Ex parte proceedings involve a legal action where only one party is present without the other party's participation, often used in urgent situations requiring immediate court intervention. These hearings can address temporary restraining orders, emergency custody, or injunctions to prevent harm before a full hearing occurs. Explore the rest of the article to understand when and how ex parte motions might impact your legal strategy.
Table of Comparison
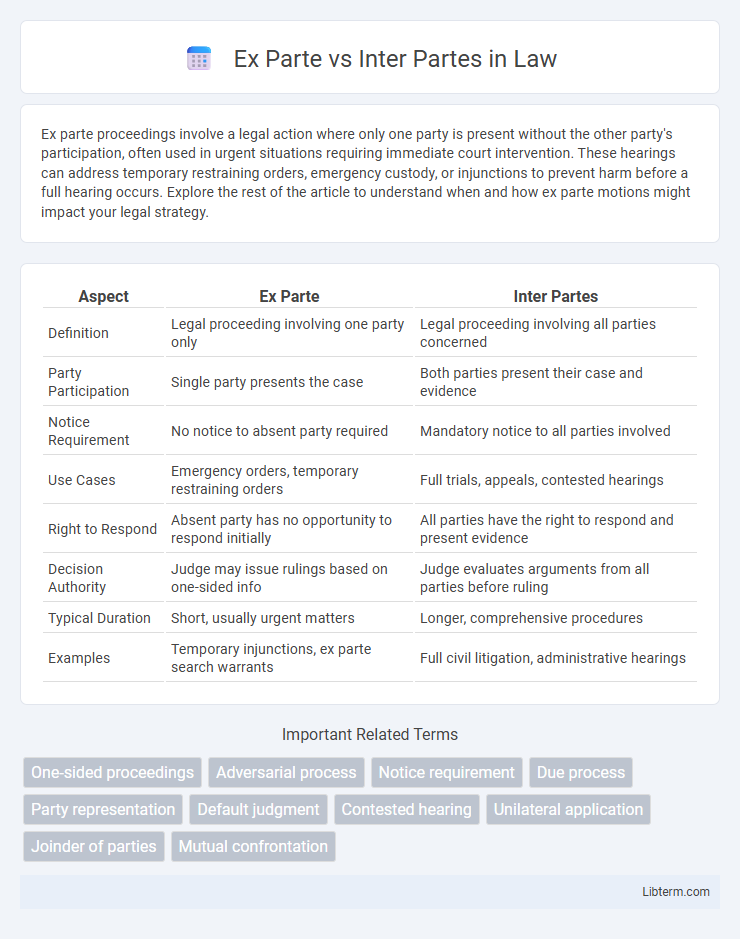
| Aspect | Ex Parte | Inter Partes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal proceeding involving one party only | Legal proceeding involving all parties concerned |
| Party Participation | Single party presents the case | Both parties present their case and evidence |
| Notice Requirement | No notice to absent party required | Mandatory notice to all parties involved |
| Use Cases | Emergency orders, temporary restraining orders | Full trials, appeals, contested hearings |
| Right to Respond | Absent party has no opportunity to respond initially | All parties have the right to respond and present evidence |
| Decision Authority | Judge may issue rulings based on one-sided info | Judge evaluates arguments from all parties before ruling |
| Typical Duration | Short, usually urgent matters | Longer, comprehensive procedures |
| Examples | Temporary injunctions, ex parte search warrants | Full civil litigation, administrative hearings |
Introduction to Ex Parte and Inter Partes
Ex parte and inter partes are types of legal proceedings differentiated by the number of parties involved; ex parte involves one party requesting relief without the presence or participation of the other party, while inter partes includes all interested parties from the beginning. In ex parte cases, decisions are often made based on one-sided information, commonly used in emergency or temporary situations such as restraining orders or injunctions. Inter partes proceedings provide a full hearing where both sides present evidence, typical in trials or disputes requiring a comprehensive evaluation.
Defining Ex Parte Proceedings
Ex parte proceedings involve one party presenting a case or request to the court without requiring the presence or participation of the opposing party, typically used in urgent or preliminary matters such as temporary restraining orders or emergency relief. These proceedings prioritize immediate judicial intervention based on the evidence and arguments provided solely by the requesting party, often without full adversarial input. Ex parte actions require careful judicial scrutiny to balance urgency against the risk of prejudice to absent parties, ensuring due process rights are respected.
Defining Inter Partes Proceedings
Inter Partes proceedings involve a legal process where all relevant parties are given the opportunity to be heard and present evidence before a decision is made. These proceedings are characterized by adversarial participation, ensuring fairness and transparency through the exchange of arguments and documentation. Inter Partes procedures are commonly used in patent and trademark disputes, allowing both the patent office and third parties to challenge the validity of intellectual property rights.
Key Differences Between Ex Parte and Inter Partes
Ex Parte proceedings involve one party presenting a case without the presence or participation of the opposing party, commonly used in urgent or preliminary matters such as restraining orders or emergency relief. Inter Partes procedures include both parties actively participating, ensuring a full adversarial process typically seen in trials, hearings, or patent oppositions. The key difference lies in the level of party involvement, with Ex Parte hearings favoring unilateral decisions and Inter Partes promoting bilateral engagement and due process.
Legal Implications of Ex Parte Actions
Ex parte actions, conducted without the presence or notification of the opposing party, carry significant legal implications, such as the potential for judgments or orders issued without adversarial input, which can raise concerns regarding fairness and due process. Courts often impose stringent requirements on ex parte motions to prevent abuse, requiring clear and convincing evidence of urgency or harm that cannot be addressed through normal procedural channels. The unilateral nature of ex parte proceedings necessitates careful judicial scrutiny to balance the need for immediate relief against the rights of absent parties.
Legal Implications of Inter Partes Actions
Inter Partes actions involve all affected parties, ensuring due process and fairness by allowing each side to present evidence and arguments, which strengthens judicial transparency and legitimacy. These proceedings often result in legally binding decisions enforceable against all participants, reducing the risk of future litigation by establishing clear case law or administrative rulings. Courts and regulatory bodies rely on Inter Partes procedures to uphold rights, balance interests, and prevent unilateral or arbitrary determinations common in Ex Parte actions.
Common Examples of Ex Parte Cases
Ex parte cases typically involve urgent matters such as restraining orders, temporary injunctions, and emergency child custody decisions where one party seeks immediate relief without notifying the opposing side. Common examples include applications for search warrants, probate matters when dealing with estates, and requests for emergency protective orders in domestic violence situations. These cases prioritize swift judicial intervention to prevent imminent harm or preserve the status quo before a full hearing can be conducted.
Typical Scenarios for Inter Partes Proceedings
Inter partes proceedings typically arise in disputes requiring active participation from multiple parties, such as patent oppositions, trademark oppositions, or interferences before intellectual property offices. These scenarios involve both parties presenting evidence, arguments, and responses to each other under procedural rules designed to ensure fairness and thorough examination. The adversarial nature allows examiners or adjudicators to evaluate the merits of competing claims through a balanced exchange of information.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Procedure
Ex parte proceedings offer the advantage of faster resolution since only one party presents evidence, but they lack input from opposing sides which may result in biased or incomplete outcomes. Inter partes procedures provide a more balanced and thorough examination by allowing all parties to participate and challenge evidence, enhancing fairness and reliability. However, this method often requires more time and higher costs due to extended hearings and procedural complexities.
Choosing Between Ex Parte and Inter Partes Proceedings
Choosing between ex parte and inter partes proceedings depends on the urgency and nature of the legal matter. Ex parte proceedings are suitable for situations requiring immediate relief without notifying the opposing party, often used in temporary restraining orders or emergency injunctions. Inter partes proceedings involve both parties, ensuring due process and comprehensive adjudication, ideal for disputes requiring full hearing and evidence presentation.
Ex Parte Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com