Custody determines the legal responsibility and care for a child following a separation or divorce. Understanding the different types of custody, such as physical and legal custody, is crucial to ensuring the child's well-being and maintaining your parental rights. Explore the rest of this article to learn how custody arrangements work and what might be best for your family.
Table of Comparison
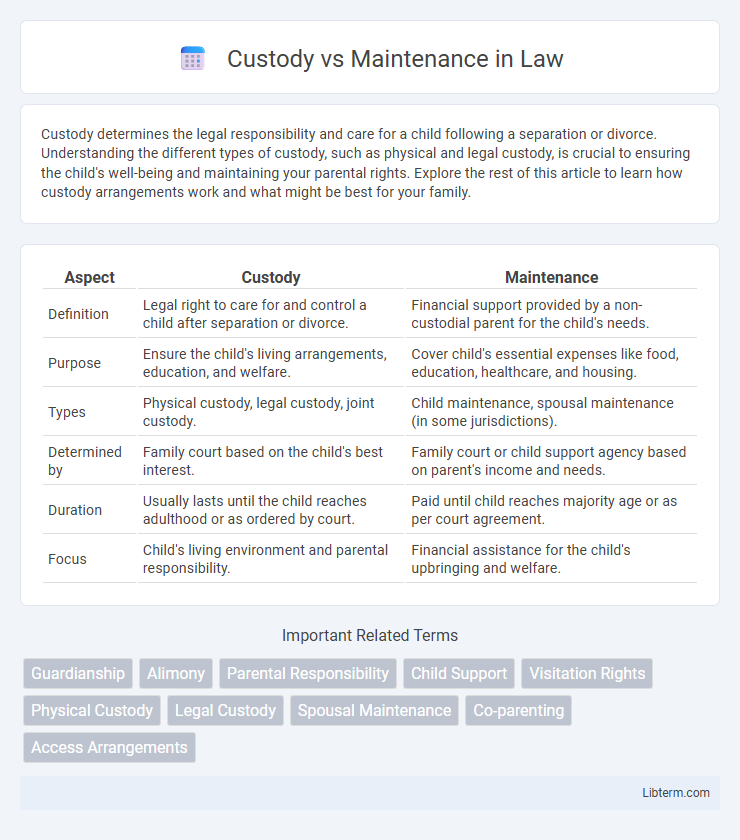
| Aspect | Custody | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal right to care for and control a child after separation or divorce. | Financial support provided by a non-custodial parent for the child's needs. |
| Purpose | Ensure the child's living arrangements, education, and welfare. | Cover child's essential expenses like food, education, healthcare, and housing. |
| Types | Physical custody, legal custody, joint custody. | Child maintenance, spousal maintenance (in some jurisdictions). |
| Determined by | Family court based on the child's best interest. | Family court or child support agency based on parent's income and needs. |
| Duration | Usually lasts until the child reaches adulthood or as ordered by court. | Paid until child reaches majority age or as per court agreement. |
| Focus | Child's living environment and parental responsibility. | Financial assistance for the child's upbringing and welfare. |
Understanding Custody and Maintenance
Custody refers to the legal right and responsibility to care for and make decisions about a child's welfare, encompassing physical and legal aspects that directly impact the child's upbringing. Maintenance, often known as child support, involves financial contributions from a non-custodial parent to cover the child's living expenses, education, healthcare, and other needs. Understanding the distinction between custody and maintenance is crucial for parents navigating family law, as custody determines who cares for the child, while maintenance ensures financial support for the child's well-being.
Legal Definitions: Custody vs Maintenance
Custody refers to the legal right and responsibility to care for and make decisions about a child's upbringing, including living arrangements, education, and health. Maintenance, also known as child support, is the financial provision one parent is required to pay to the other for the child's living expenses, ensuring the child's welfare is adequately met. Custody involves physical and legal control, while maintenance focuses exclusively on monetary support.
Types of Child Custody
Types of child custody include legal custody, which grants the right to make important decisions about the child's welfare, education, and health, and physical custody, referring to where the child primarily resides. Joint custody allows both parents to share legal and/or physical custody, promoting cooperative parenting, while sole custody assigns one parent full responsibility for decision-making and physical care. Understanding these distinctions is essential in custody disputes, as they directly affect the child's living arrangements and parental responsibilities.
Key Principles of Maintenance
Maintenance primarily ensures financial support for the dependent spouse or children post-separation, covering essentials like food, shelter, clothing, education, and medical expenses. It is guided by principles such as the payer's income capacity, the recipient's reasonable needs, and the standard of living enjoyed during the marriage. Courts assess factors like earning ability, age, health, and the duration of the marriage to determine fair and just maintenance awards.
Factors Influencing Custody Decisions
Custody decisions are primarily influenced by factors such as the child's best interests, including emotional, physical, and educational needs, as well as each parent's ability to provide a stable and nurturing environment. Courts also consider the child's age, preference, and the history of parental involvement or any evidence of abuse or neglect. Parental fitness, including mental and physical health, financial stability, and willingness to facilitate the child's relationship with the other parent, plays a crucial role in determining custody arrangements.
Calculating Maintenance Payments
Calculating maintenance payments involves assessing factors such as the income of the paying parent, the financial needs of the receiving parent, and the child's living expenses. Custody arrangements, whether joint or sole, directly impact the maintenance amount, as shared custody often reduces payment obligations due to the division of time and costs. Courts typically use standardized guidelines supplemented by the specifics of each case to ensure fair and adequate maintenance support.
Rights and Responsibilities of Parents
Custody defines the legal right and responsibility to make decisions about a child's upbringing, including education, health, and welfare, while maintenance refers to the financial support provided by a non-custodial parent to meet the child's living expenses. Parents with custody typically have the authority to determine daily care and long-term planning, whereas the non-custodial parent's role centers on providing consistent monetary contributions to ensure the child's needs are met. Both parents share the obligation to support the child's physical, emotional, and educational well-being, regardless of custody arrangements.
Court Procedures for Custody and Maintenance
Court procedures for custody involve filing a petition with the family court, where evidence regarding the child's best interests, parental fitness, and living conditions is presented. Maintenance cases require submitting financial documents and proof of dependency to establish the paying party's obligation to provide support. Both processes typically include hearings, mediation sessions, and judicial orders based on statutory guidelines and the evidence provided.
Challenging or Modifying Orders
Challenging or modifying custody and maintenance orders requires presenting significant changes in circumstances, such as shifts in a parent's living situation, income, or the child's needs. Courts prioritize the child's best interests, evaluating evidence like financial records, parenting ability, and living conditions to determine adjustments. Legal procedures often involve filing petitions, attending mediation, and potentially court hearings to seek revisions of existing orders.
Frequently Asked Questions on Custody and Maintenance
Custody determines which parent has the legal right to make decisions for the child and where the child will reside, while maintenance refers to the financial support paid by one parent to the other for the child's upbringing. Frequently asked questions often address how custody is awarded, whether joint or sole custody is preferable, and the criteria courts use in custody decisions, such as the child's best interests and parental fitness. Questions on maintenance commonly focus on the calculation of support amounts, duration of payments, and modifications based on changes in income or custody arrangements.
Custody Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com