Constitutional interpretation determines how the principles and clauses of the Constitution apply to contemporary issues and legal challenges. Understanding different interpretive methods, such as textualism, originalism, and the living Constitution approach, is crucial for grasping judicial decisions and their impact on society. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your insight into how constitutional interpretation shapes legal and political landscapes.
Table of Comparison
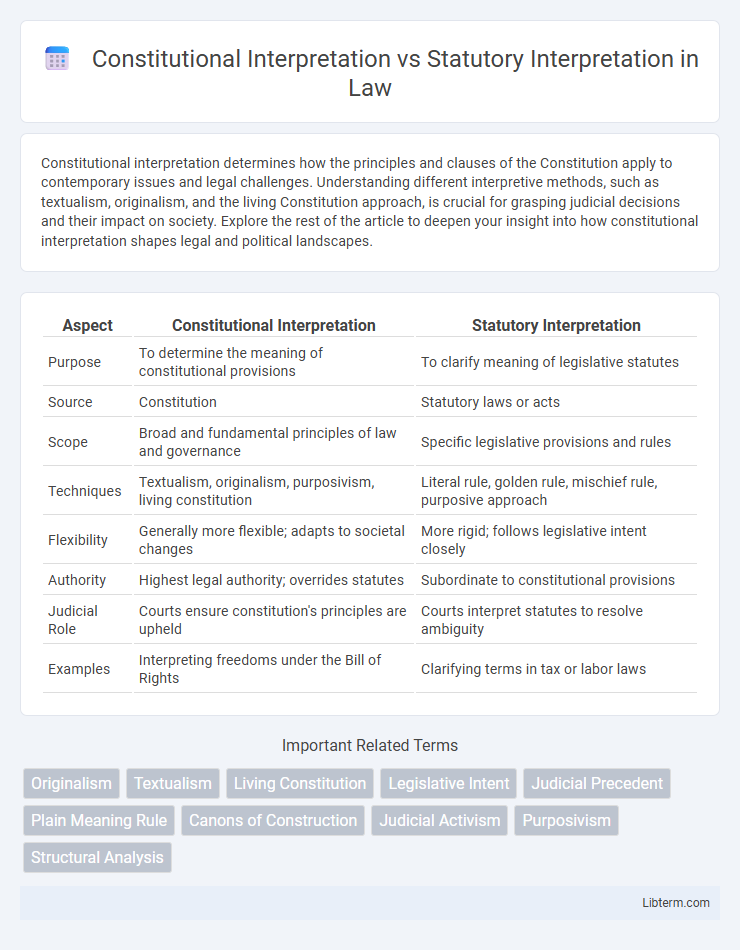
| Aspect | Constitutional Interpretation | Statutory Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To determine the meaning of constitutional provisions | To clarify meaning of legislative statutes |
| Source | Constitution | Statutory laws or acts |
| Scope | Broad and fundamental principles of law and governance | Specific legislative provisions and rules |
| Techniques | Textualism, originalism, purposivism, living constitution | Literal rule, golden rule, mischief rule, purposive approach |
| Flexibility | Generally more flexible; adapts to societal changes | More rigid; follows legislative intent closely |
| Authority | Highest legal authority; overrides statutes | Subordinate to constitutional provisions |
| Judicial Role | Courts ensure constitution's principles are upheld | Courts interpret statutes to resolve ambiguity |
| Examples | Interpreting freedoms under the Bill of Rights | Clarifying terms in tax or labor laws |
Introduction to Legal Interpretation
Constitutional interpretation involves analyzing the foundational legal document to determine the meaning of its provisions, often balancing historical context with evolving societal values. Statutory interpretation focuses on construing specific legislative texts, emphasizing the intent of lawmakers and the text's ordinary meaning within the statute's framework. Both methods require tools such as textual analysis, precedent, and principles like the purposive approach to ensure accurate application of the law.
Defining Constitutional Interpretation
Constitutional interpretation involves analyzing and explaining the meaning of a constitution's text, principles, and provisions to apply them to specific legal issues. It requires understanding the framers' intent, historical context, and the constitution's broader structure to ensure laws align with fundamental rights and governmental powers. This process differs from statutory interpretation, which focuses specifically on understanding and applying ordinary legislation passed by the legislature.
Defining Statutory Interpretation
Statutory interpretation involves the process by which courts analyze and apply legislation to specific cases, aiming to ascertain the legislature's intent by examining the text, context, and purpose of the statute. This legal practice prioritizes the plain meaning of statutory language, legislative history, and canons of construction to resolve ambiguities and ensure consistent application of laws. Unlike constitutional interpretation, which deals with the broader principles and framework of the Constitution, statutory interpretation focuses narrowly on clarifying and enforcing legislative enactments.
Key Principles Guiding Each Approach
Constitutional interpretation emphasizes the original intent, text, and the principle of judicial review to ensure laws align with constitutional mandates. Statutory interpretation relies on legislative intent, plain meaning of the text, and canons of construction like ejusdem generis and noscitur a sociis to resolve ambiguities. Both methods prioritize context but differ in scope; constitutional interpretation addresses fundamental legal frameworks, while statutory interpretation focuses on applying specific legislative provisions.
Differences in Textual Authority
Constitutional interpretation relies primarily on the text and original intent of the constitution, emphasizing its foundational and supreme legal status, while statutory interpretation centers on the language and purpose of specific legislative statutes within that constitutional framework. Constitutional texts are fixed and broad, requiring principles like originalism or living constitutionalism to guide meaning, whereas statutory texts are often more detailed and adaptable, interpreted using tools like legislative history and canons of construction. The authority of constitutional text overrides statutory provisions, reflecting its higher hierarchical position in the legal system.
Judicial Approaches to Interpretation
Judicial approaches to constitutional interpretation primarily include originalism, which emphasizes the framers' intent and the text's original meaning, and living constitutionalism, which views the Constitution as a dynamic document adapting to modern contexts. In contrast, statutory interpretation often employs methods like textualism, focusing strictly on the statutory language, and purposivism, aiming to fulfill the legislature's intended purpose. Courts frequently balance these approaches by considering precedent, legislative history, and the broader legal framework to ensure consistent and coherent application of laws.
The Role of Precedent in Both Interpretations
Precedent plays a crucial role in both constitutional and statutory interpretation by providing judicial decisions that guide courts in applying laws consistently. In constitutional interpretation, precedents often set foundational principles that shape the understanding of fundamental rights and government powers over time. Statutory interpretation relies heavily on prior rulings to clarify ambiguous legislative language and ensure uniform application of statutes across cases.
Impact on Legal Outcomes and Society
Constitutional interpretation shapes foundational legal principles and long-term societal norms by establishing the scope of fundamental rights and government powers, often influencing landmark judicial decisions that define national identity. Statutory interpretation directly affects the application of laws in everyday cases, guiding courts in resolving ambiguities and ensuring legislative intent aligns with social and economic realities. The interplay between these interpretations impacts legal stability and adaptability, balancing rigid constitutional mandates with the flexible enforcement of statutes to reflect evolving societal values.
Contemporary Debates and Challenges
Contemporary debates in constitutional interpretation center on originalism versus living constitutionalism, grappling with how historical context aligns with modern values. Statutory interpretation faces challenges in balancing legislative intent with textualism and dynamic societal changes, often leading to judicial activism critiques. Both fields confront tensions between stability in law and adaptability to evolving social norms and technological advancements.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Constitutional interpretation emphasizes evolving societal values and fundamental rights, ensuring the Constitution remains relevant amid changing contexts. Statutory interpretation demands precise application of legislative intent, balancing textual analysis with pragmatic considerations to uphold legal predictability. Future perspectives suggest increased integration of technological tools, such as AI-driven analysis, to enhance interpretive accuracy and adapt to complex legal challenges.
Constitutional Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com