Opinions shape how we interpret information and influence our decision-making processes in everyday life. Understanding the basis of your own opinions can help you communicate more effectively and engage in meaningful discussions. Explore the rest of this article to learn how opinions form and impact your perspective.
Table of Comparison
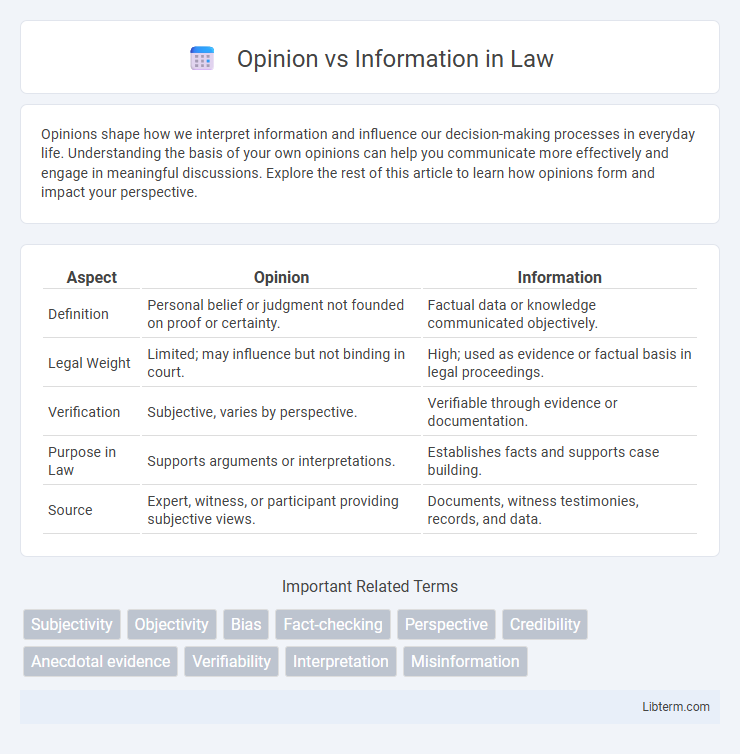
| Aspect | Opinion | Information |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal belief or judgment not founded on proof or certainty. | Factual data or knowledge communicated objectively. |
| Legal Weight | Limited; may influence but not binding in court. | High; used as evidence or factual basis in legal proceedings. |
| Verification | Subjective, varies by perspective. | Verifiable through evidence or documentation. |
| Purpose in Law | Supports arguments or interpretations. | Establishes facts and supports case building. |
| Source | Expert, witness, or participant providing subjective views. | Documents, witness testimonies, records, and data. |
Understanding the Difference Between Opinion and Information
Understanding the difference between opinion and information is crucial for critical thinking and effective communication. Information consists of objective facts, data, and evidence that can be verified, while opinion reflects personal beliefs, interpretations, or judgments, often subjective and influenced by emotions or experiences. Recognizing this distinction helps individuals evaluate sources accurately, avoid misinformation, and make informed decisions based on evidence rather than bias.
Defining Opinion: Subjectivity in Communication
Opinion reflects personal beliefs, emotions, and interpretations, shaped by individual experiences and biases, making it inherently subjective in communication. Unlike factual information, opinions cannot be universally verified and often vary between people based on cultural, social, and psychological factors. Understanding the distinction between opinion and information is crucial for assessing the credibility and intent behind messages in media, discourse, and everyday interactions.
What Constitutes Information? Facts and Objectivity
Information consists of verifiable facts and objective data that can be independently confirmed through evidence and observation. It is free from personal bias and subjective interpretation, providing a reliable foundation for understanding reality. Accurate information is essential for informed decision-making, critical analysis, and effective communication across various fields and disciplines.
The Role of Opinion in Shaping Perspectives
Opinions play a crucial role in shaping perspectives by providing subjective interpretations that influence individual and collective understanding of information. Unlike factual data, opinions incorporate personal beliefs and emotions, which can lead to diverse viewpoints and drive meaningful discussions. This dynamic interaction between opinion and information fosters critical thinking and helps people navigate complex social, political, and cultural issues.
Why Accurate Information Matters in Media
Accurate information in media establishes trust and credibility, enabling audiences to make informed decisions and participate effectively in society. Misinformation or biased opinions can distort public perception, leading to misunderstandings and poor policy choices. Prioritizing factual reporting safeguards democracy and promotes transparency, accountability, and social cohesion.
Blurring the Line: When Opinion Masquerades as Information
Blurring the line between opinion and information occurs when subjective viewpoints are presented with the authority and objectivity typical of factual reporting, leading to misinformation and audience confusion. This phenomenon often thrives in digital media environments where echo chambers amplify biased content disguised as news, compromising critical thinking and informed decision-making. Recognizing indicators such as emotional language, lack of credible sources, and absence of verifiable data helps distinguish opinion pieces from legitimate information.
Evaluating Sources: Distinguishing Opinion from Fact
Evaluating sources requires identifying whether content presents verifiable facts or subjective opinions, with factual information supported by evidence and data from credible entities such as academic institutions or government agencies. Reliable sources often provide citations, transparent methodologies, and balanced perspectives, whereas opinion pieces typically include personal viewpoints, persuasive language, and lack impartial verification. Understanding the distinction between opinion and fact is essential for critical thinking and making informed decisions based on accurate, evidence-based information.
The Impact of Opinion vs Information on Public Discourse
Opinions shape public discourse by reflecting personal beliefs and emotional responses, often driving engagement and debate but risking bias and misinformation. Information provides factual, evidence-based content that enhances understanding, supports informed decision-making, and fosters credible dialogue. Balancing opinion with accurate information is crucial for a well-informed public and healthy democratic processes.
Strategies for Balancing Opinion and Information in Writing
Effective strategies for balancing opinion and information in writing include clearly distinguishing subjective viewpoints from objective facts to enhance credibility and reader trust. Integrating evidence-based data alongside personal insights allows writers to support opinions with reliable information, enriching the content's depth and persuasiveness. Employing balanced language and providing multiple perspectives ensures an informative and nuanced narrative that respects diverse viewpoints.
The Importance of Critical Thinking in Navigating Opinion and Information
Critical thinking is essential for distinguishing between opinion and information by evaluating the credibility, relevance, and evidence behind statements. It empowers individuals to analyze biases, recognize logical fallacies, and separate subjective viewpoints from factual data. Developing these skills enhances decision-making, fosters informed discussions, and promotes a deeper understanding of complex issues.
Opinion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com