Incarceration significantly impacts individuals, families, and communities by disrupting social ties and limiting economic opportunities. Understanding the causes, consequences, and alternatives to imprisonment helps in addressing the systemic issues underlying mass incarceration. Explore the rest of this article to learn how incarceration affects society and what steps you can take toward meaningful reform.
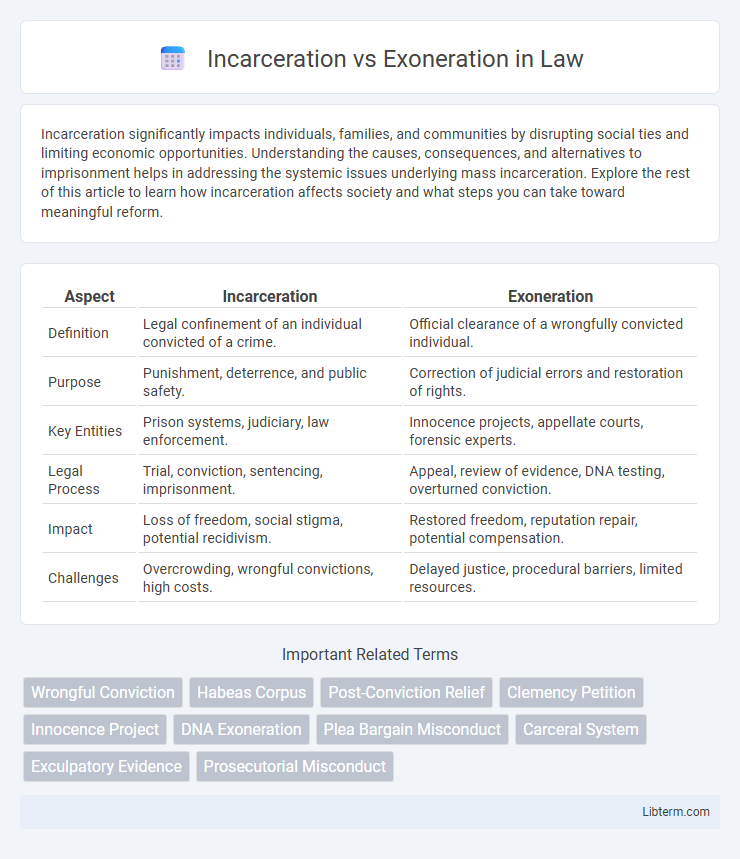
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Incarceration | Exoneration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal confinement of an individual convicted of a crime. | Official clearance of a wrongfully convicted individual. |
| Purpose | Punishment, deterrence, and public safety. | Correction of judicial errors and restoration of rights. |
| Key Entities | Prison systems, judiciary, law enforcement. | Innocence projects, appellate courts, forensic experts. |
| Legal Process | Trial, conviction, sentencing, imprisonment. | Appeal, review of evidence, DNA testing, overturned conviction. |
| Impact | Loss of freedom, social stigma, potential recidivism. | Restored freedom, reputation repair, potential compensation. |
| Challenges | Overcrowding, wrongful convictions, high costs. | Delayed justice, procedural barriers, limited resources. |
Understanding Incarceration: Definition and Impact
Incarceration refers to the state of being confined in prison as a legal penalty for committing a crime, significantly impacting individuals' mental health, family dynamics, and economic stability. The widespread use of incarceration, especially in countries with high imprisonment rates like the United States, underscores systemic issues such as racial disparities and socioeconomic inequalities within the justice system. Understanding incarceration involves examining its long-term consequences on recidivism, community safety, and the overall social fabric.
The Legal Journey to Exoneration
Navigating the legal journey to exoneration involves complex processes such as filing post-conviction relief, presenting new evidence like DNA testing, and overcoming procedural barriers to reopen cases. Legal professionals and innocence organizations play a critical role in advocating for wrongly convicted individuals, highlighting flaws such as eyewitness misidentification and prosecutorial misconduct. The journey often requires persistent litigation, forensic advancements, and appellate reviews to secure a wrongful conviction reversal and rightful freedom.
Causes of Wrongful Convictions
Wrongful convictions often stem from causes such as eyewitness misidentification, false confessions, and prosecutorial misconduct. Inadequate legal defense and reliance on faulty forensic evidence also contribute significantly to incarceration errors. These systemic issues highlight the urgent need for reforms to prevent unjust imprisonment and ensure exoneration of innocent individuals.
The Psychological Toll of Incarceration
Incarceration imposes severe psychological tolls, including chronic anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder, which often persist long after release. The stigma and isolation inherent in confinement exacerbate mental health challenges, hindering successful reintegration into society. Studies indicate that prolonged incarceration correlates with heightened risk of suicide and diminished cognitive functioning, underscoring the urgent need for mental health interventions within correctional systems.
Evidence and Advocacy in Exoneration Cases
Evidence plays a crucial role in exoneration cases, where new DNA analysis or witness recantations can overturn wrongful convictions and highlight systemic flaws in the justice system. Advocacy organizations such as the Innocence Project utilize advanced forensic technology and legal support to challenge incarceration by proving factual innocence and securing release for wrongfully imprisoned individuals. Strong collaboration between evidence experts and legal advocates ensures that exoneration efforts effectively address evidentiary gaps and promote justice reform.
Societal Perceptions: Guilt vs. Innocence
Societal perceptions often equate incarceration with guilt, reinforcing stigmatization and social exclusion for the convicted. In contrast, exoneration challenges these perceptions by revealing wrongful convictions, fostering public awareness about judicial errors. This shift impacts trust in the legal system and advocates for reforms promoting fairness and accuracy in criminal justice.
The Role of DNA and Forensic Science
DNA and forensic science have revolutionized the criminal justice system by providing objective evidence that distinguishes wrongful incarceration from rightful conviction. Advances in DNA analysis enable the re-examination of old evidence, leading to increased exonerations of individuals wrongfully imprisoned and highlighting systemic flaws. Forensic techniques such as STR profiling and mitochondrial DNA testing improve accuracy in linking suspects to crime scenes, reducing the risk of false convictions and promoting justice.
Rebuilding Lives After Exoneration
Rebuilding lives after exoneration involves overcoming significant psychological, social, and economic challenges caused by wrongful incarceration. Access to comprehensive support services, including mental health care, job training, and legal assistance, plays a critical role in successful reintegration. Programs tailored to exonerees, such as those offered by the Innocence Project, help restore dignity and facilitate rebuilding connections within communities.
Policy Reforms for Justice System Accountability
Policy reforms targeting incarceration and exoneration emphasize enhancing justice system accountability through improved transparency and rigorous oversight mechanisms. Implementing evidence-based sentencing reforms and expanding access to post-conviction DNA testing address wrongful convictions and reduce prison overcrowding. Strengthening independent review boards and mandating regular audits of prosecutorial practices improve the accuracy and fairness of criminal justice outcomes.
Preventing Future Wrongful Incarcerations
Implementing advanced forensic technologies and comprehensive case reviews enhances the accuracy of convictions, significantly reducing wrongful incarcerations. Establishing independent innocence commissions and increasing funding for public defenders ensure thorough investigations and fair trials. Educating legal professionals on cognitive biases and updating evidentiary standards supports the prevention of future wrongful incarcerations.
Incarceration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com