Effective administrative skills streamline organizational processes, improve communication, and enhance overall productivity by ensuring tasks are completed accurately and on time. Mastering administrative functions empowers you to manage resources efficiently and support team collaboration seamlessly. Explore the rest of this article to discover actionable strategies for optimizing your administrative capabilities.
Table of Comparison
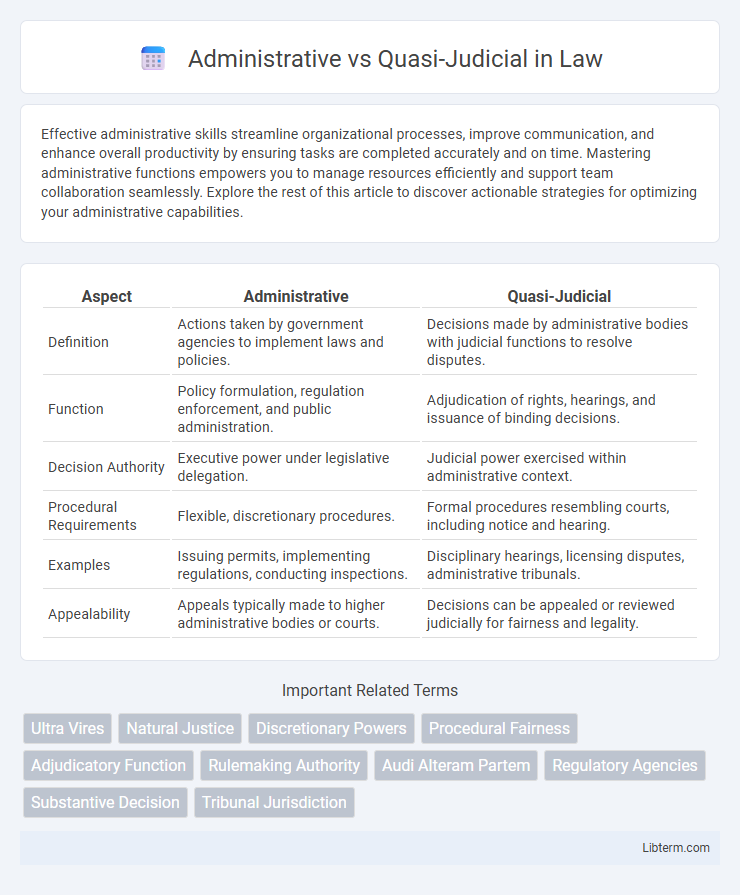
| Aspect | Administrative | Quasi-Judicial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actions taken by government agencies to implement laws and policies. | Decisions made by administrative bodies with judicial functions to resolve disputes. |
| Function | Policy formulation, regulation enforcement, and public administration. | Adjudication of rights, hearings, and issuance of binding decisions. |
| Decision Authority | Executive power under legislative delegation. | Judicial power exercised within administrative context. |
| Procedural Requirements | Flexible, discretionary procedures. | Formal procedures resembling courts, including notice and hearing. |
| Examples | Issuing permits, implementing regulations, conducting inspections. | Disciplinary hearings, licensing disputes, administrative tribunals. |
| Appealability | Appeals typically made to higher administrative bodies or courts. | Decisions can be appealed or reviewed judicially for fairness and legality. |
Introduction to Administrative and Quasi-Judicial Functions
Administrative functions involve executing government policies through rule-making, enforcement, and management of public programs, ensuring efficient public service delivery. Quasi-judicial functions entail decision-making processes where administrative agencies or officials resolve disputes, interpret laws, and impose penalties, similar to judicial proceedings but within an administrative framework. Understanding the distinction helps clarify the scope of regulatory authority and the procedural safeguards applicable in governance.
Defining Administrative Functions
Administrative functions involve implementing policies, managing public programs, and executing laws within government agencies, emphasizing routine operational tasks and regulatory enforcement. These functions focus on decision-making processes related to public administration, resource allocation, and service delivery without involving formal adjudication. In contrast, quasi-judicial functions contain elements of judicial processes such as hearings and rulings but remain within administrative bodies rather than courts.
Explaining Quasi-Judicial Functions
Quasi-judicial functions involve administrative agencies or bodies that have the authority to interpret laws, hold hearings, and make decisions affecting the rights of individuals, similar to a court but within an administrative framework. These functions include evaluating evidence, conducting investigations, and issuing rulings or orders that carry legal consequences, often in regulatory, labor, or licensing contexts. Unlike purely administrative tasks, quasi-judicial activities require impartiality, due process, and adherence to established legal standards, ensuring fair resolution of disputes within government agencies.
Key Differences Between Administrative and Quasi-Judicial Actions
Administrative actions involve routine governmental functions such as rule-making, policy implementation, and management, focusing on executing laws and regulations. Quasi-judicial actions require decision-makers to adjudicate disputes, assess evidence, and render binding decisions resembling judicial proceedings. Key differences lie in their scope, with administrative actions emphasizing regulatory enforcement and quasi-judicial actions emphasizing impartial dispute resolution and legal determination.
Legal Authority and Power Source
Administrative bodies derive their legal authority from statutory laws enacted by legislatures, granting them power to implement and enforce regulations within specific government frameworks. Quasi-judicial bodies operate under delegated authority that allows them to adjudicate disputes, make determinations, and issue rulings similar to courts, often established by enabling legislation. The power source for administrative agencies is primarily regulatory and executive in nature, whereas quasi-judicial entities possess adjudicative power grounded in legal mandates to ensure fair resolution of individual rights and obligations.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Administrative decision-making involves enforcing laws and managing public policies through routine actions, often following established guidelines and regulations within executive agencies. Quasi-judicial decision-making requires a formal hearing process, assessing evidence, and making determinations based on legal principles similar to court proceedings, typically conducted by administrative tribunals or boards. The key difference lies in quasi-judicial bodies' authority to issue binding decisions affecting rights, while administrative actions primarily involve policy implementation and regulatory oversight.
Procedural Safeguards and Fairness
Administrative actions are governed by procedural safeguards designed to ensure transparency, opportunity for hearing, and impartial decision-making, often emphasizing efficiency and adherence to rules. Quasi-judicial bodies provide more formal procedural protections similar to courts, including the right to present evidence, cross-examination, and issuance of reasoned decisions, promoting greater fairness in adjudication. The key distinction lies in the degree of due process, with quasi-judicial processes offering enhanced procedural fairness to protect individual rights against administrative overreach.
Role in Regulatory and Dispute Resolution Frameworks
Administrative bodies enforce regulatory compliance by implementing policies and overseeing adherence to laws within their jurisdiction, ensuring efficient governance and public administration. Quasi-judicial entities resolve disputes by interpreting statutes and applying legal principles to individual cases, providing a formal mechanism for conflict resolution outside traditional courts. Their combined roles strengthen the regulatory framework by balancing enforcement with fair adjudication, promoting accountability and legal certainty.
Examples of Administrative and Quasi-Judicial Bodies
Administrative bodies include government agencies like the Social Security Administration and the Environmental Protection Agency, which implement laws and manage public policies. Quasi-judicial bodies such as the National Labor Relations Board and the Securities and Exchange Commission conduct hearings, make rulings, and resolve disputes with authority similar to courts. These entities operate within their specialized domains to ensure regulatory compliance and adjudicate specific issues.
Impact on Accountability and Legal Recourse
Administrative actions primarily ensure organizational compliance and operational efficiency, limiting direct judicial oversight but enhancing internal accountability mechanisms. Quasi-judicial decisions, involving adjudication with legal principles, offer affected parties clearer avenues for legal recourse through appeals and compliance reviews. The distinction significantly impacts accountability; administrative functions rely on hierarchical supervision, whereas quasi-judicial roles enforce procedural fairness and independent judgment subject to judicial scrutiny.
Administrative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com