A writ of habeas corpus serves as a fundamental legal instrument that safeguards individual freedom by compelling authorities to justify the detention of a prisoner. It acts as a critical check against unlawful imprisonment, ensuring that your right to liberty is protected under the law. Explore the rest of this article to understand how this vital legal tool operates and when it can be invoked.
Table of Comparison
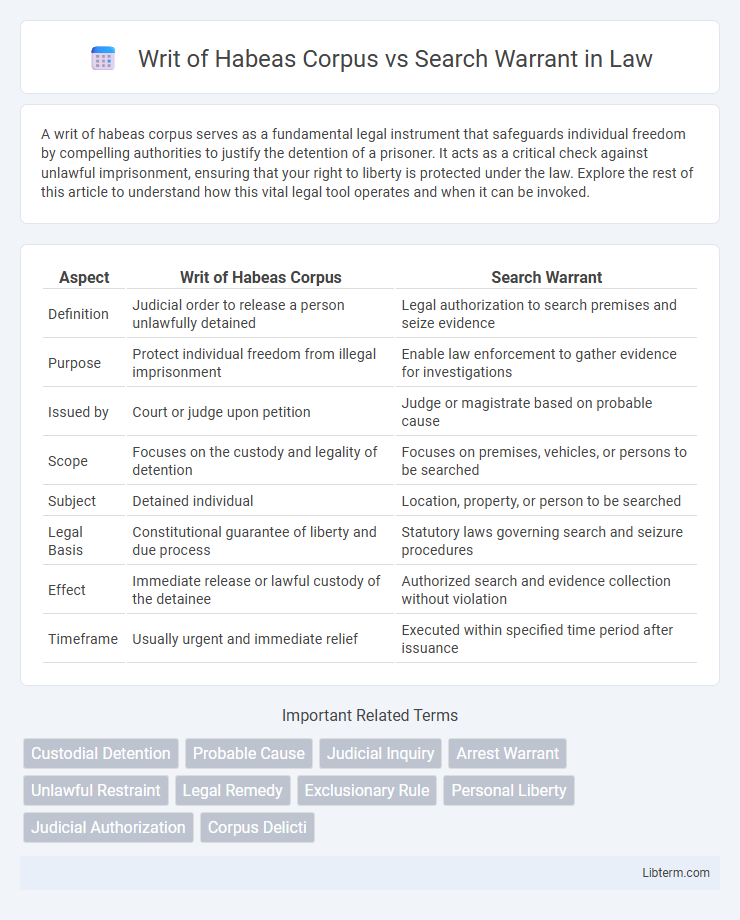
| Aspect | Writ of Habeas Corpus | Search Warrant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial order to release a person unlawfully detained | Legal authorization to search premises and seize evidence |
| Purpose | Protect individual freedom from illegal imprisonment | Enable law enforcement to gather evidence for investigations |
| Issued by | Court or judge upon petition | Judge or magistrate based on probable cause |
| Scope | Focuses on the custody and legality of detention | Focuses on premises, vehicles, or persons to be searched |
| Subject | Detained individual | Location, property, or person to be searched |
| Legal Basis | Constitutional guarantee of liberty and due process | Statutory laws governing search and seizure procedures |
| Effect | Immediate release or lawful custody of the detainee | Authorized search and evidence collection without violation |
| Timeframe | Usually urgent and immediate relief | Executed within specified time period after issuance |
Introduction to Writ of Habeas Corpus
The writ of habeas corpus is a fundamental legal instrument designed to protect individual freedom by challenging unlawful detention or imprisonment. It compels authorities to present a detained person before the court to examine the legality of their custody. This safeguard ensures that no one is held without just cause, contrasting with a search warrant, which authorizes law enforcement to search premises for evidence.
Understanding Search Warrants
Search warrants are legal documents issued by a judge or magistrate that authorize law enforcement officers to search a specific location and seize evidence related to a crime; they must be supported by probable cause and clearly specify the place to be searched and the items sought. Unlike a writ of habeas corpus, which challenges unlawful detention, search warrants protect privacy rights by ensuring searches are conducted lawfully and with judicial oversight. Proper execution of a search warrant helps prevent violations of the Fourth Amendment against unreasonable searches and seizures.
Legal Foundations of Habeas Corpus
The writ of habeas corpus is a fundamental legal instrument rooted in common law that protects individual freedom by ensuring a person's unlawful detention can be challenged in court. It requires authorities to present the detainee before a judge to assess the legality of the detention, reflecting the principle against arbitrary imprisonment. In contrast, a search warrant is a judicial authorization permitting law enforcement to conduct searches and seizures based on probable cause, emphasizing procedural safeguards rather than personal liberty.
Legal Grounds for Issuing Search Warrants
Search warrants are issued based on probable cause supported by oath or affirmation, detailing the specific place to be searched and the items sought, as mandated by the Fourth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. Unlike writs of habeas corpus, which challenge unlawful detention, search warrants require judicial approval to prevent unreasonable searches and seizures. Courts strictly scrutinize affidavits or testimonies presented, ensuring that law enforcement presents concrete evidence linking the location or person to criminal activity before issuing the warrant.
Key Differences Between Habeas Corpus and Search Warrant
Writ of Habeas Corpus is a legal order demanding that a person detained be brought before a court to determine the lawfulness of their detention, serving as a protection against unlawful imprisonment. A Search Warrant, on the other hand, is an authorization issued by a court permitting law enforcement to search a specific place and seize evidence related to a crime. The key difference lies in Habeas Corpus focusing on the legality of detention, while a Search Warrant authorizes the search and seizure of property.
Rights Protected by Writ of Habeas Corpus
The writ of habeas corpus primarily protects an individual's right to freedom from unlawful detention by requiring authorities to justify the legality of a person's imprisonment. This constitutional safeguard ensures that no one can be held without lawful cause, preventing arbitrary arrests and prolonged confinement without trial. Unlike a search warrant, which authorizes law enforcement to search property, habeas corpus directly upholds personal liberty and due process rights.
Safeguards Ensured by Search Warrants
Search warrants serve as critical safeguards by requiring law enforcement to obtain judicial authorization before conducting searches, thereby protecting individuals' Fourth Amendment rights against unreasonable searches and seizures. They ensure that searches are limited in scope, specifying the exact location and items sought to prevent arbitrary or overly broad intrusions. With search warrants, evidence collection follows legal protocols, enhancing the integrity of investigations and upholding due process.
Procedures for Filing Habeas Corpus Petitions
Filing a writ of habeas corpus requires a petitioner to submit a written petition to the appropriate court, typically including the petitioner's personal details, the name of the detention facility, grounds for unlawful detention, and relevant supporting evidence. The court then reviews the petition for sufficiency and, if meritorious, issues an order requiring the custodian to bring the detainee before the court to examine the legality of the detention. This procedure contrasts with search warrants, which involve law enforcement officers applying to a judge or magistrate with probable cause to conduct a specific search.
Steps in Obtaining a Search Warrant
Obtaining a search warrant requires law enforcement to present sworn affidavits demonstrating probable cause to a judge or magistrate, specifying the location and items to be searched for. The judge reviews the affidavit and, if satisfied with the evidence, issues the warrant authorizing the search within a limited scope and time frame. Execution of the warrant must comply with constitutional protections, ensuring searches are reasonable and particularized to prevent unlawful searches and seizures.
Practical Implications in Criminal Proceedings
The writ of habeas corpus safeguards individual liberty by allowing detainees to challenge unlawful imprisonment, ensuring judicial review of the legality of detention in criminal proceedings. A search warrant authorizes law enforcement to legally search premises and seize evidence, providing procedural safeguards against unreasonable searches under the Fourth Amendment. Practical implications include habeas corpus serving as a post-arrest remedy to prevent wrongful detention, while search warrants are preventative tools ensuring admissible evidence, both critical for upholding constitutional protections in criminal justice.
Writ of Habeas Corpus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com