Outside counsel provides specialized legal expertise and flexible support tailored to your business needs, ensuring access to industry-specific knowledge without the overhead of in-house staff. Engaging experienced external lawyers can enhance your company's risk management and compliance strategies while optimizing legal costs. Explore the article to uncover how outside counsel can strategically benefit your organization in today's complex legal environment.
Table of Comparison
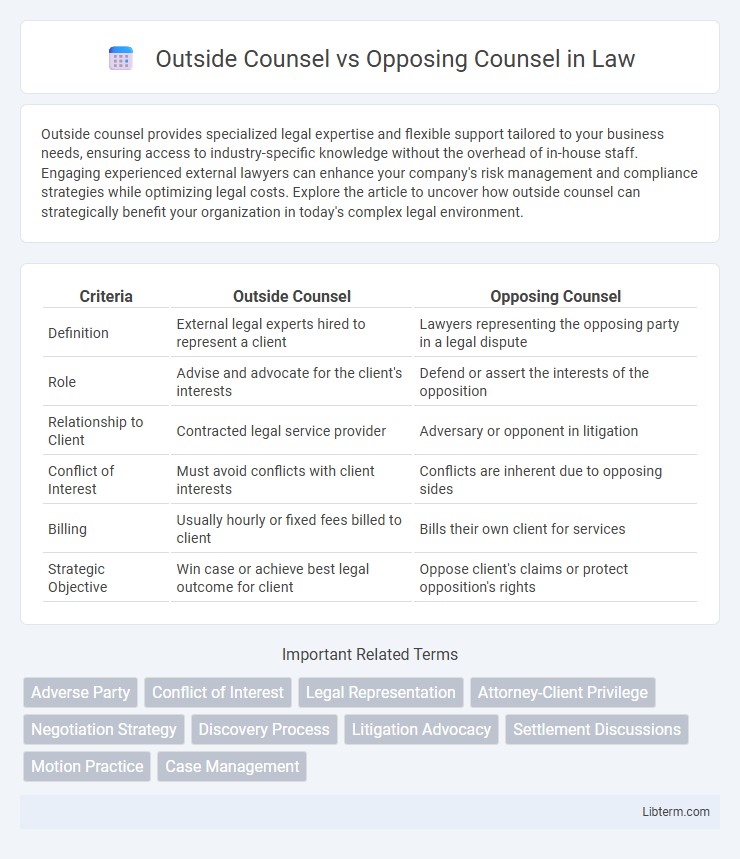
| Criteria | Outside Counsel | Opposing Counsel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | External legal experts hired to represent a client | Lawyers representing the opposing party in a legal dispute |
| Role | Advise and advocate for the client's interests | Defend or assert the interests of the opposition |
| Relationship to Client | Contracted legal service provider | Adversary or opponent in litigation |
| Conflict of Interest | Must avoid conflicts with client interests | Conflicts are inherent due to opposing sides |
| Billing | Usually hourly or fixed fees billed to client | Bills their own client for services |
| Strategic Objective | Win case or achieve best legal outcome for client | Oppose client's claims or protect opposition's rights |
Defining Outside Counsel and Opposing Counsel
Outside counsel refers to external attorneys or law firms hired by a company or individual to provide specialized legal services beyond the scope of in-house legal teams. Opposing counsel denotes the attorneys representing the adversarial party in legal proceedings, tasked with advocating against their opponent's interests. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective legal strategy and communication in litigation or transactional matters.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Outside counsel provides specialized legal expertise and strategic advice to an organization, often handling complex litigation, regulatory compliance, and contract negotiations. Opposing counsel represents the adverse party in a legal dispute, tasked with advocating their client's interests, challenging evidence, and negotiating settlements. Both roles require deep legal knowledge, strategic thinking, and effective communication to influence case outcomes.
Differences in Client Representation
Outside counsel represents a client hired from an external law firm, providing specialized legal expertise and managing complex cases with dedicated resources. Opposing counsel represents the adversary party in litigation or negotiation, advocating against the interests of the opposing client. The key difference lies in allegiance: outside counsel advocates for their client's goals, while opposing counsel works to challenge or counter those objectives.
Confidentiality and Ethical Considerations
Outside counsel must adhere strictly to client confidentiality agreements, ensuring that sensitive information is protected through secure communication channels and limited disclosure only to authorized personnel. Opposing counsel, bound by professional ethics, must avoid conflicts of interest and maintain fairness during legal proceedings while respecting confidentiality rules, including refraining from obtaining privileged information inadvertently. Both parties are governed by ethical codes such as the ABA Model Rules, which emphasize candor, confidentiality, and the duty to maintain the integrity of the legal process.
Communication Protocols and Boundaries
Outside counsel and opposing counsel adhere to distinct communication protocols to ensure ethical conduct and maintain professional boundaries. Outside counsel must communicate internally with clients and other stakeholders while respecting confidentiality and avoiding direct negotiation with opposing counsel unless expressly authorized. Opposing counsel maintains a formal communication channel, typically limited to case-related matters, ensuring clear boundaries that prevent conflicts of interest and uphold the integrity of legal proceedings.
Fee Structures and Billing Practices
Outside counsel typically operates on hourly billing, fixed fees, or contingency arrangements tailored to the client's needs, emphasizing transparency and budget predictability. Opposing counsel's fee structures may vary but often reflect standard hourly rates that influence negotiation dynamics and litigation strategy. Understanding these differences enhances cost management and strategic planning in legal proceedings.
Coordination with In-House Legal Teams
Coordination between outside counsel and in-house legal teams is essential for aligning litigation strategy, managing risks, and ensuring compliance with corporate policies. Outside counsel provides specialized expertise and external perspectives while in-house counsel offers institutional knowledge and facilitates communication across departments. Effective collaboration streamlines case management, optimizes resource allocation, and enhances the overall legal defense or transactional process.
Strategies for Managing Opposing Counsel
Effective strategies for managing opposing counsel include maintaining clear, professional communication to reduce misunderstandings and foster cooperation. Utilizing thorough preparation and anticipating opposing counsel's tactics enhances negotiation leverage and case strategy. Establishing firm boundaries and documenting all interactions helps protect client interests and ensures ethical compliance throughout litigation.
Common Challenges and Conflict Resolution
Outside Counsel often faces challenges such as limited access to internal resources and communication barriers, while Opposing Counsel navigates conflicts arising from adversarial roles and strategic disagreements. Both parties frequently encounter disputes over discovery processes, confidentiality issues, and case strategy alignment. Effective conflict resolution hinges on clear communication, negotiation skills, and adherence to professional ethics to maintain procedural fairness and client interests.
Best Practices for Effective Collaboration and Advocacy
Effective collaboration between Outside Counsel and Opposing Counsel hinges on clear communication, mutual respect, and adherence to ethical standards. Maintaining transparency in case developments and promptly addressing procedural issues fosters trust and streamlines dispute resolution processes. Emphasizing professional courtesy while rigorously advocating for client interests balances advocacy with cooperation, enhancing overall legal outcomes.
Outside Counsel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com