Competition laws protect markets from unfair business practices by promoting fair competition and preventing monopolies. These regulations ensure that companies cannot engage in activities like price-fixing, market division, or abuse of dominant positions, safeguarding consumer interests and fostering innovation. Explore this article to understand how competition laws impact your business and the broader economy.
Table of Comparison
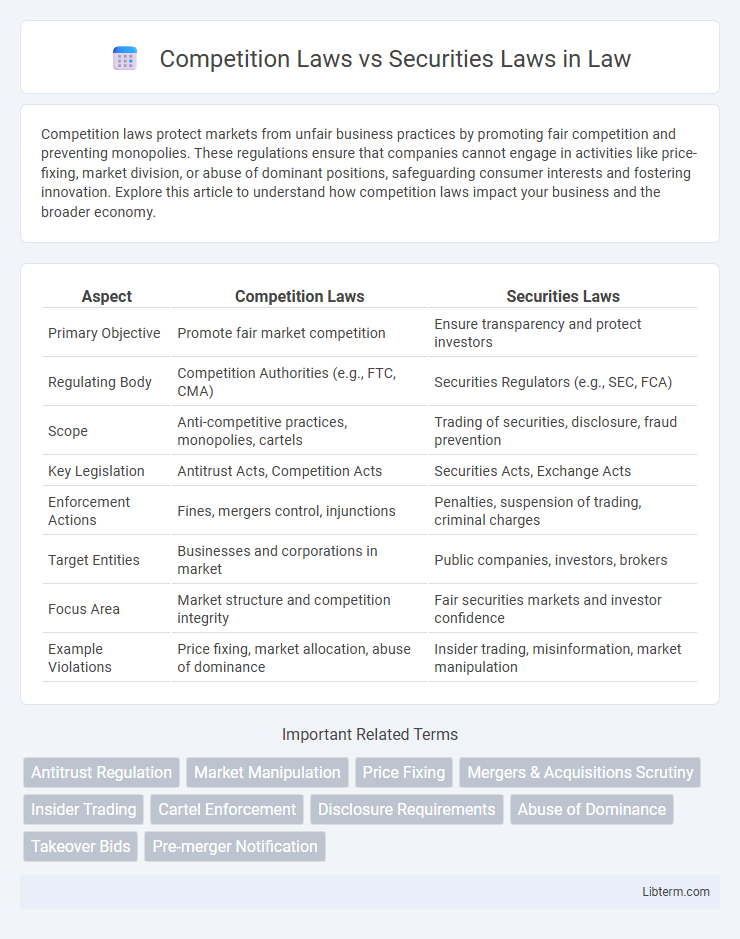
| Aspect | Competition Laws | Securities Laws |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Objective | Promote fair market competition | Ensure transparency and protect investors |
| Regulating Body | Competition Authorities (e.g., FTC, CMA) | Securities Regulators (e.g., SEC, FCA) |
| Scope | Anti-competitive practices, monopolies, cartels | Trading of securities, disclosure, fraud prevention |
| Key Legislation | Antitrust Acts, Competition Acts | Securities Acts, Exchange Acts |
| Enforcement Actions | Fines, mergers control, injunctions | Penalties, suspension of trading, criminal charges |
| Target Entities | Businesses and corporations in market | Public companies, investors, brokers |
| Focus Area | Market structure and competition integrity | Fair securities markets and investor confidence |
| Example Violations | Price fixing, market allocation, abuse of dominance | Insider trading, misinformation, market manipulation |
Introduction to Competition Laws and Securities Laws
Competition laws regulate market behavior to promote fair competition, prevent monopolies, and protect consumer interests, ensuring efficient market functioning. Securities laws govern the issuance, trading, and disclosure of financial instruments, aiming to maintain market integrity, protect investors, and prevent fraud. Both frameworks serve distinct roles but collectively support transparent, competitive, and trustworthy economic environments.
Key Objectives of Competition Laws
Competition laws primarily aim to promote fair market practices by preventing monopolies, cartels, and anti-competitive mergers that restrict consumer choice and inflate prices. These laws ensure a competitive marketplace that fosters innovation, improves product quality, and leads to efficient resource allocation. Unlike securities laws that regulate financial markets and protect investors, competition laws focus on maintaining market integrity and consumer welfare through enforcement actions against collusion and abuse of dominant market positions.
Core Principles of Securities Laws
Securities laws primarily aim to ensure transparency, fairness, and investor protection in financial markets by regulating the issuance, trading, and disclosure of securities. Core principles include mandatory disclosure of material information, prevention of fraud and insider trading, and the enforcement of registration requirements for securities offerings. These laws promote market integrity and investor confidence, distinguishing their focus from competition laws, which address anti-competitive practices and market monopoly issues.
Scope and Coverage: Competition vs Securities Laws
Competition laws regulate market behavior to promote fair competition and prevent monopolistic practices, focusing on pricing, market sharing, and abuse of dominant position. Securities laws govern the issuance, trading, and disclosure of financial instruments to protect investors and ensure market transparency, covering activities such as insider trading, fraud, and securities registration. While competition laws address market structure and conduct, securities laws emphasize investor protection and the integrity of capital markets.
Regulatory Authorities and Enforcement Mechanisms
Competition laws are primarily enforced by regulatory authorities such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ) in the United States, which focus on preventing anti-competitive practices like monopolies and cartels. Securities laws are overseen by entities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), tasked with regulating securities markets, ensuring transparency, and protecting investors from fraud and insider trading. Enforcement mechanisms for competition laws often involve investigations, fines, and structural remedies, while securities law enforcement includes civil penalties, criminal prosecutions, and administrative actions to maintain market integrity.
Anti-Competitive Practices vs Securities Violations
Competition laws target anti-competitive practices such as price fixing, market allocation, and monopolistic conduct that harm consumer welfare and restrict market competition. Securities laws address securities violations including insider trading, false disclosures, and market manipulation that undermine investor confidence and market integrity. Both frameworks aim to preserve fair market conditions but focus on different aspects of economic regulation and enforcement.
Overlapping Jurisdictions and Legal Conflicts
Competition laws and securities laws often intersect in regulating corporate behavior, particularly concerning mergers, acquisitions, and market manipulation. Overlapping jurisdictions arise when both antitrust authorities and securities regulators examine the same transactions for anti-competitive effects and investor protection, potentially leading to conflicting legal standards and enforcement actions. Legal conflicts frequently occur due to differing objectives: competition laws aim to maintain market fairness and prevent monopolies, while securities laws focus on transparency, disclosure, and fraud prevention in financial markets.
Impact on Businesses and Market Participants
Competition laws promote fair market conditions by preventing monopolistic practices and ensuring a level playing field for businesses, which fosters innovation and consumer choice. Securities laws regulate the issuance and trading of financial instruments to protect investors from fraud and maintain market integrity, thus enhancing investor confidence. Together, these legal frameworks impact market participants by balancing competitive behavior with transparent, secure investment environments, ultimately supporting sustainable economic growth.
Recent Developments and Case Studies
Recent developments in competition laws emphasize stricter scrutiny of mergers to prevent monopolistic practices that harm market competition, as seen in the 2023 FTC challenge against a major tech acquisition. Securities laws have evolved to enhance transparency and investor protection, highlighted by the SEC's 2024 enforcement action targeting insider trading in cryptocurrency markets. Case studies such as the European Commission's antitrust investigation into Google's advertising practices demonstrate the intersection of competition and securities regulations in regulating digital economy giants.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gaps between Competition and Securities Laws
Bridging the gaps between competition laws and securities laws requires harmonizing regulatory frameworks to enhance market efficiency and investor protection. Integrated enforcement strategies reduce regulatory arbitrage, ensuring fair competition and transparent securities markets. Collaborative policymaking fosters legal coherence, promoting economic growth through balanced oversight of antitrust and capital market activities.
Competition Laws Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com