Repeal refers to the official revocation or annulment of a law, regulation, or policy, effectively removing its legal force. This process can impact various sectors including healthcare, taxation, or environmental regulations, influencing how rules are applied and enforced. Discover how repeal affects your rights and regulations by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
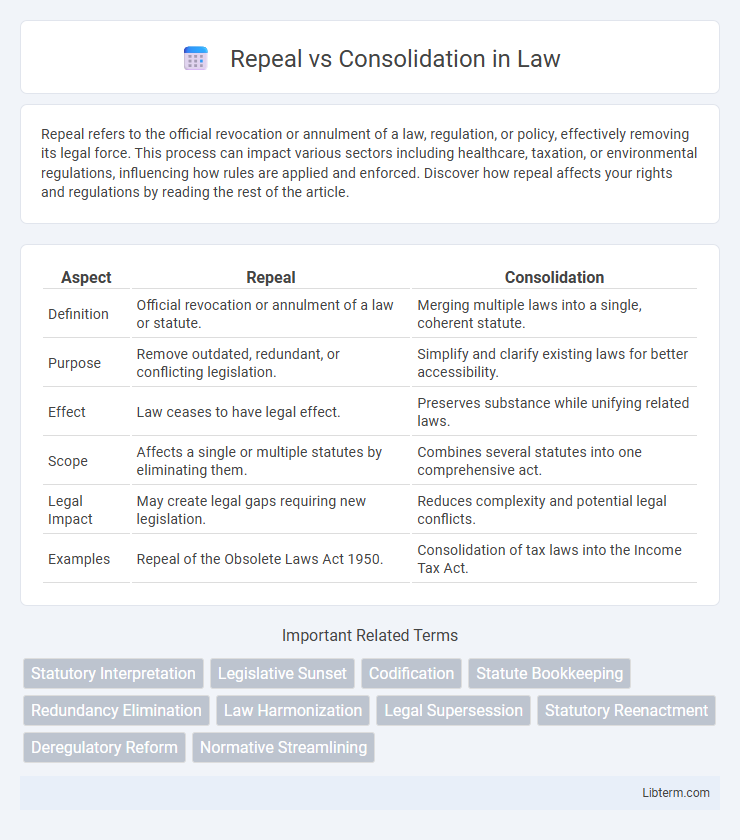
| Aspect | Repeal | Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official revocation or annulment of a law or statute. | Merging multiple laws into a single, coherent statute. |
| Purpose | Remove outdated, redundant, or conflicting legislation. | Simplify and clarify existing laws for better accessibility. |
| Effect | Law ceases to have legal effect. | Preserves substance while unifying related laws. |
| Scope | Affects a single or multiple statutes by eliminating them. | Combines several statutes into one comprehensive act. |
| Legal Impact | May create legal gaps requiring new legislation. | Reduces complexity and potential legal conflicts. |
| Examples | Repeal of the Obsolete Laws Act 1950. | Consolidation of tax laws into the Income Tax Act. |
Understanding Repeal and Consolidation
Understanding repeal involves recognizing it as the formal process of revoking or annulling existing laws, thereby removing their legal effect. Consolidation refers to combining multiple statutes or regulations into a single, coherent legal text to simplify and clarify the legislative framework. Both processes serve to enhance legal clarity but achieve this through distinct methods--repeal eliminates outdated or conflicting laws, while consolidation streamlines and organizes current statutes.
Key Differences Between Repeal and Consolidation
Repeal involves the formal withdrawal or annulment of a law, effectively removing it from the legal system, whereas consolidation refers to the process of combining several existing statutes into a single, coherent legal text without changing the substance of the law. Key differences include that repeal eliminates legal provisions, while consolidation reorganizes and clarifies them for easier understanding and application. Repeal affects legal validity, whereas consolidation impacts legal presentation and accessibility without altering the legal effect.
Legal Foundations of Repeal
The legal foundations of repeal rest on the principle that a later statute can nullify or modify an earlier statute to avoid conflicts within the legal system. Repeal can be express, where legislation explicitly states the annulment of a previous law, or implied, where inconsistencies between statutes lead courts to interpret the earlier law as repealed. Understanding these foundations is crucial for ensuring clarity in statutory interpretation and maintaining the hierarchy of laws.
The Process of Legislative Consolidation
The process of legislative consolidation involves combining multiple statutes or legal provisions into a single, coherent act to simplify and clarify the law. This method enhances legal accessibility by reducing redundancies and resolving inconsistencies between various legislative texts without altering the law's substantive effect. Unlike repeal, which completely removes existing laws, consolidation reorganizes and restates laws for improved coherence and usability in the legislative framework.
Historical Examples of Repeal
Historical examples of repeal highlight significant shifts in legal and political landscapes, such as the repeal of Prohibition in the United States through the 21st Amendment in 1933, which ended the nationwide ban on alcohol. The repeal of the Corn Laws in Britain during 1846 marked a transformative move towards free trade and economic liberalization. These repeals demonstrate legislative corrections responding to evolving social, economic, and political pressures, contrasting with consolidation efforts aimed at unifying existing laws.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Repeal
Repealing outdated or redundant laws streamlines the legal system, reducing complexity and improving clarity for citizens and businesses. However, repeal can lead to regulatory gaps or unintended consequences if not carefully evaluated, potentially creating uncertainty and enforcement challenges. While repeal fosters legal modernization and efficiency, it requires thorough impact assessment to avoid destabilizing existing frameworks.
Advantages and Challenges of Consolidation
Consolidation in legal and organizational contexts streamlines overlapping laws or entities, enhancing clarity, efficiency, and consistency by merging multiple statutes or units into a single framework. Advantages include reduced complexity, easier compliance, and cost savings from minimized duplication of efforts and resources. Challenges involve potential loss of specialized provisions, resistance from stakeholders accustomed to existing structures, and the need for extensive review to ensure all relevant elements are integrated effectively without creating new ambiguities.
Impact on Legal Clarity and Governance
Repeal removes outdated or conflicting laws, directly enhancing legal clarity by eliminating ambiguities and reducing regulatory burdens for businesses and citizens. Consolidation combines multiple related statutes into a single, coherent framework, improving governance through streamlined compliance and easier legislative updates. Both processes contribute to a more transparent legal system, but repeal simplifies the landscape by cutting redundant rules, while consolidation organizes complex legal provisions into unified codes.
Choosing Between Repeal and Consolidation
Choosing between repeal and consolidation depends on the legislative objective and the current legal framework's complexity. Repeal eliminates outdated or redundant laws to simplify the legal system, while consolidation merges multiple statutes to create a coherent and accessible legal text. Assessing the impact on legal clarity, administrative efficiency, and stakeholder compliance is essential for making an informed decision.
Future Trends in Law Reform: Repeal vs Consolidation
Future trends in law reform emphasize the strategic use of repeal to eliminate outdated legislation, streamlining the statutory framework to enhance legal clarity and efficiency. Consolidation efforts will increasingly integrate fragmented laws into coherent codes, facilitating better access and understanding for legal practitioners and the public. Emerging technologies and data analytics are expected to support dynamic consolidation, enabling continuous updates and harmonization across legal systems.
Repeal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com