Replevin is a legal remedy allowing you to recover personal property wrongfully taken or withheld by another party. This action ensures the prompt return of your possessions while protecting your ownership rights through court intervention. Explore the full article to understand how replevin safeguards your property interests effectively.
Table of Comparison
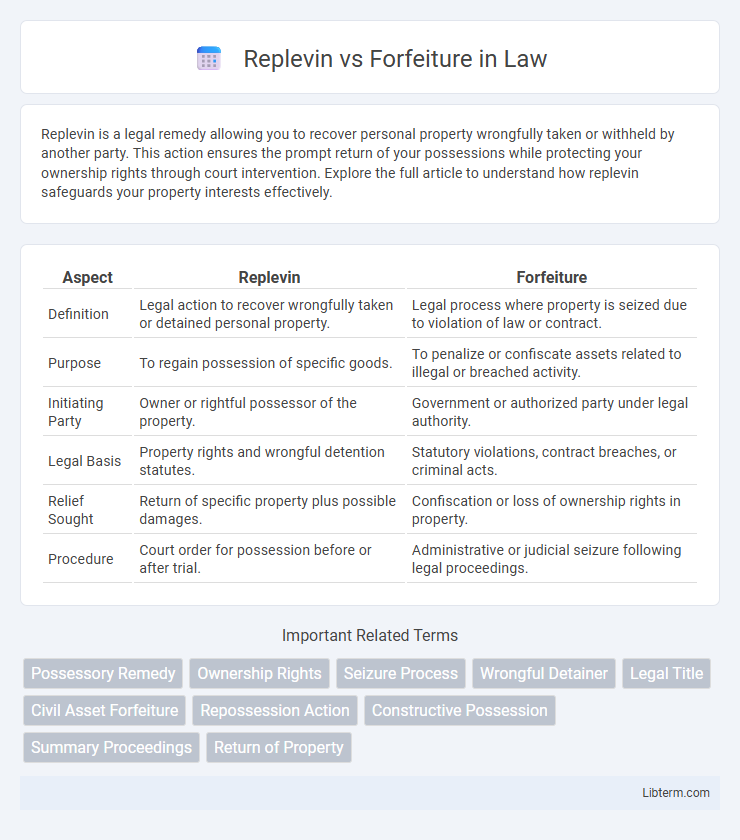
| Aspect | Replevin | Forfeiture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action to recover wrongfully taken or detained personal property. | Legal process where property is seized due to violation of law or contract. |
| Purpose | To regain possession of specific goods. | To penalize or confiscate assets related to illegal or breached activity. |
| Initiating Party | Owner or rightful possessor of the property. | Government or authorized party under legal authority. |
| Legal Basis | Property rights and wrongful detention statutes. | Statutory violations, contract breaches, or criminal acts. |
| Relief Sought | Return of specific property plus possible damages. | Confiscation or loss of ownership rights in property. |
| Procedure | Court order for possession before or after trial. | Administrative or judicial seizure following legal proceedings. |
Understanding Replevin: Definition and Legal Context
Replevin is a legal action used to recover personal property wrongfully taken or detained, allowing the rightful owner to reclaim possession through a court order. It is distinguished from forfeiture, which involves the loss of property as a penalty for legal violations rather than recovery of possession. Courts define replevin within property law, emphasizing its role in securing the return of tangible assets rather than imposing punishments.
What is Forfeiture? Key Legal Principles
Forfeiture is the legal process by which a party loses property or rights as a consequence of violating laws or contractual terms, commonly applied in cases involving criminal activity or breach of contract. Key legal principles include the requirement of due process, ensuring that forfeiture is conducted fairly and with proper notice, and the necessity that the property in question is directly connected to the illegal conduct or breach. Forfeiture differs from replevin, which focuses on the recovery of possession of specific property, as forfeiture extinguishes ownership rights, often permanently transferring title to the government or aggrieved party.
Fundamental Differences Between Replevin and Forfeiture
Replevin is a legal remedy that allows a party to recover wrongfully taken or withheld personal property, focusing on the actual return of the specific item. Forfeiture involves the permanent loss of property rights, typically as a penalty for illegal activity or breach of contract, resulting in the property being seized by the state or other authority. The fundamental difference lies in replevin seeking to restore possession to the rightful owner, while forfeiture extinguishes ownership rights as a punitive or regulatory measure.
Legal Procedures in Replevin Cases
Replevin cases require a plaintiff to file a formal complaint to recover specific personal property unlawfully taken or withheld, often accompanied by a summons to the defendant. The legal procedure involves proving rightful ownership or entitlement and securing a court order for the return of the property before or during the trial. Courts may also mandate a bond to protect the defendant against wrongful seizure, ensuring procedural fairness and adherence to due process.
Forfeiture Process: How It Works
The forfeiture process involves the government seizing property connected to criminal activity without necessarily charging the owner with a crime, typically initiated through administrative, civil, or criminal proceedings. Property owners are given notice and an opportunity to contest the forfeiture in court, where the government must prove the property's connection to illegal conduct by a preponderance of the evidence. If the court rules in favor of forfeiture, the seized property is permanently transferred to the government, often used to fund law enforcement activities.
Rights of Property Owners in Replevin Actions
Property owners pursuing replevin actions hold the right to recover possession of wrongfully withheld goods before a final judgment is rendered, emphasizing the protection of possessory interests. Replevin allows owners to assert immediate claims to personal property, distinguishing it from forfeiture, which typically involves the loss of property due to legal penalties or violations. The legal framework in replevin carefully balances the owner's right to possession against the defendant's interest, often requiring a bond to protect against wrongful seizure.
Government Authority in Forfeiture Cases
Government authority in forfeiture cases enables the state to seize property connected to criminal activity without a prior criminal conviction, relying on civil law standards. Replevin actions, in contrast, involve recovering wrongfully taken personal property through a court order requiring the return of that property to its rightful owner. While forfeiture empowers law enforcement to act preemptively against assets, replevin focuses on the resolution of ownership disputes in civil courts.
Common Scenarios for Replevin vs Forfeiture
Replevin commonly occurs in scenarios where a party seeks the return of wrongfully seized personal property, such as reclaimed goods from a defaulted lease or unlawfully detained merchandise. Forfeiture is typically applied in cases involving contraband, illegal property, or assets linked to criminal activity, where the government seizes property as part of enforcement actions. Understanding the distinction lies in replevin addressing wrongful possession disputes, while forfeiture focuses on punitive seizure related to legal violations.
Defenses Against Replevin and Forfeiture Claims
Defenses against replevin claims often include proving lawful possession, showing lack of wrongful taking, or establishing a valid lien or security interest on the disputed property. For forfeiture claims, defenses focus on disproving illegal activity, demonstrating ownership rights, and challenging the procedural validity of the forfeiture process. Both require presenting clear evidence to counter the claimant's assertion and protect property rights under relevant statutes.
Choosing the Right Legal Remedy: Replevin or Forfeiture?
Choosing the right legal remedy between replevin and forfeiture depends on the nature of the dispute and desired outcome. Replevin is specifically designed to recover possession of wrongfully withheld personal property, emphasizing prompt return without addressing ownership disputes. Forfeiture involves the loss of property rights due to violation of law or contract terms, often resulting in permanent deprivation rather than mere retrieval.
Replevin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com