Liability refers to the legal responsibility for damages or losses caused by one's actions or negligence. Understanding liability is crucial for protecting your assets and avoiding costly legal disputes. Dive deeper into this article to learn how liability affects you and ways to manage it effectively.
Table of Comparison
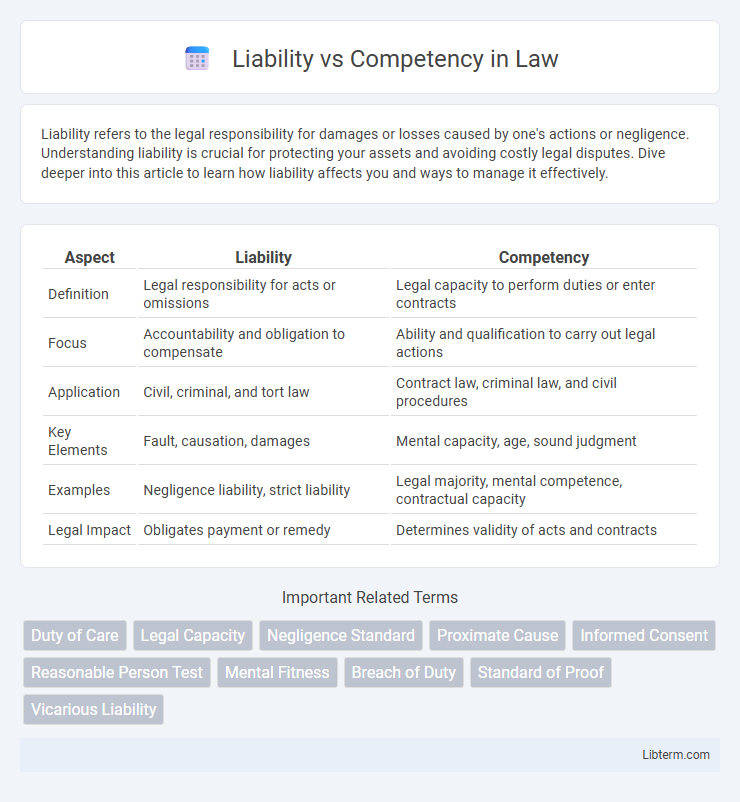
| Aspect | Liability | Competency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal responsibility for acts or omissions | Legal capacity to perform duties or enter contracts |
| Focus | Accountability and obligation to compensate | Ability and qualification to carry out legal actions |
| Application | Civil, criminal, and tort law | Contract law, criminal law, and civil procedures |
| Key Elements | Fault, causation, damages | Mental capacity, age, sound judgment |
| Examples | Negligence liability, strict liability | Legal majority, mental competence, contractual capacity |
| Legal Impact | Obligates payment or remedy | Determines validity of acts and contracts |
Understanding Liability in Legal Contexts
Liability in legal contexts refers to the state of being legally responsible for harm or damages caused to another party, often involving obligations to compensate or rectify the issue. Competency, by contrast, typically relates to an individual's capacity or ability to perform a legal act or function, such as standing trial or executing a contract. Distinguishing liability from competency is crucial for accurately assessing legal accountability and the enforceability of legal actions.
Defining Competency: What It Means
Competency refers to the ability to perform a task effectively, combining knowledge, skills, and behavior required for specific roles. Unlike liability, which involves legal responsibility for actions, competency is centered on an individual's qualifications and readiness to meet job demands. Assessing competency ensures that professionals possess the essential expertise to deliver safe and efficient outcomes.
Key Differences Between Liability and Competency
Liability refers to the legal responsibility an individual or entity has for their actions or omissions, often resulting in financial or legal obligations. Competency denotes the ability or qualification to perform a task effectively, driven by knowledge, skills, and experience. The key difference lies in liability addressing accountability for outcomes, whereas competency focuses on the capability to execute duties proficiently.
Legal Standards for Establishing Liability
Legal standards for establishing liability hinge on proving duty, breach, causation, and damages within tort law frameworks. Liability requires demonstrating that the defendant owed a legal duty to the plaintiff, breached that duty through action or inaction, and directly caused harm or loss resulting in compensable damages. Competency standards, contrastingly, address the defendant's mental capacity at the time of the event, influencing liability assessments but not substituting for the core elements required to establish fault and responsibility under civil law.
Assessing Competency in Court Cases
Assessing competency in court cases involves evaluating a defendant's mental capacity to understand legal proceedings and participate in their defense, which directly impacts their criminal liability. Psychological assessments and expert testimonies play crucial roles in determining if a defendant meets the legal criteria for competency, ensuring fair trial standards. Courts rely on established forensic evaluation protocols to differentiate competency issues from liability, thereby upholding justice while protecting defendants' rights.
The Role of Liability in Civil and Criminal Law
Liability in civil law establishes responsibility for harm or damages caused by a party, requiring compensation or restitution to the injured claimant. In criminal law, liability determines whether an individual can be held legally accountable for a crime, considering factors such as intent and negligence. The distinction between civil liability and criminal liability hinges on the nature of the offense and the corresponding legal consequences enforced by courts.
How Competency Impacts Legal Proceedings
Competency determines a defendant's ability to understand legal charges and participate meaningfully in their defense, which directly affects the fairness of legal proceedings. Courts assess mental capacity to ensure a person can make informed decisions, and a finding of incompetency may lead to delays, treatment, or dismissal of charges. Unlike liability, which concerns responsibility for actions, competency influences procedural rights and the adjudication process in criminal and civil cases.
Real-World Examples: Liability vs. Competency
Liability refers to the legal responsibility one holds for actions or omissions that cause harm or damage, often illustrated in real-world scenarios like product defects leading to consumer injury. Competency involves the ability and qualifications required to perform a task effectively, such as a licensed surgeon demonstrating the necessary skills for a medical procedure. Distinguishing between liability and competency is crucial in professional fields where negligence results in legal consequences while inadequate skills impact performance quality.
Common Misconceptions About Liability and Competency
Liability and competency are often misunderstood as interchangeable legal concepts, yet liability refers to the legal responsibility for one's actions, while competency concerns an individual's mental capacity to stand trial or make decisions. A common misconception is assuming that a person deemed incompetent is automatically free from liability, whereas incompetency affects the ability to participate in legal proceedings but does not negate the occurrence of liability. Clarifying these distinctions is essential for accurate legal assessments in criminal and civil cases.
Best Practices for Evaluating Competency and Liability
Evaluating competency requires standardized assessments tailored to the specific skills and knowledge necessary for the role, including validated tests and real-world scenario simulations to ensure accurate measurement of capabilities. Best practices for assessing liability emphasize thorough documentation, risk management protocols, and compliance with relevant legal standards to mitigate potential legal exposure. Combining both approaches fosters a comprehensive evaluation framework that promotes informed decision-making and organizational accountability.
Liability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com