Enforcement action involves legal measures taken to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, or court orders, often resulting in penalties or sanctions for violations. These actions can affect businesses and individuals by imposing fines, restricting operations, or initiating legal proceedings. Explore the rest of the article to understand how enforcement actions impact your rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
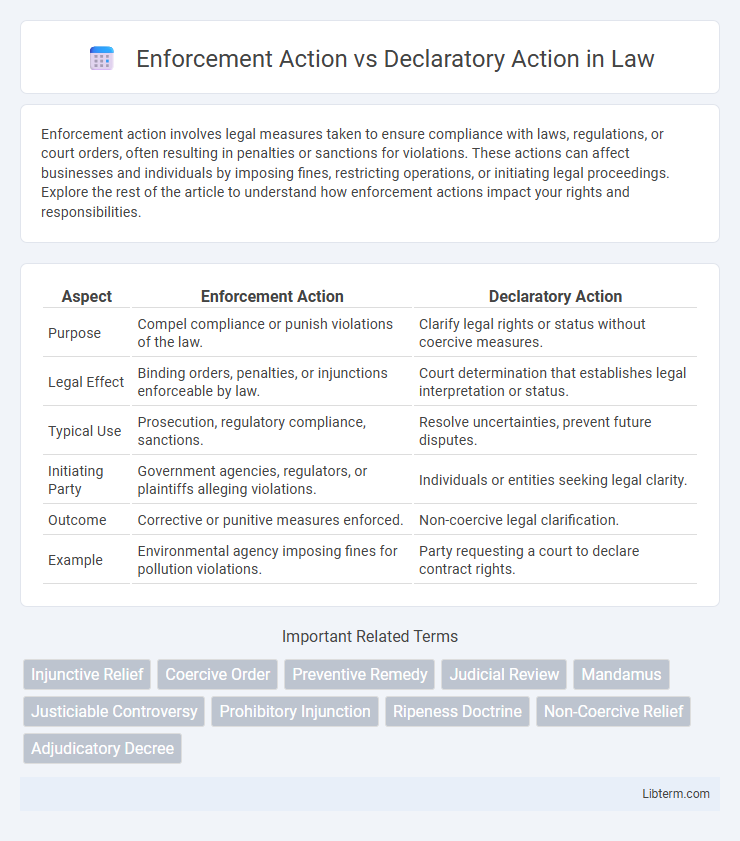
| Aspect | Enforcement Action | Declaratory Action |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Compel compliance or punish violations of the law. | Clarify legal rights or status without coercive measures. |
| Legal Effect | Binding orders, penalties, or injunctions enforceable by law. | Court determination that establishes legal interpretation or status. |
| Typical Use | Prosecution, regulatory compliance, sanctions. | Resolve uncertainties, prevent future disputes. |
| Initiating Party | Government agencies, regulators, or plaintiffs alleging violations. | Individuals or entities seeking legal clarity. |
| Outcome | Corrective or punitive measures enforced. | Non-coercive legal clarification. |
| Example | Environmental agency imposing fines for pollution violations. | Party requesting a court to declare contract rights. |
Introduction to Enforcement Action and Declaratory Action
Enforcement Action involves the process where a regulatory authority initiates legal proceedings to compel compliance with laws or regulations, ensuring that violators face penalties or corrective measures. Declaratory Action serves to resolve legal uncertainties by having a court formally declare the rights, duties, or obligations of parties without necessarily ordering any enforcement or penalty. Both mechanisms play critical roles in the legal system to address and clarify compliance and regulatory issues.
Legal Definitions and Core Concepts
Enforcement action refers to legal proceedings initiated by a regulatory authority or government agency to compel compliance with laws or regulations, often involving penalties or sanctions. Declaratory action involves a court judgment that determines the rights, duties, or legal status of parties without ordering enforcement or awarding damages, providing legal clarity and preventing future disputes. The core concept of enforcement is coercive authority to rectify violations, while declaratory action centers on judicial interpretation to clarify legal positions.
Key Differences Between Enforcement and Declaratory Actions
Enforcement actions compel compliance with a law, regulation, or court order through penalties or remedies, while declaratory actions seek a judicial determination of rights or legal status without immediate enforcement. Enforcement actions involve active remedies such as injunctions or fines, whereas declaratory actions establish legal clarity to prevent future disputes. The primary difference lies in enforcement aiming to correct or punish misconduct, whereas declaratory actions focus on resolving uncertainty.
Typical Scenarios for Enforcement Actions
Enforcement actions typically arise in scenarios where regulatory bodies detect violations such as environmental pollution, securities fraud, or labor law breaches requiring immediate compliance or penalties. Common cases include unauthorized discharge of hazardous materials, insider trading activities, and failure to adhere to workplace safety standards. These actions compel corrective measures or sanctions to uphold legal and regulatory frameworks.
Common Uses of Declaratory Actions
Declaratory actions are commonly used to establish the rights, duties, or obligations of parties without seeking enforcement or damages, providing legal clarity and preventing future disputes. These actions are favored in contract disputes, insurance claims, and constitutional issues where parties need a definitive court interpretation before proceeding. In contrast, enforcement actions are typically pursued to compel compliance or remedy a violation after rights have been established.
Procedural Steps in Enforcement Actions
Enforcement actions involve a formal process initiated by regulatory agencies or authorities to compel compliance with laws or regulations, beginning with investigation and notice of violations. The procedural steps include the issuance of a complaint or enforcement order, an opportunity for the respondent to present defenses or settle, followed by administrative hearings or court proceedings if necessary. Enforcement actions culminate in penalties, fines, injunctions, or mandated corrective measures, emphasizing strict adherence to procedural rules to ensure due process.
Procedural Steps in Declaratory Actions
Declaratory actions initiate with filing a complaint seeking a court's determination on the legal status or interpretation of a dispute without requesting enforcement or damages. The court examines pleadings, allows briefings from both parties, and may hold hearings to clarify the issues without compelling any direct action. This procedural framework establishes legal clarity, guiding future conduct or litigation rather than mandating immediate enforcement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Approach
Enforcement actions provide a direct and authoritative resolution by compelling compliance or punishing violations, ensuring swift legal effect, but they often involve lengthy litigation and higher costs. Declaratory actions, on the other hand, offer a clear legal determination of rights without immediate enforcement, reducing conflict and uncertainty, yet they may lack the power to compel action or provide immediate remedies. Choosing between enforcement and declaratory actions depends on the need for immediate compliance versus legal clarity and risk management.
Case Law Illustrating Enforcement vs Declaratory Actions
Case law highlights the distinction between enforcement actions, which compel compliance or punishment for violations, and declaratory actions, which seek judicial determination of rights without coercive consequences. In *MedImmune, Inc. v. Genentech, Inc.*, the Supreme Court emphasized that declaratory judgments resolve legal uncertainty preemptively, avoiding unnecessary enforcement proceedings. Conversely, *SEC v. W.J. Howey Co.* demonstrates enforcement action's role in imposing penalties to uphold regulatory statutes, underscoring the practical differences in remedies and judicial intervention.
Choosing the Right Legal Action: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right legal action between enforcement action and declaratory action requires careful evaluation of the case's objectives and urgency. Enforcement actions are suited for compelling compliance with existing rights or court orders, often involving immediate remedies or sanctions. Declaratory actions are appropriate when parties seek a judicial determination of their rights without necessarily pursuing enforcement, making them ideal for clarifying legal relationships and preventing future disputes.
Enforcement Action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com