Operative clauses specify the essential obligations, rights, or actions agreed upon within a contract or legal document. Understanding these clauses ensures your responsibilities and entitlements are clearly defined, minimizing potential disputes. Explore the rest of the article to learn how operative clauses impact your agreements effectively.
Table of Comparison
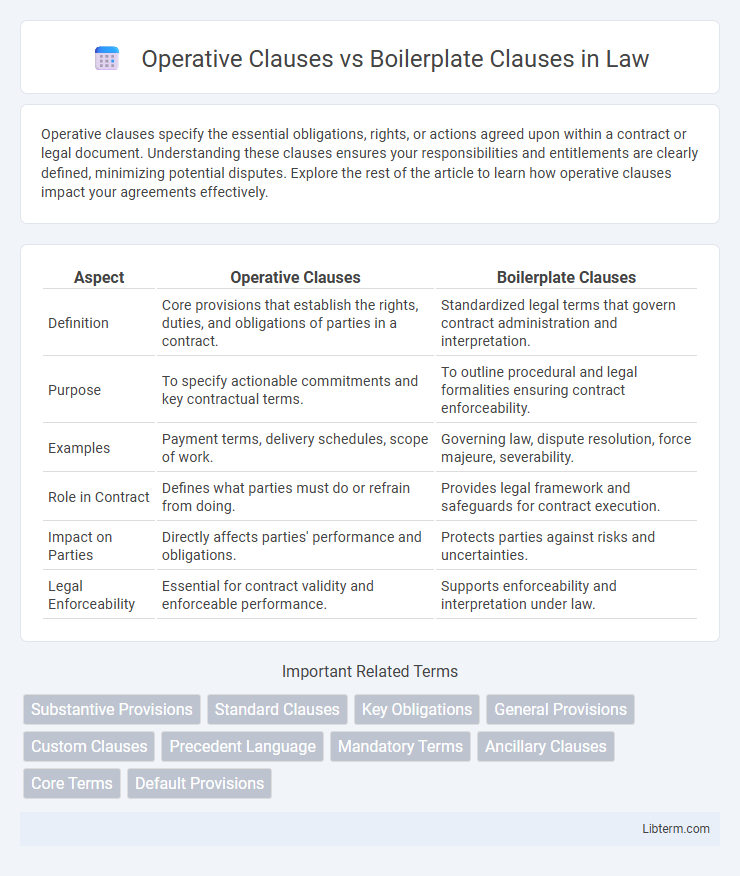
| Aspect | Operative Clauses | Boilerplate Clauses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Core provisions that establish the rights, duties, and obligations of parties in a contract. | Standardized legal terms that govern contract administration and interpretation. |
| Purpose | To specify actionable commitments and key contractual terms. | To outline procedural and legal formalities ensuring contract enforceability. |
| Examples | Payment terms, delivery schedules, scope of work. | Governing law, dispute resolution, force majeure, severability. |
| Role in Contract | Defines what parties must do or refrain from doing. | Provides legal framework and safeguards for contract execution. |
| Impact on Parties | Directly affects parties' performance and obligations. | Protects parties against risks and uncertainties. |
| Legal Enforceability | Essential for contract validity and enforceable performance. | Supports enforceability and interpretation under law. |
Introduction to Contract Clauses
Operative clauses define the primary rights, obligations, and actions required by the parties in a contract, such as payment terms, delivery schedules, or service provisions. Boilerplate clauses consist of standardized terms that address procedural and legal aspects like dispute resolution, governing law, and amendment processes designed to ensure contract stability and interpretation consistency. Understanding the distinction and proper integration of these clauses is crucial for drafting comprehensive contracts that effectively allocate responsibilities and mitigate risks.
Defining Operative Clauses
Operative clauses are the core provisions in a contract that outline the specific rights, duties, and obligations of the parties involved, directly impacting the contract's enforceability. These clauses define actions to be performed, conditions to be met, or consequences for non-compliance, serving as the operative engine of the agreement. In contrast, boilerplate clauses consist of standard, repetitive language that governs procedural aspects like dispute resolution, jurisdiction, and notice requirements, supporting but not defining the contract's substantive terms.
What Are Boilerplate Clauses?
Boilerplate clauses are standard provisions included at the end of contracts to govern the interpretation, enforcement, and general administration of the agreement. These clauses typically cover topics such as dispute resolution, governing law, force majeure, assignment, and notice requirements, ensuring predictable legal outcomes and protecting parties' rights. Unlike operative clauses, which define the main rights and obligations, boilerplate clauses provide the essential legal framework that supports and stabilizes the contract's operation.
Key Features of Operative Clauses
Operative clauses in contracts define the primary rights, duties, and obligations of the parties, establishing the legal framework for enforcement and performance. These clauses include essential terms such as payment obligations, delivery schedules, and scope of work, ensuring clarity and precision in contractual intent. Unlike boilerplate clauses, which address procedural or administrative matters, operative clauses form the core substantive provisions critical to the contract's execution.
Common Examples of Boilerplate Clauses
Common examples of boilerplate clauses include arbitration agreements, force majeure, indemnity, confidentiality, and governing law provisions, which establish standardized terms that apply across various contracts. These clauses provide legal certainty and procedural frameworks, reducing ambiguity and disputes in contractual relationships. In contrast, operative clauses specifically define the parties' rights and obligations, detailing the core actions and performance duties under the agreement.
Differences Between Operative and Boilerplate Clauses
Operative clauses establish the core obligations, rights, and duties of the parties involved in a contract, defining what each party must perform or refrain from doing. Boilerplate clauses consist of standard contractual provisions that address administrative and procedural matters such as dispute resolution, jurisdiction, and contract modification. The primary difference lies in operative clauses shaping the substantive deal terms, while boilerplate clauses provide the structural framework ensuring the contract's enforceability and interpretation.
Legal Significance of Operative Clauses
Operative clauses in legal documents define the specific rights, duties, and obligations that directly impact the parties involved, making them crucial for the enforceability of contracts. These clauses establish the substantive terms of the agreement, such as payment obligations, delivery schedules, and performance standards, thereby determining the legal framework within which the contract operates. In contrast, boilerplate clauses cover procedural and administrative aspects, like dispute resolution and jurisdiction, which support but do not directly create or alter the core contractual obligations.
The Role of Boilerplate Clauses in Contracts
Boilerplate clauses play a critical role in contracts by establishing the foundational legal framework that governs contract interpretation, enforcement, and dispute resolution. These standardized provisions, such as jurisdiction, force majeure, and severability clauses, ensure consistency and predictability across various agreements while protecting parties from unforeseen legal complications. They complement operative clauses, which outline specific rights and obligations, by addressing overarching contractual mechanisms and procedural safeguards.
Best Practices for Drafting Contract Clauses
Operative clauses define the fundamental rights and obligations of the parties, making clarity and precision essential to avoid ambiguity and disputes. Boilerplate clauses, such as force majeure, governing law, and dispute resolution, provide standardized contractual terms that require careful customization to fit the specific context of the agreement. Best practices for drafting contract clauses emphasize using clear, unambiguous language, tailoring boilerplate terms to the transaction's nature, and ensuring that operative clauses align with the overall contractual intent and legal requirements.
Conclusion: Crafting Balanced Contractual Agreements
Operative clauses define the core obligations and rights that drive the performance of a contract, ensuring clear accountability between parties. Boilerplate clauses provide standardized legal protections and procedural mechanisms to manage risk and enforceability across various scenarios. Crafting balanced contractual agreements requires integrating precise operative terms with well-tailored boilerplate provisions to create clarity, minimize disputes, and secure mutual benefit.
Operative Clauses Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com