Foreclosure occurs when a homeowner fails to make mortgage payments, leading the lender to seize and sell the property to recover the loan balance. Understanding the foreclosure process and its impact on your credit score is crucial to navigating financial difficulties effectively. Read on to learn how to protect your home and explore strategies to avoid foreclosure.
Table of Comparison
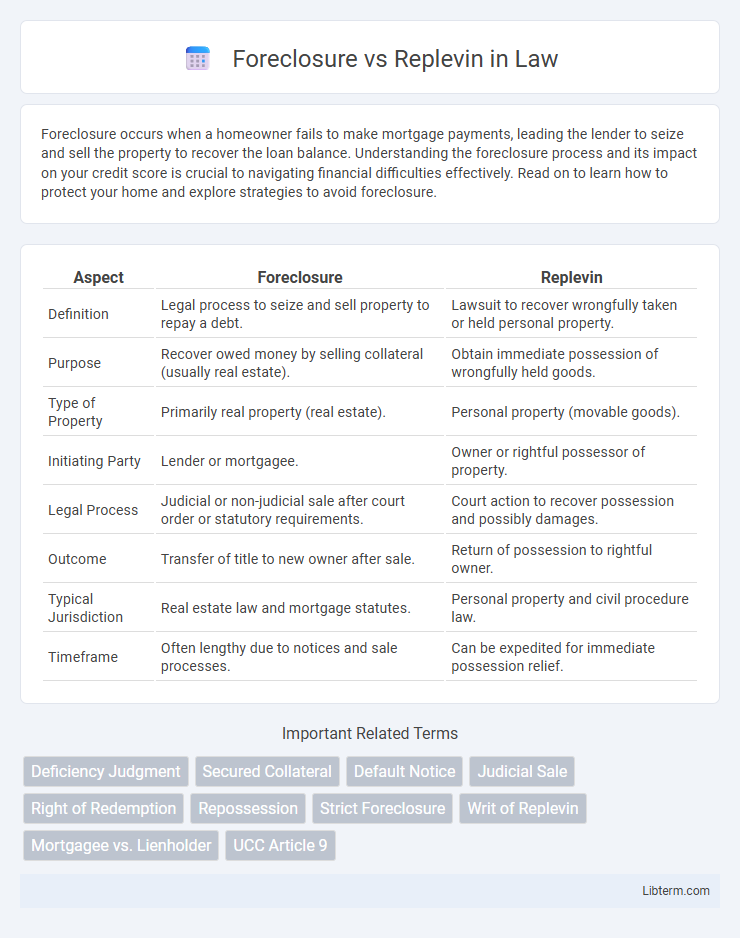
| Aspect | Foreclosure | Replevin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process to seize and sell property to repay a debt. | Lawsuit to recover wrongfully taken or held personal property. |
| Purpose | Recover owed money by selling collateral (usually real estate). | Obtain immediate possession of wrongfully held goods. |
| Type of Property | Primarily real property (real estate). | Personal property (movable goods). |
| Initiating Party | Lender or mortgagee. | Owner or rightful possessor of property. |
| Legal Process | Judicial or non-judicial sale after court order or statutory requirements. | Court action to recover possession and possibly damages. |
| Outcome | Transfer of title to new owner after sale. | Return of possession to rightful owner. |
| Typical Jurisdiction | Real estate law and mortgage statutes. | Personal property and civil procedure law. |
| Timeframe | Often lengthy due to notices and sale processes. | Can be expedited for immediate possession relief. |
Understanding Foreclosure: Definition and Process
Foreclosure is a legal process initiated by a lender to recover the balance of a loan from a borrower who has defaulted, typically through the sale of the secured property. This process involves strict steps including issuing a notice of default, allowing a foreclosure period for repayment, and conducting a public auction or sheriff's sale to transfer ownership. Understanding foreclosure requires recognizing its impact on credit scores and the borrower's right to redeem the property before sale completion.
What is Replevin? A Legal Overview
Replevin is a legal action used to recover possession of personal property wrongfully taken or withheld by another party. Unlike foreclosure, which involves reclaiming real property due to loan default, replevin specifically addresses disputes over tangible assets and aims to return the specific item to its rightful owner. Courts issuing replevin orders prioritize restoring possession before resolving ownership disputes through trial or settlement.
Key Differences Between Foreclosure and Replevin
Foreclosure involves a legal process where a lender seeks to recover the balance of a loan by forcing the sale of a property after a borrower's default, primarily concerning real estate collateral. Replevin is a legal action for recovering personal property wrongfully taken or withheld, emphasizing the return of specific goods rather than monetary recovery. Key differences include the type of property involved--real estate in foreclosure versus personal property in replevin--and the legal remedy sought, with foreclosure focusing on debt recovery through sale and replevin focusing on possession restoration.
Legal Grounds for Foreclosure Actions
Foreclosure actions are primarily based on the legal grounds of borrower default, including missed mortgage payments or violation of loan agreement terms, which lead to lender enforcement rights on the collateral property. Replevin, by contrast, involves the recovery of wrongfully possessed personal property rather than real estate, focusing on ownership rights rather than financial default. Foreclosure requires strict adherence to state-specific statutes and court procedures to terminate the borrower's equity and facilitate property transfer or sale.
When is Replevin Used Instead of Foreclosure?
Replevin is used instead of foreclosure when the primary goal is to recover specific personal property wrongfully held by another party, rather than to enforce a lien on real estate or collateral. It is commonly employed in cases involving disputed possession of goods, such as vehicles, equipment, or inventory, where the claimant seeks immediate return rather than monetary compensation. Foreclosure applies to real property or secured loans, whereas replevin addresses property disputes requiring prompt retrieval of tangible items.
Rights of Debtors in Foreclosure Cases
In foreclosure cases, debtors retain the right to redeem the property by paying off the outstanding mortgage debt before the foreclosure sale occurs, protecting their ownership interest. They are entitled to receive proper notice and due process, ensuring the foreclosure complies with state laws, and may have the opportunity to contest the lender's claim. Unlike replevin, foreclosure focuses on real property and involves different procedural safeguards specifically designed to balance creditor recovery with debtor protections.
Debtor and Creditor Rights in Replevin Proceedings
In replevin proceedings, the creditor holds the right to reclaim specific property wrongfully withheld by the debtor before a final judgment, often requiring a bond to protect the debtor against wrongful seizure. The debtor retains the right to defend against the creditor's claim by proving lawful possession or disputing ownership, ensuring due process under property laws. Debtor protections include prompt hearings and potential recovery of wrongfully taken goods, balancing creditor interests in property recovery with debtor safeguards.
Consequences of Foreclosure vs. Replevin for Borrowers
Foreclosure results in the borrower losing ownership of the property and a significant negative impact on credit scores, often making future borrowing more difficult. Replevin allows the borrower to recover possession of specific personal property but does not affect ownership rights or credit reports directly. While foreclosure leads to long-term financial consequences, replevin primarily addresses the immediate return of wrongfully taken goods without altering the borrower's overall credit standing.
Foreclosure and Replevin: State Law Variations
Foreclosure and replevin are legal remedies subject to significant state law variations, impacting property rights enforcement and procedural requirements. Foreclosure laws differ widely in timelines, notice requirements, and types such as judicial or non-judicial foreclosures, influencing creditor recovery processes. Replevin statutes also vary, particularly in the conditions under which possession of wrongfully held goods is restored, reflecting diverse state-level protections for debtors and creditors.
Choosing the Appropriate Remedy: Foreclosure or Replevin?
Choosing the appropriate remedy between foreclosure and replevin depends on the nature of the dispute and the type of property involved. Foreclosure is typically used to resolve disputes involving real property or secured interests, where a lender seeks to enforce a lien due to default, leading to the sale of the property. Replevin serves as a remedy for recovering personal property wrongfully taken or withheld, allowing the rightful owner to regain possession without addressing ownership rights through a formal court process.
Foreclosure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com