Regulation plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance, safety, and fairness across various industries by establishing clear standards and guidelines. Effective regulation protects consumers and promotes transparency while fostering market stability and innovation. Explore the rest of this article to understand how regulations impact your industry and what changes you should anticipate.
Table of Comparison
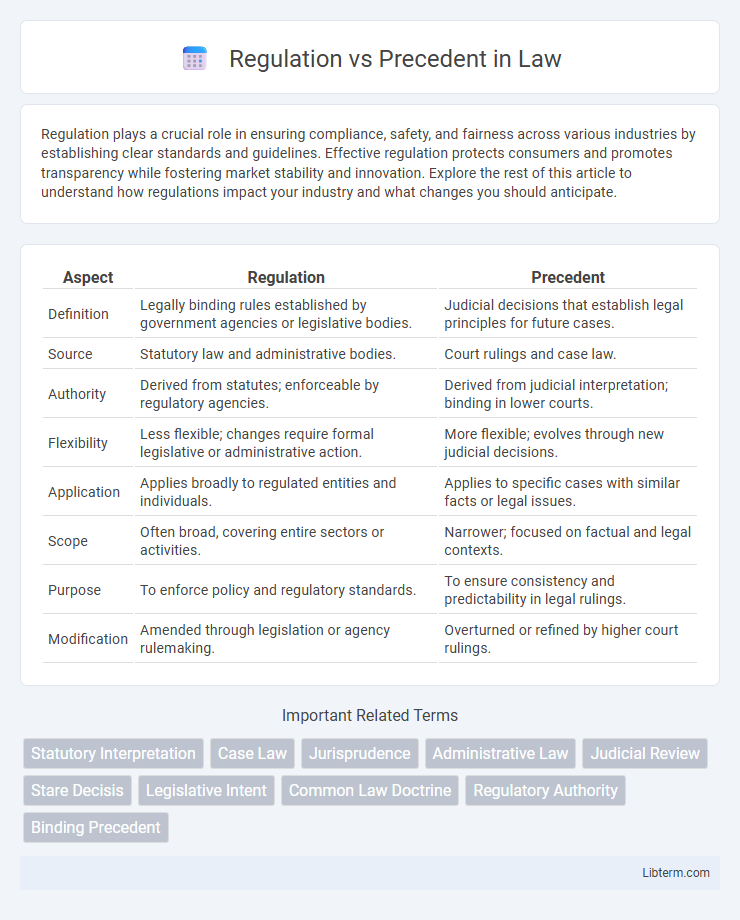
| Aspect | Regulation | Precedent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legally binding rules established by government agencies or legislative bodies. | Judicial decisions that establish legal principles for future cases. |
| Source | Statutory law and administrative bodies. | Court rulings and case law. |
| Authority | Derived from statutes; enforceable by regulatory agencies. | Derived from judicial interpretation; binding in lower courts. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; changes require formal legislative or administrative action. | More flexible; evolves through new judicial decisions. |
| Application | Applies broadly to regulated entities and individuals. | Applies to specific cases with similar facts or legal issues. |
| Scope | Often broad, covering entire sectors or activities. | Narrower; focused on factual and legal contexts. |
| Purpose | To enforce policy and regulatory standards. | To ensure consistency and predictability in legal rulings. |
| Modification | Amended through legislation or agency rulemaking. | Overturned or refined by higher court rulings. |
Understanding Regulation and Precedent
Regulation consists of rules established by governmental agencies designed to control and govern behavior within specific sectors, providing clear statutory guidelines. Precedent, or case law, arises from judicial decisions interpreting laws, shaping future rulings through the principle of stare decisis. Understanding both involves recognizing that regulations offer proactive directives, while precedents deliver reactive, interpretative frameworks influencing legal consistency and adaptability.
Historical Foundations of Regulation and Precedent
Regulation emerged from formal legislative actions and authoritative government frameworks designed to control specific economic or social activities, tracing back to early codified laws such as Hammurabi's Code and Roman legal statutes. Precedent, or stare decisis, developed through the judicial practice of relying on prior court decisions to guide rulings, firmly established in common law traditions from medieval England. Both regulation and precedent have shaped modern legal systems by balancing codified rules with adaptive judicial interpretations to ensure consistency and predictability.
Legal Authority: Statutes vs Judicial Decisions
Legal authority distinguishes regulation, which is grounded in statutes enacted by legislative bodies, from precedent, which arises from judicial decisions interpreting and applying those statutes. Statutes provide explicit legal directives and frameworks authorized by constitutions, while precedents establish binding interpretations through case law, guiding future court rulings. Understanding the interplay between these forms of authority is essential for navigating legal systems and ensuring compliance with both codified law and evolving judicial interpretations.
Flexibility of Precedent in Evolving Law
Precedent offers significant flexibility in the evolution of law by allowing courts to interpret past decisions contextually, adapting legal principles to contemporary societal values and technological advancements. Unlike rigid regulations, precedent encourages incremental changes through judicial reasoning, promoting legal stability while accommodating necessary reforms. This adaptability ensures that law remains relevant and responsive in dynamic and complex legal landscapes.
Stability Through Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory frameworks provide stability by establishing clear, consistent rules that govern behavior across industries, reducing uncertainty for businesses and individuals. Unlike precedent, which relies on judicial decisions that can vary and evolve over time, regulations offer predictable guidelines enforced by government agencies. This structured approach ensures ongoing compliance and helps maintain orderly markets and social systems.
Implementation Challenges in Regulation and Precedent
Implementation challenges in regulation include rigid compliance requirements and frequent updates that create uncertainty for businesses. Precedent faces difficulties in consistency and predictability, as judicial decisions vary across jurisdictions and cases. Both approaches struggle with balancing flexibility and stability in governance frameworks.
Impact on Judicial Decision-Making
Regulation provides explicit legal standards established by legislative bodies that guide judicial decision-making by setting clear rules and expectations, reducing ambiguity in court rulings. Precedent, derived from prior judicial decisions, influences courts through the principle of stare decisis, promoting consistency and predictability but allowing adaptive interpretation in evolving contexts. The interplay between regulation and precedent shapes the judiciary's ability to balance statutory mandates with case-specific nuances, impacting legal certainty and flexibility.
Regulatory Change vs Precedential Overruling
Regulatory change involves formal amendments to laws or rules enacted by legislative or administrative bodies, providing clear and authoritative guidance for future conduct. Precedential overruling occurs in judicial contexts where courts overturn prior decisions, altering legal interpretations without changing the underlying statutes. Regulatory change offers stability and predictability through codified norms, whereas precedential overruling allows the law to evolve dynamically based on shifting judicial perspectives.
Harmonizing Regulation with Case Law
Harmonizing regulation with case law ensures consistent legal interpretation and application, promoting stability in judicial decisions. Regulatory frameworks provide clear statutory guidelines, while case law offers nuanced interpretations that adapt to evolving societal contexts. Integrating these sources enables coherent legal systems that balance legislative intent with judicial flexibility.
Future Trends: Balancing Regulation and Precedent
Future trends in legal frameworks emphasize balancing regulation and precedent to adapt to rapid technological advances and complex societal changes. Integrating dynamic regulatory policies with established judicial precedents fosters legal certainty while allowing flexibility for innovation. This balance supports evolving industries like artificial intelligence and biotechnology by providing clear guidelines without stifling progress.
Regulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com