A defendant is an individual or entity accused of a crime or lawsuit, required to respond to the charges presented in court. Understanding the defendant's rights and legal obligations is crucial for navigating the judicial process effectively. Explore the rest of this article to learn how being a defendant impacts your case and what steps you should take.
Table of Comparison
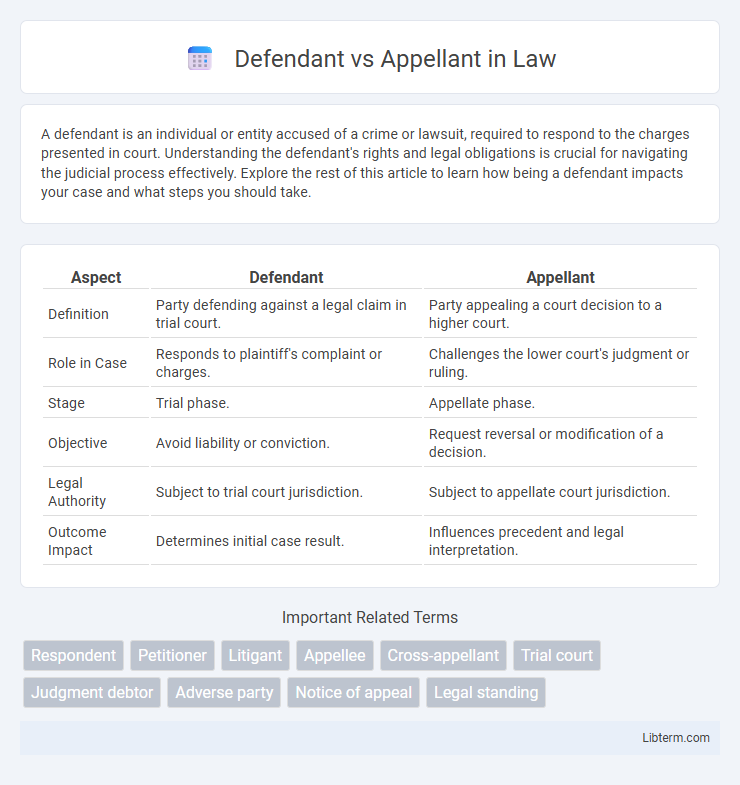
| Aspect | Defendant | Appellant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Party defending against a legal claim in trial court. | Party appealing a court decision to a higher court. |
| Role in Case | Responds to plaintiff's complaint or charges. | Challenges the lower court's judgment or ruling. |
| Stage | Trial phase. | Appellate phase. |
| Objective | Avoid liability or conviction. | Request reversal or modification of a decision. |
| Legal Authority | Subject to trial court jurisdiction. | Subject to appellate court jurisdiction. |
| Outcome Impact | Determines initial case result. | Influences precedent and legal interpretation. |
Understanding the Roles: Defendant vs Appellant
The defendant is the party against whom a criminal or civil lawsuit is filed, responsible for responding to the claims made by the plaintiff or prosecution. In contrast, the appellant is the party who appeals a court's decision, seeking a review and potential reversal of the judgment from a higher appellate court. Understanding these distinct roles clarifies the procedural context within the legal system, where defendants participate at the trial level and appellants engage in the post-trial appellate process.
Legal Definitions: Who is a Defendant?
A defendant is the party against whom a lawsuit is filed in a civil case or who is accused of a crime in a criminal case, tasked with responding to the charges or claims presented by the plaintiff or prosecution. This role involves defending one's rights and interests in court, often with the assistance of legal counsel. Understanding the defendant's position is crucial for grasping the dynamics of legal proceedings and the burden of proof required to establish liability or guilt.
Legal Definitions: Who is an Appellant?
An appellant is a party who appeals a court's decision, seeking a higher court's review and possible reversal of the lower court's ruling. Unlike a defendant, who is the party responding to a lawsuit in the trial court, the appellant initiates the appeal process after an unfavorable judgment. Understanding the distinction between a defendant and an appellant is crucial for navigating appellate procedures and legal rights.
Key Differences Between Defendant and Appellant
A defendant is the party against whom a criminal or civil lawsuit is filed, responsible for answering the charges or claims in the trial court, whereas an appellant is the party who files an appeal seeking to overturn or modify the lower court's decision. The defendant's role occurs primarily during the initial trial phase, while the appellant engages in the appellate process after a final judgment has been rendered. Key differences include their functions in the legal system, timing of involvement, and the type of court proceedings they participate in--trial courts for defendants and appellate courts for appellants.
Stages of Legal Proceedings: From Defendant to Appellant
The defendant is the party initially accused or sued in a trial court, facing the claims brought by the plaintiff or prosecution. If the defendant disputes the trial court's decision, they become the appellant by filing a notice of appeal to a higher court, seeking review and possible reversal of the judgment. This transition from defendant to appellant marks a critical stage in legal proceedings, shifting from trial court adjudication to appellate review focused on legal errors or procedural issues.
Rights and Responsibilities of a Defendant
A defendant holds the right to a fair trial, legal representation, and to remain silent to avoid self-incrimination during court proceedings. Responsibilities of a defendant include responding to charges, attending all court hearings, and complying with court orders such as bail conditions or sentencing mandates. Understanding these rights and responsibilities is crucial for ensuring due process and protecting the defendant's legal interests throughout the judicial process.
Rights and Responsibilities of an Appellant
An appellant has the right to challenge a court's decision by filing an appeal, seeking a review for legal errors or procedural mistakes during the original trial. Responsibilities of an appellant include submitting the appeal within statutory deadlines, preparing a concise appellate brief outlining legal arguments, and ensuring all necessary records from the lower court are filed properly. Unlike a defendant, whose focus is on defense during a trial, an appellant must demonstrate specific grounds for reversal or modification of the judgment.
Common Misconceptions About Defendant and Appellant
Defendants are often mistakenly believed to only be parties in criminal cases, but they can also appear in civil litigation, while appellants specifically refer to parties who challenge a court decision on appeal, regardless of their original role. Another common misconception is that appellants are always defendants, yet plaintiffs can also become appellants if they appeal a judgment. Understanding these distinctions clarifies legal procedures and the roles each party plays in different stages of a case.
Importance of Legal Representation in Both Roles
Effective legal representation is crucial for both defendants and appellants to safeguard their rights and ensure a fair trial or appeal process. Defendants rely on attorneys to develop a strong defense strategy, navigate complex criminal procedures, and challenge evidence, while appellants need skilled lawyers to identify legal errors, draft persuasive briefs, and advocate for reversal or modification of lower court decisions. Inadequate representation in either role can result in wrongful convictions, unjust verdicts, or missed opportunities for relief, highlighting the vital role of experienced defense counsel throughout the criminal justice process.
Real-World Examples: Defendant vs Appellant in Court Cases
In court cases, a defendant is the party responding to criminal charges or civil complaints, such as O.J. Simpson in his 1995 criminal trial, while an appellant is a party who appeals a court's decision, like Michael Flynn appealing his conviction in 2020. The defendant's role centers around the initial trial, whereas the appellant engages the appellate court to review and possibly overturn the trial outcome. Real-world examples highlight how defendants may become appellants if they challenge rulings, emphasizing distinct procedural phases within the judicial system.
Defendant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com