Habeas Corpus is a fundamental legal principle that protects individuals from unlawful detention by ensuring the right to challenge the legality of their imprisonment. This writ serves as a critical safeguard for personal freedom and prevents arbitrary arrest or imprisonment by authorities. Discover how the concept of habeas corpus impacts your rights and the justice system by reading the rest of the article.
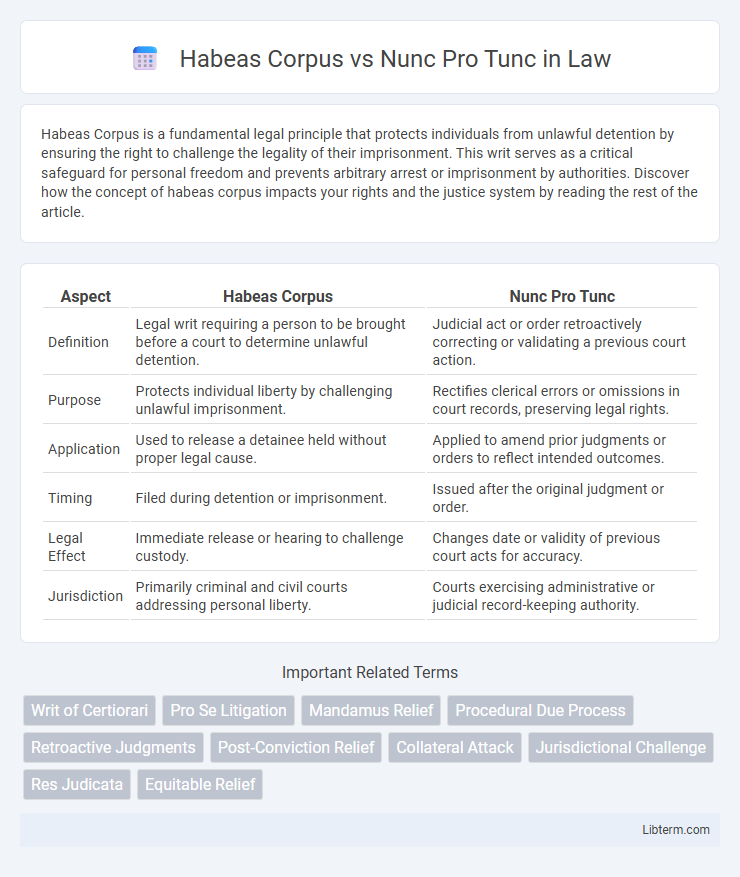
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Habeas Corpus | Nunc Pro Tunc |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal writ requiring a person to be brought before a court to determine unlawful detention. | Judicial act or order retroactively correcting or validating a previous court action. |
| Purpose | Protects individual liberty by challenging unlawful imprisonment. | Rectifies clerical errors or omissions in court records, preserving legal rights. |
| Application | Used to release a detainee held without proper legal cause. | Applied to amend prior judgments or orders to reflect intended outcomes. |
| Timing | Filed during detention or imprisonment. | Issued after the original judgment or order. |
| Legal Effect | Immediate release or hearing to challenge custody. | Changes date or validity of previous court acts for accuracy. |
| Jurisdiction | Primarily criminal and civil courts addressing personal liberty. | Courts exercising administrative or judicial record-keeping authority. |
Introduction to Habeas Corpus and Nunc Pro Tunc
Habeas Corpus is a legal writ requiring a person under arrest to be brought before a judge or court to determine if the detention is lawful. Nunc Pro Tunc is a judicial device used to retroactively correct or validate a previous court order or judgment as if it had been entered at an earlier date. Both serve important functions in legal procedure, with Habeas Corpus protecting individual liberty and Nunc Pro Tunc ensuring judicial accuracy and fairness.
Defining Habeas Corpus: Meaning and Legal Origins
Habeas Corpus is a fundamental legal principle that protects individual freedom by ensuring a person's right to challenge unlawful detention before a court. Originating from English common law, this writ compels authorities to produce the detained individual and justify the legality of their confinement. It serves as a crucial safeguard against arbitrary imprisonment and abuse of state power.
Nunc Pro Tunc Explained: Concept and Application
Nunc Pro Tunc, a Latin term meaning "now for then," is a legal doctrine allowing courts to correct earlier clerical or procedural errors retroactively to reflect the true intent or facts. This remedy is applied to amend records, judgments, or orders to ensure accuracy while preserving the original effective date, thus preventing injustice caused by administrative mistakes. Unlike Habeas Corpus, which challenges unlawful detention, Nunc Pro Tunc focuses on validating and correcting official legal documents and proceedings.
Historical Background: Habeas Corpus vs Nunc Pro Tunc
Habeas Corpus originated in 12th-century England as a legal remedy to prevent unlawful detention, establishing a fundamental protection of personal liberty by requiring authorities to justify imprisonment. Nunc Pro Tunc, meaning "now for then," evolved later as an equitable doctrine allowing courts to retroactively correct clerical errors in judgments or records, ensuring that the official record reflects what should have occurred at an earlier date. While Habeas Corpus safeguards individual freedom by challenging wrongful custody, Nunc Pro Tunc serves to maintain the accuracy and integrity of judicial records, reflecting distinct historical purposes within the legal system.
Key Legal Differences Between Habeas Corpus and Nunc Pro Tunc
Habeas corpus is a legal remedy used to challenge unlawful detention or imprisonment, ensuring a person's right to liberty by requiring the custodian to justify the detention before a court. Nunc pro tunc, meaning "now for then," is a judicial order correcting a previous record or judgment to reflect what should have been entered at an earlier date, effectively retroactively validating actions or decisions. The key legal difference lies in habeas corpus addressing personal liberty and unlawful custody, while nunc pro tunc concerns procedural accuracy and correcting clerical errors in court records.
Procedural Aspects: Filing Habeas Corpus vs Nunc Pro Tunc
Filing a Habeas Corpus petition involves challenging unlawful detention or imprisonment through a post-conviction remedy, typically requiring proof that the detention violates constitutional rights. In contrast, a Nunc Pro Tunc filing requests a court to correct clerical errors or omissions in previous judgments or orders to reflect the intended decisions, without altering substantive rights. Habeas Corpus petitions follow strict procedural timelines and evidentiary standards, while Nunc Pro Tunc motions are generally filed within the same case to amend records and do not serve as independent remedies for detentions.
Use Cases: When to Apply Habeas Corpus or Nunc Pro Tunc
Habeas Corpus is primarily used to challenge unlawful detention or imprisonment, ensuring a person's right to freedom if held without legal justification. Nunc Pro Tunc applies to correcting clerical or procedural errors in court records, effectively retroactively validating actions or judgments as if properly done at an earlier date. Use Habeas Corpus when contesting wrongful custody, while Nunc Pro Tunc is suitable for amending official documents to reflect the true intent of judicial rulings.
Impact on Criminal and Civil Proceedings
Habeas Corpus serves as a critical safeguard against unlawful detention by allowing individuals to challenge the legality of their imprisonment, profoundly impacting criminal proceedings by ensuring due process and preventing arbitrary confinement. Nunc Pro Tunc orders correct earlier judicial errors or omissions in records, significantly influencing both criminal and civil cases by preserving parties' rights and maintaining procedural fairness without reopening final judgments. Together, these legal mechanisms uphold the integrity of the justice system by addressing different procedural needs: Habeas Corpus protects individual liberty, while Nunc Pro Tunc ensures accurate and just court records.
Landmark Cases Involving Habeas Corpus and Nunc Pro Tunc
Landmark cases involving habeas corpus, such as Brown v. Allen (1953), emphasize the protection against unlawful detention and the right to challenge imprisonment through federal habeas review. Nunc pro tunc orders, exemplified in cases like McCarty v. McCarty (1981), address the correction of judicial records to reflect actions retroactively, ensuring legal accuracy without infringing on substantive rights. The interplay of habeas corpus and nunc pro tunc remedies in these precedents reinforces procedural fairness and the proper administration of justice.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Legal Remedy
Selecting between Habeas Corpus and Nunc Pro Tunc depends on the specific legal issue and desired outcome, as Habeas Corpus addresses unlawful detention while Nunc Pro Tunc corrects clerical errors in court records retroactively. Habeas Corpus provides immediate relief for constitutional violations related to personal liberty, making it ideal for challenging unlawful imprisonment. Nunc Pro Tunc serves to ensure accuracy and fairness in judicial records, often used in appeals or to validate procedural mistakes, thus choosing the appropriate remedy requires a clear understanding of the legal context and objectives.
Habeas Corpus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com