Using something for an illegal purpose violates laws designed to maintain order and protect rights. Engaging in activities with unlawful intent can result in serious legal consequences, including fines, imprisonment, or both. Explore the full article to understand how illegal purposes are defined and the potential impact on your responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
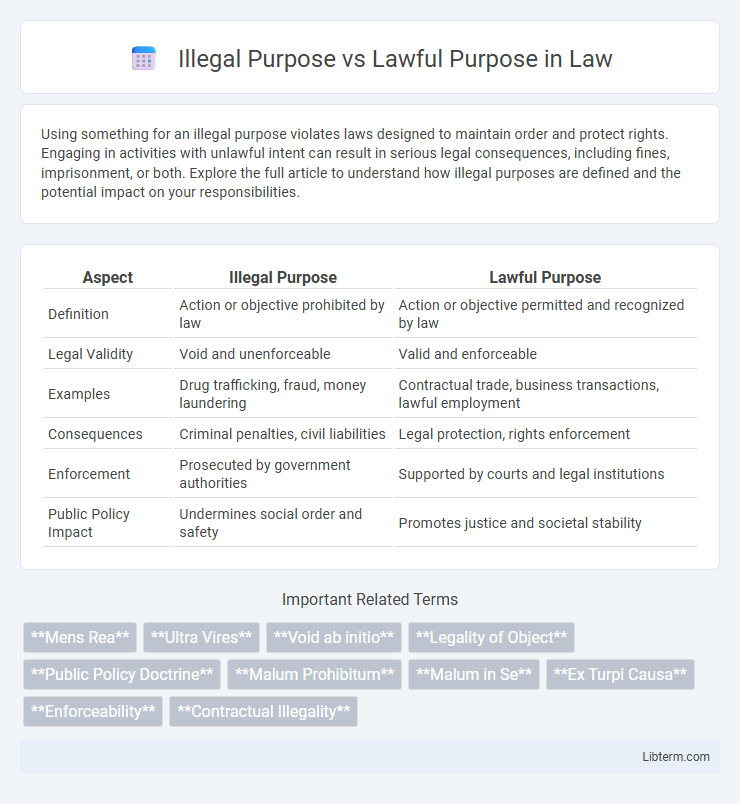
| Aspect | Illegal Purpose | Lawful Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Action or objective prohibited by law | Action or objective permitted and recognized by law |
| Legal Validity | Void and unenforceable | Valid and enforceable |
| Examples | Drug trafficking, fraud, money laundering | Contractual trade, business transactions, lawful employment |
| Consequences | Criminal penalties, civil liabilities | Legal protection, rights enforcement |
| Enforcement | Prosecuted by government authorities | Supported by courts and legal institutions |
| Public Policy Impact | Undermines social order and safety | Promotes justice and societal stability |
Understanding Legal Purpose and Illegal Purpose
Understanding legal purpose requires recognizing actions or objectives that comply with laws, regulations, and public policy, ensuring contracts or activities are valid and enforceable. Illegal purpose involves actions that violate statutory laws, ethical standards, or public policies, rendering agreements void or unenforceable and potentially subject to penalties. Distinguishing between lawful and illegal purposes is crucial in contract law and business activities to avoid legal disputes and protect rights.
Key Differences Between Lawful and Illegal Purposes
Lawful purposes comply with legal standards and regulations, ensuring actions are authorized and protected by law, whereas illegal purposes violate statutory provisions and are subject to penalties and enforcement actions. Key differences include the legitimacy of the objective, the adherence to legal frameworks, and the consequences faced upon engagement--lawful purposes foster trust and compliance, while illegal purposes result in criminal or civil liability. Understanding these distinctions is critical for contract validity, regulatory compliance, and risk management strategies.
Examples of Lawful vs Illegal Purposes in Contracts
Contracts with a lawful purpose include agreements for the sale of goods, employment contracts, and lease agreements, all operating within legal frameworks. Illegal purposes involve contracts for activities such as drug trafficking, fraud, or unlawful gambling, which are void and unenforceable by law. Distinguishing lawful from illegal purposes is critical to ensuring contract validity and enforceability in legal disputes.
The Role of Intention in Defining Purpose
The role of intention in defining purpose is pivotal in distinguishing illegal purpose from lawful purpose within legal frameworks. Intention guides the interpretation of an action's legality by revealing whether the actor aims to achieve an outcome permitted or prohibited by law. Courts often assess evidence of intent to determine if a purpose is lawful, emphasizing that identical actions can be lawful or unlawful based on the intent behind them.
Legal Consequences of Illegal Purpose
Engaging in contracts for an illegal purpose results in void agreements that cannot be enforced by courts, leading to significant legal consequences including fines, penalties, and potential criminal charges. Parties involved in illegal contracts risk civil liabilities and the inability to seek remedies or damages for non-performance. Lawful purpose contracts, by contrast, are upheld by law, allowing parties to enforce terms and obtain legal protections.
Court Interpretation of Lawful and Unlawful Purpose
Courts interpret lawful purpose as actions explicitly permitted by statute or public policy, emphasizing compliance with legal standards and intent consistent with societal norms. Illegal purpose involves objectives that violate statutory provisions, public order, or morality, rendering agreements or actions void or unenforceable. Judicial analysis often examines the purpose's substance and context, distinguishing valid contracts from those tainted by illegality or fraud.
Impact on Contract Validity and Enforceability
Contracts formed for an illegal purpose are inherently void and unenforceable, as courts refuse to uphold agreements that promote unlawful activities or violate public policy. Conversely, contracts with lawful purposes are valid and enforceable, provided all other contract elements such as capacity, consent, and consideration are met. The impact on contract validity hinges on the legality of the objective; illegal purpose undermines enforceability, while lawful objectives ensure contractual obligations are binding and protectable under law.
Case Studies: Legal vs Illegal Purpose
Case studies reveal contrasting outcomes between illegal and lawful purposes in contract enforcement. In the landmark case of *Everet v. Williams* (1725), the court refused to enforce a contract for a joint illegal venture, emphasizing the principle that agreements involving illegal activities lack legal validity. Conversely, in *Lucy v. Zehmer* (1954), the court upheld a contract for a lawful sale of land, demonstrating that contracts entered into for lawful purposes are binding and enforceable under the law.
Preventing Unintentional Illegal Purpose
Ensuring contract clauses explicitly define lawful purposes helps prevent unintentional illegal use by clarifying prohibited activities and reducing ambiguities. Implementing regular compliance training and monitoring mechanisms enables early detection of potential illegal purposes, safeguarding businesses from legal risks. Employing clear legal guidelines and standardized documentation supports transparent agreements, promoting lawful objectives and minimizing inadvertent violations.
Best Practices for Ensuring Lawful Purpose
Implementing rigorous verification processes ensures that all activities comply with applicable laws and regulations, minimizing the risk of engaging in illegal purposes. Maintaining clear documentation and conducting regular audits strengthens transparency and accountability, facilitating compliance with lawful purpose requirements. Training employees on legal standards and ethical guidelines reinforces commitment to lawful practices and prevents inadvertent violations.
Illegal Purpose Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com