Arraignment is a critical step in the criminal justice process where a defendant is formally charged and informed of their rights, including the right to counsel and to enter a plea. Understanding the arraignment phase can help you navigate the legal system more confidently and prepare for the next stages of your case. Read on to learn more about what to expect during an arraignment and how it impacts your defense strategy.
Table of Comparison
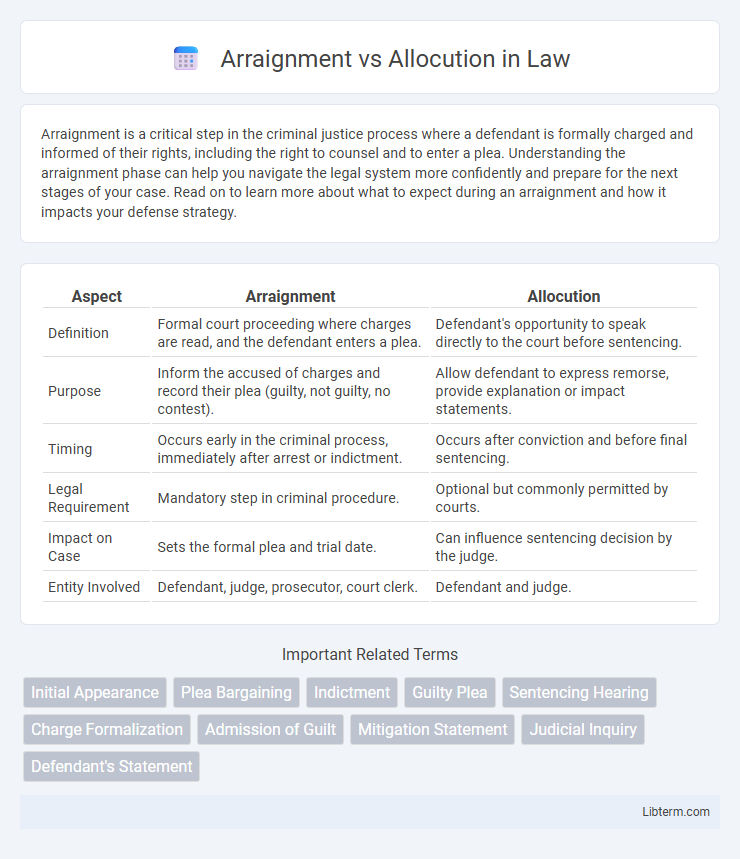
| Aspect | Arraignment | Allocution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal court proceeding where charges are read, and the defendant enters a plea. | Defendant's opportunity to speak directly to the court before sentencing. |
| Purpose | Inform the accused of charges and record their plea (guilty, not guilty, no contest). | Allow defendant to express remorse, provide explanation or impact statements. |
| Timing | Occurs early in the criminal process, immediately after arrest or indictment. | Occurs after conviction and before final sentencing. |
| Legal Requirement | Mandatory step in criminal procedure. | Optional but commonly permitted by courts. |
| Impact on Case | Sets the formal plea and trial date. | Can influence sentencing decision by the judge. |
| Entity Involved | Defendant, judge, prosecutor, court clerk. | Defendant and judge. |
Understanding Arraignment: Definition and Purpose
Arraignment is a critical early step in the criminal justice process where a defendant is formally presented with charges and asked to enter a plea, ensuring their understanding of the accusations. This proceeding helps establish the court's jurisdiction over the defendant and informs them of their legal rights, including the right to counsel. The purpose of arraignment is to clarify the charges, facilitate an initial plea, and set the stage for future trial proceedings or negotiations.
What Is Allocution in Criminal Proceedings?
Allocution in criminal proceedings is a defendant's formal opportunity to speak directly to the court before sentencing, allowing them to express remorse, explain circumstances, or request leniency. Unlike arraignment, which is a procedural step to inform the accused of charges and enter a plea, allocution focuses on personal statements to impact the judge's sentencing decision. Courts view allocution as a critical component of justice, providing defendants a voice in their sentencing phase and potentially influencing outcomes.
Key Differences Between Arraignment and Allocution
Arraignment is a court proceeding where the defendant is formally charged and asked to enter a plea, while allocution occurs after conviction, allowing the defendant to make a statement before sentencing. The key difference lies in their timing and purpose: arraignment establishes the defendant's plea to the charges, whereas allocution provides an opportunity to present mitigating factors or express remorse. Arraignment ensures the defendant's understanding of the charges, whereas allocution aims to influence the severity of the sentence.
The Role of the Defendant During Arraignment
During arraignment, the defendant's role centers on formally hearing the charges and entering a plea, such as guilty, not guilty, or no contest. This stage ensures the defendant is informed of their legal rights and the nature of the accusations, setting the foundation for the subsequent trial process. Unlike allocution, which allows the defendant to speak on their own behalf before sentencing, arraignment primarily focuses on procedural adherence and plea recording.
The Defendant’s Rights During Allocution
During allocution, the defendant has the right to address the court personally before sentencing, presenting factors such as remorse, mitigating circumstances, or reasons for leniency. This stage ensures the defendant's voice is heard, influencing the judge's sentencing decision within the framework established during arraignment. Allocution upholds procedural fairness by allowing the defendant to impact outcomes beyond the formal plea entered earlier.
Legal Procedures: How Arraignment Works
Arraignment is a critical initial step in criminal legal procedures where the defendant is formally charged and informed of their rights in court. During arraignment, the judge reads the charges aloud, ensures the defendant understands them, and requests a plea of guilty, not guilty, or no contest. This process sets the stage for subsequent proceedings, including bail considerations and trial scheduling, highlighting its role in maintaining legal due process.
Legal Procedures: The Allocution Process
The allocution process in legal procedures allows a defendant to personally address the court before sentencing, providing an opportunity to express remorse or explain mitigating circumstances. This stage follows arraignment, where formal charges are read, and pleas are entered, setting the framework for the trial or resolution. Allocution is a critical part of sentencing hearings, influencing judicial discretion and potentially affecting the severity of the punishment.
Importance of Arraignment in Criminal Justice
Arraignment is a critical step in the criminal justice process where the defendant is formally charged and informed of their rights, ensuring procedural fairness and due process. This hearing establishes the court's jurisdiction and sets the stage for plea entry, bail decisions, and case scheduling, directly impacting the progression of a criminal case. Proper arraignment safeguards the defendant's constitutional rights and maintains the integrity of the judicial system by clarifying charges early in prosecution.
The Significance of Allocution Before Sentencing
Allocution before sentencing allows defendants to directly address the court, providing a crucial opportunity to express remorse, offer explanations, and present personal circumstances that may influence the judge's sentencing decision. Unlike arraignment, which mainly involves reading charges and entering pleas, allocution humanizes the defendant and impacts judicial discretion by adding a personal narrative to the legal process. This practice enhances fairness and can lead to more tailored, compassionate sentencing outcomes within the criminal justice system.
Common Myths About Arraignment and Allocution
Common myths about arraignment include the belief that it determines guilt or innocence, when in fact it primarily serves to inform the defendant of the charges and set bail or release conditions. Allocution is often misunderstood as a chance to argue the case, but it is actually an opportunity for defendants to personally address the court, express remorse, or provide mitigating circumstances before sentencing. Both stages are procedural steps designed to ensure fairness and give defendants a voice within the judicial process.
Arraignment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com