Administrative regulations establish the framework within which government agencies operate, ensuring policies are implemented consistently and legally. These rules are essential for maintaining order, protecting public interests, and providing transparency in administrative actions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these regulations impact your daily life and business operations.
Table of Comparison
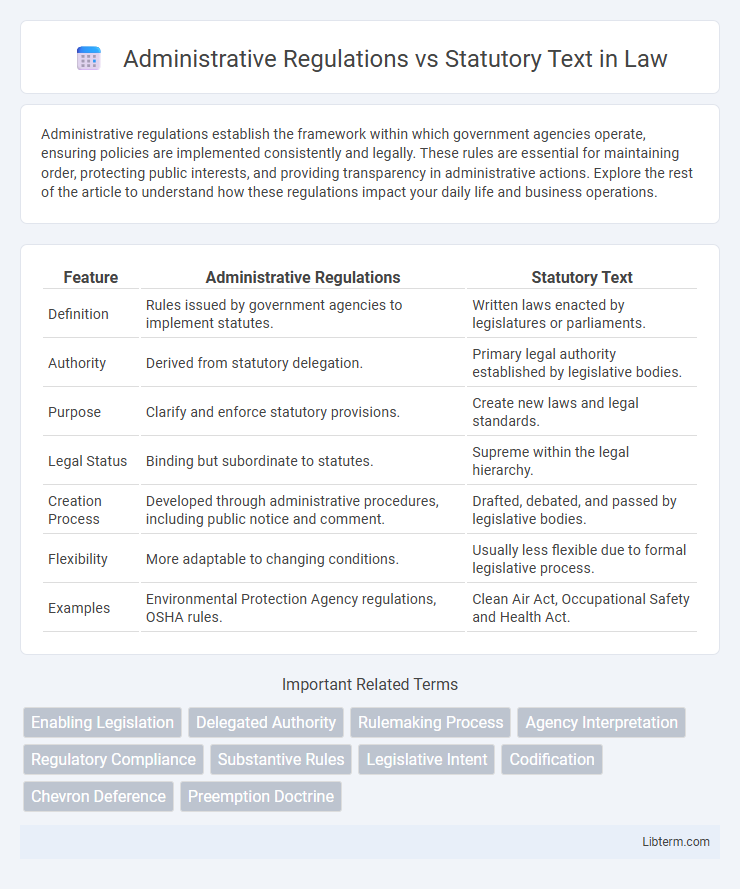
| Feature | Administrative Regulations | Statutory Text |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules issued by government agencies to implement statutes. | Written laws enacted by legislatures or parliaments. |
| Authority | Derived from statutory delegation. | Primary legal authority established by legislative bodies. |
| Purpose | Clarify and enforce statutory provisions. | Create new laws and legal standards. |
| Legal Status | Binding but subordinate to statutes. | Supreme within the legal hierarchy. |
| Creation Process | Developed through administrative procedures, including public notice and comment. | Drafted, debated, and passed by legislative bodies. |
| Flexibility | More adaptable to changing conditions. | Usually less flexible due to formal legislative process. |
| Examples | Environmental Protection Agency regulations, OSHA rules. | Clean Air Act, Occupational Safety and Health Act. |
Introduction to Administrative Regulations and Statutory Text
Administrative regulations are rules created by government agencies based on authority granted by statutory law, providing detailed guidelines for implementing and enforcing statutes. Statutory text refers to the exact language of laws passed by legislative bodies, serving as the foundational legal authority. Understanding the relationship between statutory text and administrative regulations is essential for interpreting legal requirements and government policies accurately.
Defining Statutory Text: Origins and Purpose
Statutory text originates from legislatures and embodies formal laws passed by governing bodies to establish legal standards and obligations. It serves as the authoritative source for legal interpretation, providing clear, codified rules that regulate behavior and government functions. Defining statutory text involves understanding its role in establishing binding duties and rights, distinct from administrative regulations, which interpret and implement these legal mandates.
Understanding Administrative Regulations: Scope and Function
Administrative regulations are rules issued by government agencies based on statutory authority, defining the practical implementation of laws. These regulations have the force of law but operate within the scope set by the statutory text, providing detailed guidelines and procedures to ensure compliance. Understanding the scope and function of administrative regulations is essential for interpreting how agencies enforce statutes and manage public policies effectively.
The Legal Authority Behind Statutes and Regulations
Statutory text represents laws enacted directly by legislatures, carrying the highest legal authority as formal acts or statutes. Administrative regulations are detailed rules created by government agencies, authorized by statutes to implement and enforce legislative intent. The legal authority behind statutes originates from constitutional or legislative powers, while regulations derive their force from enabling statutes that delegate specific regulatory responsibilities.
Differences in Drafting and Language
Administrative regulations are drafted with detailed, technical language tailored for implementation and enforcement by specific agencies, reflecting interpretative authority within legislative frameworks. Statutory texts, in contrast, are written in broader, more general language intended to establish legal principles and mandates enacted by legislative bodies. The drafting of statutes emphasizes clarity and permanence, while regulations prioritize adaptability and specificity to address practical policy applications.
Implementation: From Statute to Regulation
Statutory text provides the legal foundation by outlining broad legislative mandates enacted by government bodies, while administrative regulations translate these mandates into detailed, actionable rules enforced by regulatory agencies. The implementation process involves agencies interpreting statutory language to develop specific standards, procedures, and compliance requirements that ensure effective enforcement and public adherence. This transformation from statute to regulation bridges legislative intent and practical application, enabling adaptive governance in complex regulatory environments.
Judicial Interpretation: Statutory Text vs. Regulations
Judicial interpretation often prioritizes statutory text as the primary source of legal authority, ensuring that courts adhere closely to the language enacted by legislatures. Regulations, created by administrative agencies, must align with statutory mandates, but courts evaluate their validity by examining whether they reasonably interpret or implement the underlying statutes. When conflicts arise, judges generally defer to the plain meaning of statutory provisions unless the regulatory interpretation falls within the agency's expertise and does not contradict clear legislative intent.
Compliance and Enforcement Mechanisms
Administrative regulations provide detailed rules developed by government agencies to implement statutory text, ensuring precise compliance standards. These regulations establish enforcement mechanisms like inspections, penalties, and administrative hearings, facilitating effective oversight beyond the statutory framework. Statutory text outlines broad legal mandates, while enforcement authority primarily resides within the administrative regulations that specify procedural and substantive requirements.
Impact on Organizations and Individuals
Administrative regulations, issued by government agencies, provide detailed rules that directly affect organizations' operational compliance and impose specific obligations on individuals within regulated sectors. Statutory text, enacted by legislatures, establishes the fundamental legal framework and broad mandates that shape organizational policies and protect individual rights. The interaction between statutory laws and administrative regulations determines the scope of legal responsibilities and enforcement mechanisms impacting both entities and persons.
Conclusion: Navigating Statutes and Administrative Rules
Statutory text constitutes the formal laws enacted by legislative bodies, providing clear legal mandates, while administrative regulations interpret and implement these statutes through detailed rules. Understanding the hierarchy and relationship between statutes and administrative rules is essential for effective legal navigation and compliance. Mastery of both statutory provisions and administrative regulations ensures accurate application of law and informed decision-making in regulatory environments.
Administrative Regulations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com