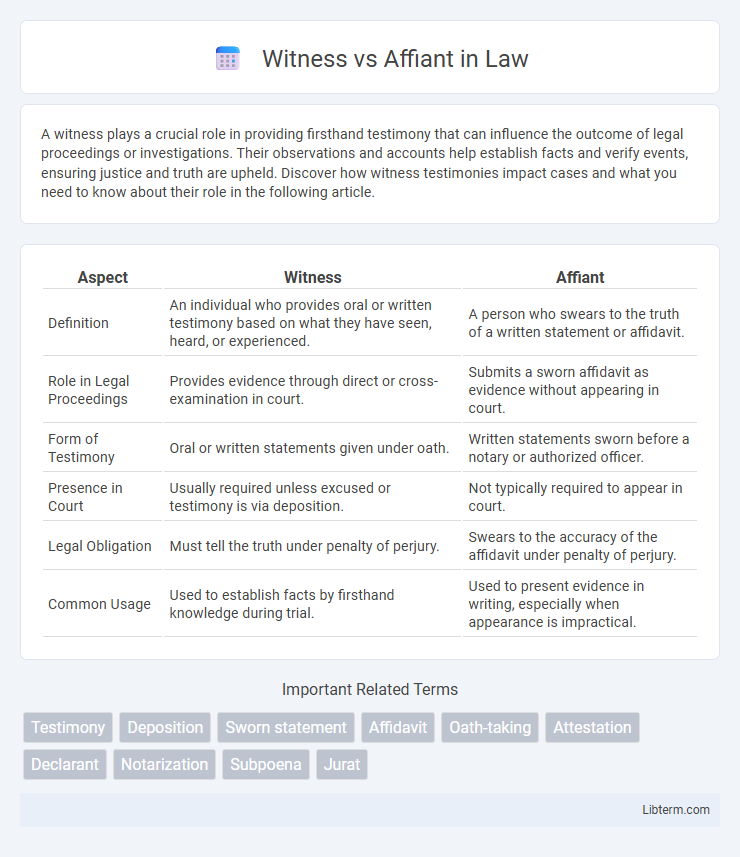
| Aspect | Witness | Affiant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An individual who provides oral or written testimony based on what they have seen, heard, or experienced. | A person who swears to the truth of a written statement or affidavit. |
| Role in Legal Proceedings | Provides evidence through direct or cross-examination in court. | Submits a sworn affidavit as evidence without appearing in court. |
| Form of Testimony | Oral or written statements given under oath. | Written statements sworn before a notary or authorized officer. |
| Presence in Court | Usually required unless excused or testimony is via deposition. | Not typically required to appear in court. |
| Legal Obligation | Must tell the truth under penalty of perjury. | Swears to the accuracy of the affidavit under penalty of perjury. |
| Common Usage | Used to establish facts by firsthand knowledge during trial. | Used to present evidence in writing, especially when appearance is impractical. |
Understanding the Terms: Witness and Affiant
A witness is an individual who observes an event or occurrence and can provide a firsthand account, while an affiant is a person who makes a sworn statement or affidavit under oath. The key distinction lies in the affiant's formal declaration of facts in a legal document, whereas a witness may simply testify based on personal observation. Understanding these roles is essential for accurately interpreting testimony and affidavits in legal proceedings.
Legal Definitions: Witness vs Affiant
A witness is an individual who observes an event or provides testimony based on personal knowledge, often appearing in court to verify facts. An affiant is a person who makes a sworn statement or affidavit, declaring facts under oath for legal purposes. The key legal difference lies in a witness recounting firsthand observations, while an affiant formally affirms information through a written and notarized affidavit.
Roles and Responsibilities in Legal Proceedings
A witness in legal proceedings provides firsthand testimony or evidence based on personal knowledge or observation, playing a crucial role in establishing facts during trials or hearings. An affiant, on the other hand, is a person who makes a sworn affidavit, a written statement confirmed by oath or affirmation for use as evidence in court, often summarizing facts or circumstances relevant to the case. While witnesses typically present oral evidence in court, affiants contribute documented, sworn statements that support motions, case filings, or pre-trial discoveries.
The Function of a Witness in Court
A witness in court provides firsthand testimony or evidence based on their direct observations or experiences relevant to the case. Their primary function is to establish facts and corroborate or refute statements presented by parties involved, ensuring the tribunal evaluates credible and reliable information. Witness credibility and consistency significantly impact the judicial outcome and the court's determination of truth.
Duties and Significance of an Affiant
An affiant is a person who provides a sworn written statement or affidavit under oath, bearing legal responsibility for the truthfulness of the content. Unlike a witness who may verbally testify based on personal knowledge or observation, the affiant's duties include verifying facts in a legally binding document used as evidence in court proceedings. The significance of an affiant lies in their role to formally assert the accuracy of statements, which holds substantial weight in judicial decisions and legal processes.
Affidavits: The Affiant’s Perspective
An affiant is the individual who provides a sworn statement or affidavit, asserting facts based on personal knowledge under oath. From the affiant's perspective, the accuracy and truthfulness of the affidavit are paramount, as it carries legal significance and potential consequences for false declarations. The affidavit serves as direct evidence, with the affiant's credibility critically impacting the document's weight in judicial or administrative proceedings.
Key Differences Between Witness and Affiant
A witness provides firsthand testimony based on direct observation or experience, often recounting events they personally saw or heard, while an affiant makes sworn statements or affidavits, affirming the truth of specific facts under oath. Witnesses typically testify in court or legal proceedings without necessarily swearing an affidavit, whereas affiants present written declarations that are legally binding and used as evidence. The primary distinction lies in the format and context of their statements: oral testimony for witnesses versus sworn written statements for affiants.
Situations Requiring a Witness or Affiant
Situations requiring a witness or affiant often involve legal documents such as affidavits, contracts, or sworn statements where verification of identity and authenticity is crucial. A witness is typically present to observe the signing or occurrence of an event, ensuring the validity of the act, while an affiant provides a sworn statement under oath, confirming the truthfulness of the content. Courts and legal processes frequently mandate the presence of either a witness or an affiant to establish credibility and prevent disputes or fraud.
Legal Implications: Who Can Serve as Each?
A witness is any individual who personally observes an event or signs a document, providing testimony or validation without necessarily being involved in the legal matter. An affiant is a person who makes a sworn statement or affidavit, affirming the truth of specific facts under oath, and must have personal knowledge of the information stated. Courts typically require affiants to have direct knowledge and the capacity to swear to the affidavit's accuracy, whereas witnesses can be any credible observer or signer, impacting the admissibility and weight of evidence in legal proceedings.
Importance of Witnesses and Affiants in Legal Documents
Witnesses and affiants play crucial roles in legal documents by providing verification and authenticity to statements and actions. A witness observes and attests to the execution of a document or event, ensuring its validity, while an affiant provides a sworn written statement or affidavit under oath, which serves as evidence in legal proceedings. Their involvement strengthens the credibility and enforceability of legal documents, reducing disputes and supporting judicial processes.
Witness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com