A respondent plays a crucial role in providing valuable insights by answering surveys, questionnaires, or interviews accurately. Understanding the perspective and behavior of respondents helps enhance research quality and decision-making processes. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for engaging your respondents and maximizing data reliability.
Table of Comparison
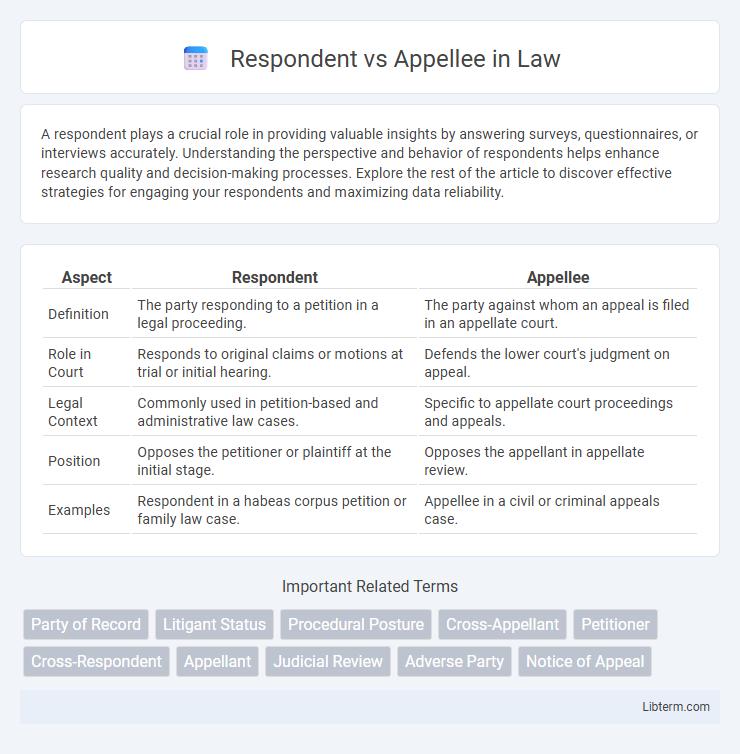
| Aspect | Respondent | Appellee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The party responding to a petition in a legal proceeding. | The party against whom an appeal is filed in an appellate court. |
| Role in Court | Responds to original claims or motions at trial or initial hearing. | Defends the lower court's judgment on appeal. |
| Legal Context | Commonly used in petition-based and administrative law cases. | Specific to appellate court proceedings and appeals. |
| Position | Opposes the petitioner or plaintiff at the initial stage. | Opposes the appellant in appellate review. |
| Examples | Respondent in a habeas corpus petition or family law case. | Appellee in a civil or criminal appeals case. |
Understanding Legal Terminology: Respondent vs Appellee
The terms "Respondent" and "Appellee" refer to parties in legal proceedings, but they differ based on the type of case and court stage. A Respondent is the party responding to a petition in cases such as family law or administrative hearings, while an Appellee is the party defending the lower court's decision in an appeal. Understanding this distinction is crucial for navigating legal terminology and effectively representing interests in both trial and appellate courts.
Definition of Respondent in Legal Proceedings
A respondent in legal proceedings is the party who answers or responds to a petition or appeal filed by another party, usually called the petitioner or appellant. This role typically arises in appellate courts, family law cases, and administrative hearings where the respondent must contest or address the claims against them. Understanding the distinction between respondent and appellee is crucial, as appellees specifically refer to parties responding to appeals in higher courts.
Definition of Appellee in Court Cases
An appellee is the party against whom an appeal is filed in a court case, typically seeking to uphold the lower court's decision. This party responds to the appellant's arguments, defending the original judgment or order. The appellee plays a crucial role in appellate litigation by presenting counterarguments and supporting evidence to maintain the ruling from the trial court.
Key Differences Between Respondent and Appellee
The key differences between a respondent and an appellee lie in their roles within court proceedings: a respondent is the party responding to a petition or complaint in a trial or administrative hearing, whereas an appellee is the party opposing an appeal after a trial court's decision. The respondent participates primarily in initial hearings, while the appellee defends the lower court's ruling during the appellate process. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for proper legal strategy and procedural compliance in both trial and appellate courts.
When to Use the Term "Respondent
The term "Respondent" is used primarily in legal contexts involving appeals or petitions, especially in cases such as family law, administrative hearings, or civil appeals. It designates the party who must respond to a petition or appeal initiated by another party, opposed to the "Appellee," who defends against an appeal in a higher court. Use "Respondent" when referring to the party responding to a petition or initiating court action at the appellate or administrative level, rather than just opposing an appeal.
When to Use the Term "Appellee
The term "Appellee" is used specifically in appellate court proceedings to refer to the party against whom an appeal is filed, typically the winner in the lower court case. Courts and legal documents employ "Appellee" to distinguish this party from the "Appellant," who is the party initiating the appeal. Understanding when to use "Appellee" ensures precise legal communication and proper identification of roles in the appeals process.
Legal Contexts for Respondent and Appellee
In legal contexts, the respondent is the party who responds to a petition or appeal filed in a court of equity or administrative proceeding, such as family law or regulatory cases, where the initial petition triggers the respondent's involvement. The appellee, however, is the party who responds specifically to an appeal in a higher court, defending the lower court's decision against the appellant's challenge. Understanding these roles is crucial in appellate procedure, where the respondent answers the original claim, whereas the appellee addresses reversal or modification of the judgment.
Examples of Respondent and Appellee in Court Cases
In legal proceedings, the respondent is the party who responds to a petition or appeal, such as the individual opposing a divorce petition in family court or the government agency defending a regulatory action in administrative hearings. The appellee refers specifically to the party who wins at the trial court level and responds to the appellant's appeal, for example, a plaintiff who successfully sued for damages and defends the judgment on appeal. Cases like Smith v. Jones illustrate the appellee as the original judgment holder, while in administrative court, the respondent might be the agency responding to a license challenge.
Common Misconceptions: Respondent vs Appellee
The terms Respondent and Appellee are often confused, but they represent distinct roles in legal proceedings. A Respondent is the party answering a petition, typically in appellate or administrative cases, while an Appellee is the party opposing an appeal, usually the winner in the initial trial. Misconceptions arise because both roles involve responding to legal actions, yet the Appellee specifically participates in appeals, whereas the Respondent may appear in various types of cases.
Frequently Asked Questions about Respondent and Appellee
The respondent is the party who responds to a petition or appeal in a legal case, often the party opposing the petitioner or appellant. The appellee is specifically the party who won at the lower court level and seeks to uphold that decision during an appeal. Frequently asked questions about respondents and appellees involve understanding their roles in appellate procedures, the differences between initial and appellate court cases, and the rights each has in presenting arguments and evidence.
Respondent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com