Robbery involves the unlawful taking of property from a person through force or intimidation, posing serious legal consequences and personal risks. Understanding the distinctions between robbery and other theft crimes is crucial for protecting Your rights and ensuring accurate legal representation. Explore the rest of the article to learn more about robbery laws and how they may affect You.
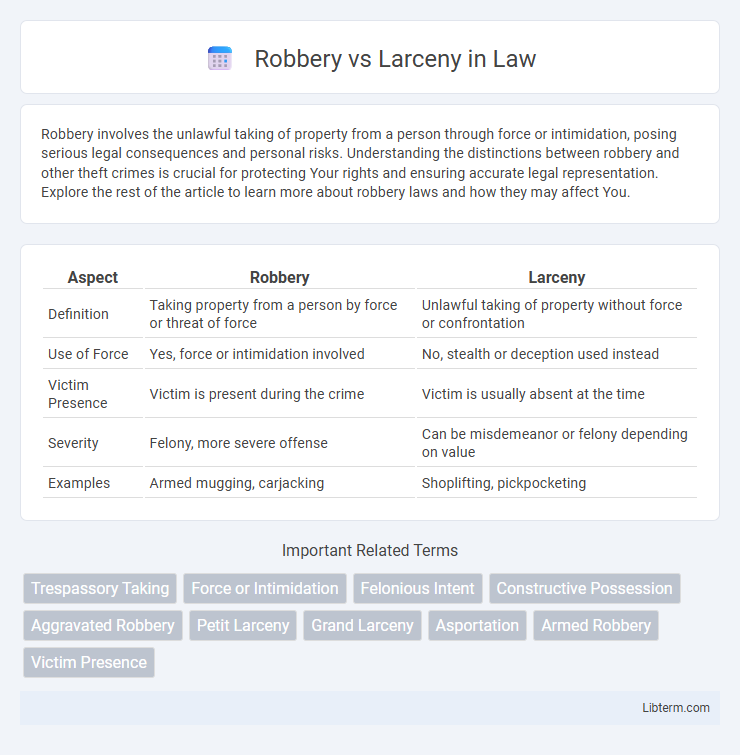
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Robbery | Larceny |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Taking property from a person by force or threat of force | Unlawful taking of property without force or confrontation |
| Use of Force | Yes, force or intimidation involved | No, stealth or deception used instead |
| Victim Presence | Victim is present during the crime | Victim is usually absent at the time |
| Severity | Felony, more severe offense | Can be misdemeanor or felony depending on value |
| Examples | Armed mugging, carjacking | Shoplifting, pickpocketing |
Definition of Robbery
Robbery is defined as the unlawful taking of property from a person or their immediate presence by force, intimidation, or threat of violence. Unlike larceny, which involves the mere unlawful taking of property without direct confrontation, robbery necessitates the element of fear or harm to the victim. This distinction highlights robbery as a violent crime that combines theft with aggression or coercion.
Definition of Larceny
Larceny is the unlawful taking and carrying away of someone else's personal property with the intent to permanently deprive the owner of its possession. Unlike robbery, larceny does not involve the use of force, threat, or intimidation against a person. It is categorized as a theft crime focused solely on the act of stealing without direct confrontation.
Key Differences Between Robbery and Larceny
Robbery involves taking property from a person through force or intimidation, making it a violent crime, whereas larceny is the unlawful taking of personal property without consent but without direct confrontation or threat. The key difference lies in the element of force or fear used during the crime, with robbery requiring this element to be charged. Larceny typically includes theft offenses such as shoplifting or pickpocketing, while robbery encompasses acts like mugging or armed theft.
Elements Required to Prove Robbery
Robbery requires proving the unlawful taking of property directly from a person or their presence through force or intimidation, distinguishing it from larceny, which involves theft without confrontation. Key elements include the intent to permanently deprive the victim of property, actual or threatened use of physical force, and immediate possession of the property during the act. Establishing these elements is essential to differentiate robbery from other theft offenses and secure a conviction.
Elements Required to Prove Larceny
Larceny requires the unlawful taking and carrying away of someone else's personal property with the intent to permanently deprive the owner of it. Proof must establish the property was taken without consent and that the defendant had the specific intent to steal at the time of the taking. Unlike robbery, which involves force or threat of force, larceny is characterized solely by the wrongful appropriation of property.
Legal Consequences of Robbery
Robbery is a violent crime that results in more severe legal consequences compared to larceny, typically classified as a felony with penalties including lengthy prison sentences, heavy fines, and potential restitution to the victim. Unlike larceny, which involves theft without confrontation, robbery involves the use of force or intimidation, leading to charges such as armed robbery or aggravated robbery. Convictions for robbery often carry longer criminal records, impacting future sentencing and legal rights.
Legal Penalties for Larceny
Legal penalties for larceny vary depending on the value of the stolen property and jurisdiction, with punishments ranging from fines and probation for petty larceny to significant prison sentences for grand larceny. In many states, felony larceny involves theft of property valued above a certain threshold, often resulting in imprisonment for several years. Repeat offenses and aggravating factors such as theft from vulnerable victims can lead to enhanced sentencing and stricter legal consequences.
Common Examples of Robbery and Larceny
Common examples of robbery include armed robbery, where a perpetrator uses a weapon to threaten a victim and steal money or valuables, and bank robbery, involving force or intimidation to take cash from financial institutions. Larceny examples commonly feature shoplifting, which is the unauthorized taking of merchandise from retail stores, and petty theft, involving the covert removal of low-value items without direct confrontation or violence. Both crimes involve unlawful taking, but robbery emphasizes force or threat, whereas larceny centers on stealth and deception.
How Law Enforcement Investigates Each Crime
Law enforcement investigates robbery by analyzing eyewitness accounts, surveillance footage, and physical evidence at the crime scene, often emphasizing the use or threat of force during the offense. In larceny cases, officers focus on tracing stolen property, reviewing security recordings, and interviewing witnesses to establish unlawful taking without direct confrontation. Investigators tailor their approach based on the presence of violence, suspect behavior, and property recovery efforts.
Preventive Measures Against Robbery and Larceny
Effective preventive measures against robbery and larceny include installing comprehensive surveillance systems such as CCTV cameras and alarm systems to deter criminal activity and enhance evidence collection; reinforcing physical security by employing strong locks, security gates, and secure storage for valuables; and implementing employee training programs focused on recognizing suspicious behavior, following safety protocols, and maintaining situational awareness. Community policing initiatives and improved street lighting contribute to reducing incidents by increasing public vigilance and creating less favorable environments for criminals. Utilizing access control technology and conducting regular security audits further minimize vulnerabilities that might be exploited in both robbery and larceny cases.
Robbery Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com