An advisory opinion provides a non-binding legal interpretation or guidance issued by a court or legal body to clarify the law on a specific issue. It helps organizations, governments, or individuals understand their rights and obligations without the risk of litigation. Dive into the article to explore how advisory opinions can impact your legal decisions.
Table of Comparison
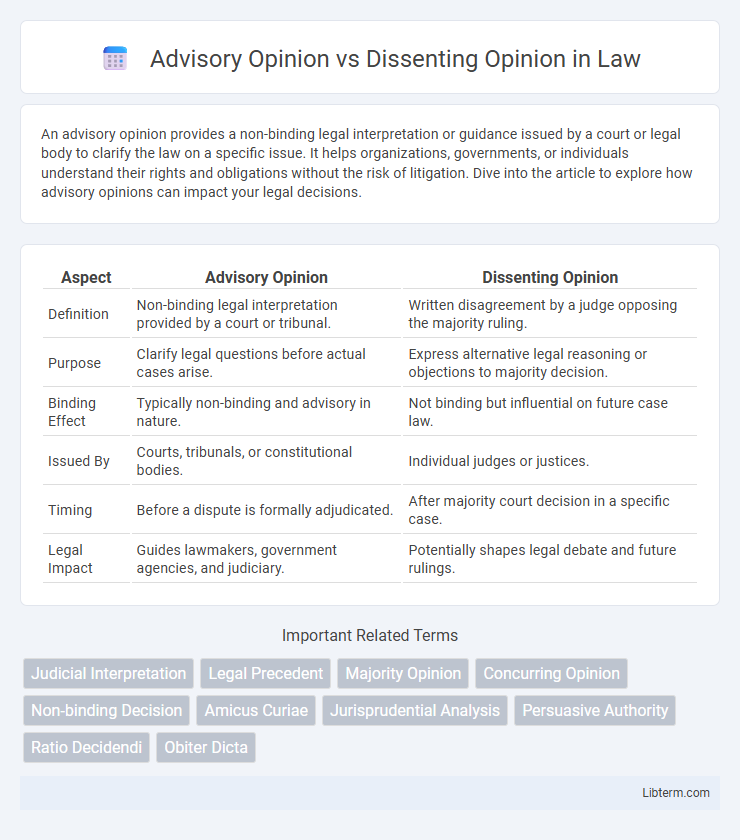
| Aspect | Advisory Opinion | Dissenting Opinion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-binding legal interpretation provided by a court or tribunal. | Written disagreement by a judge opposing the majority ruling. |
| Purpose | Clarify legal questions before actual cases arise. | Express alternative legal reasoning or objections to majority decision. |
| Binding Effect | Typically non-binding and advisory in nature. | Not binding but influential on future case law. |
| Issued By | Courts, tribunals, or constitutional bodies. | Individual judges or justices. |
| Timing | Before a dispute is formally adjudicated. | After majority court decision in a specific case. |
| Legal Impact | Guides lawmakers, government agencies, and judiciary. | Potentially shapes legal debate and future rulings. |
Definition of Advisory Opinion
Advisory opinions are formal legal interpretations provided by a court or legal authority in response to a question posed by a government body, without issuing a binding judgment in an actual case or controversy. These opinions guide future decisions and clarify legal principles without resolving specific disputes, distinguishing them from dissenting opinions, which represent a judge's disagreement with the majority ruling in a decided case. Advisory opinions play a critical role in preventive legal analysis and policy guidance by offering authoritative interpretations before legal conflicts escalate.
Definition of Dissenting Opinion
A dissenting opinion is a written judicial opinion by one or more judges expressing disagreement with the majority's decision in a case, highlighting alternative interpretations of law or facts. Unlike advisory opinions, which provide non-binding legal guidance on hypothetical situations or pending legislation, dissenting opinions directly challenge the court's final ruling and serve to influence future judicial reasoning or legal developments. Dissenting opinions are critical for transparency and legal debate, offering a lasting record of differing judicial viewpoints within the case's formal judgment.
Key Distinctions Between Advisory and Dissenting Opinions
Advisory opinions provide legal interpretations requested by a government body without binding force, serving as guidance rather than final judgments, whereas dissenting opinions are judgments written by judges who disagree with the majority decision in a case, offering alternative legal reasoning. Advisory opinions often address hypothetical scenarios or proposed legislation, influencing policy development, while dissenting opinions impact jurisprudence by challenging prevailing interpretations and may guide future legal arguments. The key distinction lies in advisory opinions' non-binding nature and consultative role compared to dissenting opinions' function within binding judicial decisions and their contribution to legal debate.
Purpose and Function of Advisory Opinions
Advisory opinions serve the purpose of providing non-binding legal interpretations on questions of law or constitutionality referred by authorized bodies, aiming to guide future actions and prevent legal disputes. Unlike dissenting opinions, which express disagreement with the majority's judgment in a binding case, advisory opinions do not resolve actual controversies but offer authoritative guidance to decision-makers. Their function is primarily consultative, enhancing legal clarity and supporting consistent application of the law without imposing immediate judicial consequences.
Purpose and Impact of Dissenting Opinions
Dissenting opinions serve to highlight alternative legal interpretations and challenge the majority's ruling, often laying the groundwork for future judicial reconsideration or legislative change. They provide transparency in judicial decision-making by documenting disagreement and fostering a richer understanding of complex legal issues. Unlike advisory opinions, which offer non-binding guidance, dissenting opinions can influence legal doctrine and public policy over time by shaping academic debate and appellate review.
Legal Status: Advisory vs. Dissenting Opinions
Advisory opinions provide non-binding legal interpretations requested by courts or government bodies, serving as guidance without enforcing judicial authority. Dissenting opinions, on the other hand, represent a judge's disagreement within a binding court ruling, offering alternative legal reasoning but lacking the force of majority decisions. The legal status of advisory opinions is consultative and lacks precedent value, while dissenting opinions hold persuasive influence but do not alter the binding outcome of a case.
Instances When Advisory Opinions are Requested
Advisory opinions are requested primarily by government branches or officials seeking non-binding legal guidance on constitutional or statutory issues before action is taken, often seen in constitutional courts or supreme courts worldwide. Dissenting opinions occur after a decision is made, where judges express disagreement with the majority ruling, contributing to legal discourse but carrying no authoritative weight. Instances when advisory opinions are requested include constitutional questions on proposed legislation, executive orders, or treaty interpretations to prevent future legal conflicts.
Notable Examples of Dissenting Opinions
Dissenting opinions reflect a judge's disagreement with the majority ruling, offering alternative legal reasoning that can influence future cases or legislation. Notable examples include Justice John Marshall Harlan's dissent in Plessy v. Ferguson, which opposed racial segregation, and Justice Hugo Black's dissent in Korematsu v. United States, which challenged the constitutionality of Japanese internment during World War II. These powerful dissents have shaped legal discourse and underscored the judiciary's role in protecting civil rights.
Influence on Judicial Decisions and Legal Precedent
Advisory opinions provide non-binding guidance that can shape judicial reasoning and inform future case law without directly altering legal precedent. Dissenting opinions, while minority views, often influence judicial decisions by presenting alternative interpretations that may be adopted in later rulings, contributing to the evolution of legal doctrine. Both opinions play crucial roles in the development of law, with advisory opinions guiding courts and dissenting opinions challenging prevailing interpretations to refine and expand jurisprudence.
Comparative Significance in Legal Systems
Advisory Opinions provide non-binding guidance on legal questions, often requested by government bodies or international organizations, shaping future judicial or legislative actions without deciding actual disputes. Dissenting Opinions express disagreement with the majority ruling in a binding case, offering alternative legal reasoning that can influence future case law and doctrinal development. The comparative significance lies in Advisory Opinions' role in preventive legal clarification and policy formation, while Dissenting Opinions contribute to the evolution of legal interpretation and potential shifts in jurisprudence within common law and civil law systems.
Advisory Opinion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com