Replevin is a legal remedy that allows you to recover personal property wrongfully taken or withheld by another party. It involves a court-ordered process to seize and return the specific items rather than obtaining monetary compensation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how replevin can protect your property rights and what steps to take next.
Table of Comparison
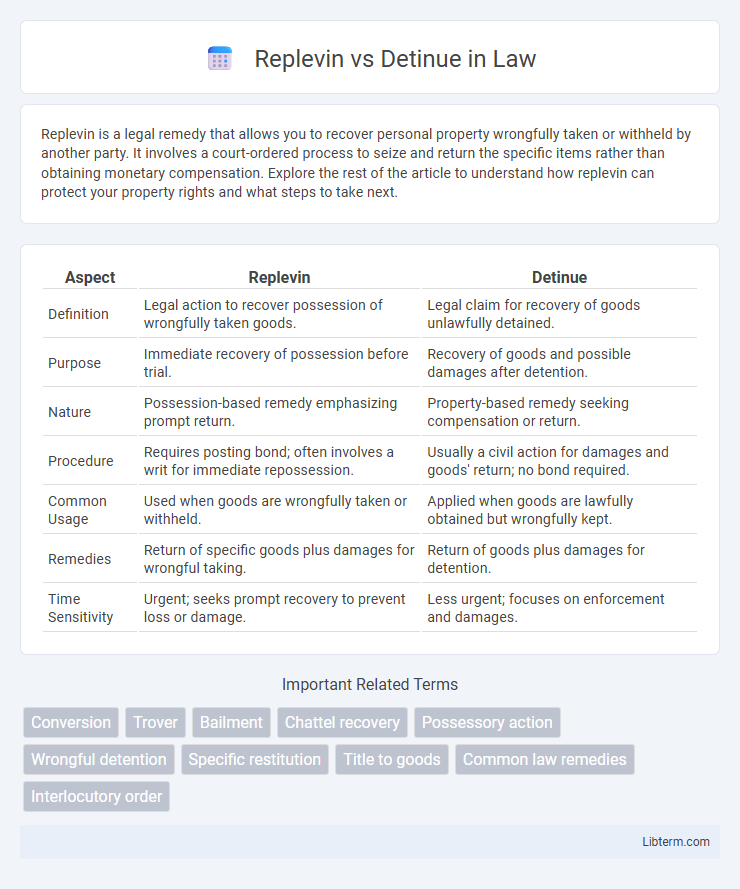
| Aspect | Replevin | Detinue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action to recover possession of wrongfully taken goods. | Legal claim for recovery of goods unlawfully detained. |
| Purpose | Immediate recovery of possession before trial. | Recovery of goods and possible damages after detention. |
| Nature | Possession-based remedy emphasizing prompt return. | Property-based remedy seeking compensation or return. |
| Procedure | Requires posting bond; often involves a writ for immediate repossession. | Usually a civil action for damages and goods' return; no bond required. |
| Common Usage | Used when goods are wrongfully taken or withheld. | Applied when goods are lawfully obtained but wrongfully kept. |
| Remedies | Return of specific goods plus damages for wrongful taking. | Return of goods plus damages for detention. |
| Time Sensitivity | Urgent; seeks prompt recovery to prevent loss or damage. | Less urgent; focuses on enforcement and damages. |
Introduction to Replevin and Detinue
Replevin is a legal remedy that allows a person to recover personal property wrongfully taken or withheld, emphasizing the return of the specific item rather than monetary compensation. Detinue similarly seeks the recovery of possession of goods unlawfully detained, but it traditionally demands proof of lawful ownership and wrongful detention. Both actions focus on possession rights, with replevin often involving immediate recovery, while detinue addresses wrongful retention after rightful possession.
Legal Definitions: Replevin vs Detinue
Replevin is a legal remedy that allows a person to recover personal property unlawfully taken or withheld, emphasizing the immediate return of the specific item. Detinue involves a claim for the wrongful detention of goods by someone who initially lawfully possessed them, focusing on the recovery of the property or its value. Both actions address possession disputes, but replevin targets wrongful taking, while detinue centers on wrongful retention.
Historical Background of Replevin and Detinue
Replevin originated in English common law as a remedy for the wrongful taking of personal property, allowing the original possessor to recover goods before trial. Detinue developed as a distinct action focused on the wrongful detention of goods, emphasizing the recovery of specific chattels rather than damages. Both remedies evolved during the Middle Ages, reflecting the legal system's effort to protect possessory rights and address property disputes efficiently.
Key Differences Between Replevin and Detinue
Replevin is a legal remedy used to recover specific personal property wrongfully taken or withheld, emphasizing the immediate return of the item, while Detinue involves a claim for compensation when the property cannot be retrieved. Replevin requires the plaintiff to prove rightful ownership and the wrongful taking, whereas Detinue focuses on the defendant's wrongful detention or refusal to return the property. The primary distinction lies in Replevin's emphasis on possession recovery, contrasting with Detinue's focus on damages for unlawful retention.
Common Legal Scenarios for Replevin
Replevin is commonly used in legal scenarios involving the wrongful taking or withholding of personal property, allowing the rightful owner to recover possession before trial. Typical cases include repossession of goods sold under conditional sales contracts, recovery of leased equipment, and retrieval of personal belongings wrongfully withheld after a tenancy ends. Courts prioritize replevin actions when immediate possession is necessary to prevent irreparable harm or loss to the plaintiff.
Common Legal Scenarios for Detinue
Detinue primarily arises in scenarios where a person wrongfully retains possession of goods that belong to another, often after a bailment or loan agreement has ended. Common legal cases involve disputes over leased equipment, borrowed personal property, or items left in possession during contractual negotiations. Courts typically assess the rightful ownership and continuous refusal to return the item despite demand, distinguishing detinue from replevin, which seeks the immediate recovery of goods.
Procedures and Remedies in Replevin Cases
Replevin involves a legal procedure allowing a claimant to recover possession of wrongfully taken or detained personal property before resolving ownership disputes, typically requiring the posting of a bond and proceeding through a prompt court hearing. The remedy in replevin primarily focuses on the immediate return of the specific chattel, with the possibility of monetary damages if the defendant wrongfully withholds the property. Unlike detinue, which seeks monetary compensation for wrongful detention, replevin aims to restore possession, emphasizing procedural safeguards to prevent abuse, including security requirements and prompt judicial review.
Procedures and Remedies in Detinue Cases
In detinue cases, the procedure begins with the plaintiff filing a claim to recover specific goods wrongfully withheld by the defendant, often accompanied by a demand for the return of the property. Courts may order the replevin of the goods or award damages for their detention, emphasizing the recovery of the exact chattel rather than monetary compensation alone. Remedies typically include the return of the property, damages for loss of use, and sometimes exemplary damages if the detention was egregiously unlawful.
Jurisdictional Variations: Replevin vs Detinue
Replevin and detinue differ significantly across jurisdictions in terms of legal procedures and remedies, with replevin primarily focused on the recovery of possession and detinue emphasizing compensation for wrongful detention of goods. In common law jurisdictions, replevin allows for the immediate return of property before trial, whereas detinue requires proof of ownership and damages after possession is withheld unlawfully. Statutory frameworks and court interpretations vary, influencing how claimants pursue remedies for personal property disputes in different regions.
Choosing Between Replevin and Detinue
Choosing between replevin and detinue hinges on the desired legal remedy: replevin allows immediate recovery of wrongfully taken goods before trial, prioritizing possession, while detinue seeks monetary damages for the wrongful detention of goods after possession is denied. Parties should opt for replevin when prompt return of specific property is critical, and for detinue if the focus is on compensation rather than the physical recovery of the item. Understanding the jurisdictional nuances and statutory requirements is essential to effectively determine which action aligns with the facts and legal objectives.
Replevin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com