Standard form is a way of expressing numbers using powers of ten, making it easier to read and compare very large or very small values. It simplifies complex numerical data by converting them into a concise format, such as 3.5 x 10^4 instead of 35,000. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to convert numbers to standard form and its practical applications.
Table of Comparison
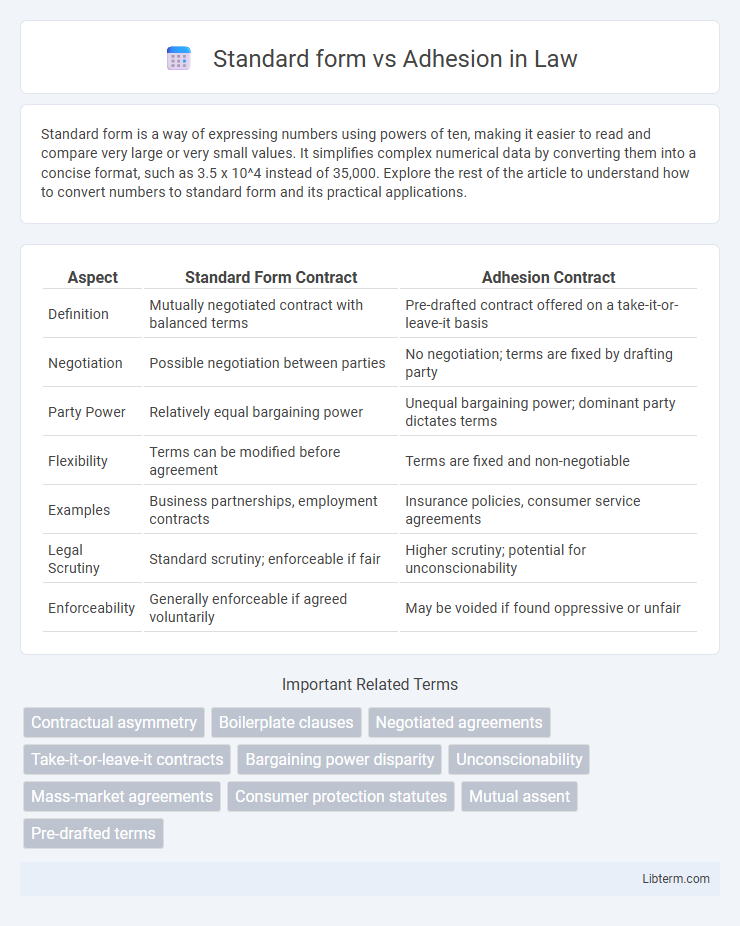
| Aspect | Standard Form Contract | Adhesion Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mutually negotiated contract with balanced terms | Pre-drafted contract offered on a take-it-or-leave-it basis |
| Negotiation | Possible negotiation between parties | No negotiation; terms are fixed by drafting party |
| Party Power | Relatively equal bargaining power | Unequal bargaining power; dominant party dictates terms |
| Flexibility | Terms can be modified before agreement | Terms are fixed and non-negotiable |
| Examples | Business partnerships, employment contracts | Insurance policies, consumer service agreements |
| Legal Scrutiny | Standard scrutiny; enforceable if fair | Higher scrutiny; potential for unconscionability |
| Enforceability | Generally enforceable if agreed voluntarily | May be voided if found oppressive or unfair |
Understanding Standard Form Contracts
Standard form contracts are pre-drafted agreements created by one party with stronger bargaining power, often used in industries like insurance, telecommunications, and real estate to streamline transactions. These contracts are non-negotiable, presenting terms on a "take it or leave it" basis, which contrasts with adhesion contracts where one party essentially has no choice but to accept terms dictated by the other. Understanding standard form contracts involves recognizing their role in reducing negotiation time and cost while acknowledging potential imbalances in fairness and the importance of scrutinizing key terms to protect consumer rights.
Defining Adhesion Contracts
Adhesion contracts are standardized agreements drafted by one party with stronger bargaining power, presenting terms on a "take it or leave it" basis to the weaker party. These contracts limit negotiation, often used in consumer transactions and insurance policies, where the adherent has little to no ability to alter terms. Courts scrutinize adhesion contracts for fairness and potential unconscionability to protect against oppressive or one-sided terms.
Key Differences Between Standard Form and Adhesion Contracts
Standard form contracts are pre-drafted agreements with fixed terms offered by one party, allowing minimal or no negotiation by the other party, commonly found in consumer transactions. Adhesion contracts, often characterized as "take-it-or-leave-it" agreements, are a subtype of standard form contracts where the stronger party imposes terms that the weaker party must accept without modification, frequently used in insurance policies and service agreements. The key differences lie in the negotiation power, with standard form contracts permitting some degree of bargaining while adhesion contracts leave no room for negotiation, often raising concerns about unconscionability and fairness.
Historical Development of Contract Types
Standard form contracts originated during the industrial revolution, streamlining transactions by providing pre-set terms to handle mass-market needs efficiently. Adhesion contracts emerged later as a response to unequal bargaining power, primarily in consumer and insurance contexts, where one party drafts terms non-negotiably imposed on the other. The historical development of these contract types reflects evolving commerce dynamics and legal approaches to fairness and enforceability.
Legal Enforceability of Standard Form Contracts
Standard form contracts are pre-drafted agreements with fixed terms, commonly used in consumer and commercial transactions, ensuring uniformity and efficiency. Adhesion contracts, often presented on a "take it or leave it" basis by a party with stronger bargaining power, raise concerns about enforceability due to potential unconscionability or lack of meaningful consent. Courts scrutinize adhesion contracts more rigorously to protect weaker parties, sometimes invalidating provisions that are unfair or oppressive, unlike standard form contracts that typically face less judicial intervention if terms are clear and reasonable.
Issues of Consent in Adhesion Contracts
Adhesion contracts often raise significant issues of consent because they are typically drafted by one party with stronger bargaining power, offering little or no opportunity for negotiation by the weaker party. This lack of meaningful choice can undermine true mutual assent, leading courts to scrutinize whether the adhering party genuinely understood and voluntarily agreed to the terms. Standard form contracts, while also pre-drafted, may present fewer consent concerns when parties have more balanced negotiation power and clearer opportunities to review and reject terms.
Advantages for Businesses and Consumers
Standard form contracts streamline business operations by reducing negotiation time, lowering legal costs, and ensuring consistency across transactions, which benefits companies by enhancing efficiency and predictability. For consumers, adhesion contracts provide clear, standardized terms that simplify understanding and access to services or products, although they reflect limited bargaining power. The uniformity of standard form contracts supports scalability for businesses while offering consumers transparent, straightforward agreements.
Common Legal Challenges and Disputes
Standard form contracts often face legal challenges related to unconscionability and lack of negotiation, triggering disputes over fairness and enforceability. Adhesion contracts, typically drafted by one party with stronger bargaining power, frequently raise issues concerning consent and the potential for hidden or oppressive terms. Courts regularly scrutinize these agreements for ambiguity, unequal bargaining power, and the adequacy of disclosure to prevent invalidation due to unfair terms.
Protecting Consumer Rights in Adhesion Agreements
Adhesion agreements often present a challenge for consumer rights due to their take-it-or-leave-it nature, contrasting with the more balanced negotiation possibilities found in standard form contracts. Legal frameworks aim to protect consumers by scrutinizing unconscionable terms and enforcing transparency in adhesion contracts, ensuring fairness and preventing exploitation. Courts frequently evaluate adhesion agreements to uphold equitable treatment and maintain consumer protection in transactions dominated by imbalanced bargaining power.
Future Trends in Contractual Practices
Future trends in contractual practices indicate a shift toward greater integration of standard form contracts with adhesion contracts, driven by the need for efficiency and uniformity in digital transactions. Advances in blockchain technology and smart contracts are expected to automate enforcement and enhance transparency, reducing disputes associated with adhesion contracts. Increasing regulatory scrutiny will push for fairer terms and greater consumer protections, balancing the rigidity of standard forms with the demands for equity in adhesion agreements.
Standard form Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com