Amparo is a vital legal remedy in many Latin American countries designed to protect individual constitutional rights against violations by authorities or private parties. This mechanism ensures the swift restoration of rights when they are threatened or infringed upon, offering an accessible form of protection. Discover how amparo can safeguard your freedoms and understand its significance in the broader legal system by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
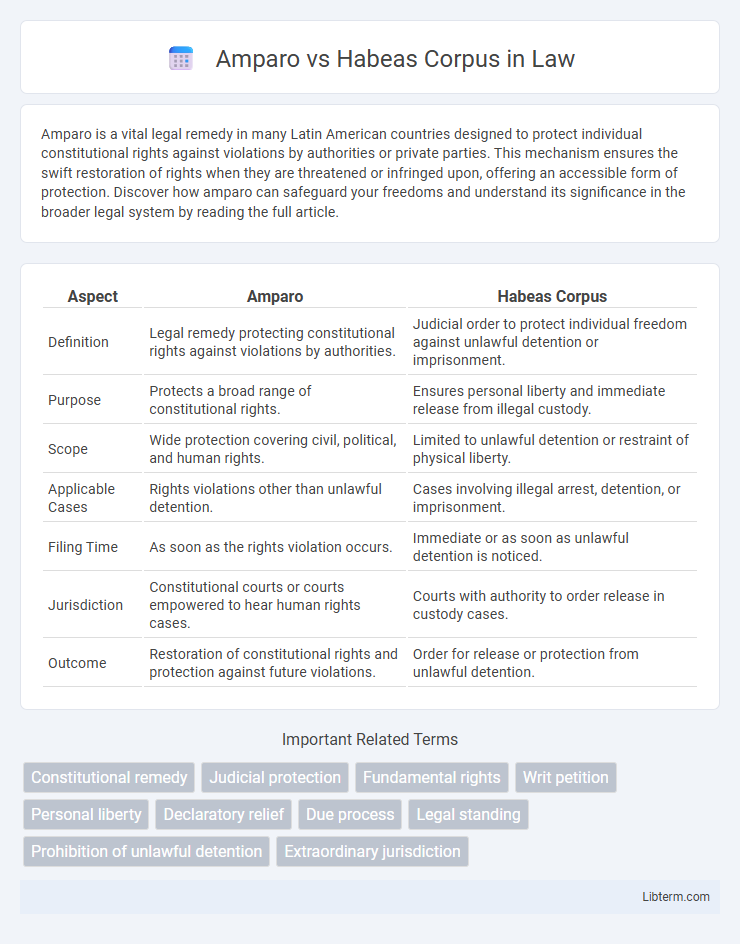
| Aspect | Amparo | Habeas Corpus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal remedy protecting constitutional rights against violations by authorities. | Judicial order to protect individual freedom against unlawful detention or imprisonment. |
| Purpose | Protects a broad range of constitutional rights. | Ensures personal liberty and immediate release from illegal custody. |
| Scope | Wide protection covering civil, political, and human rights. | Limited to unlawful detention or restraint of physical liberty. |
| Applicable Cases | Rights violations other than unlawful detention. | Cases involving illegal arrest, detention, or imprisonment. |
| Filing Time | As soon as the rights violation occurs. | Immediate or as soon as unlawful detention is noticed. |
| Jurisdiction | Constitutional courts or courts empowered to hear human rights cases. | Courts with authority to order release in custody cases. |
| Outcome | Restoration of constitutional rights and protection against future violations. | Order for release or protection from unlawful detention. |
Introduction to Amparo and Habeas Corpus
Amparo and Habeas Corpus are fundamental legal remedies designed to protect individual rights against unlawful actions by the state. Amparo offers a broader spectrum of protection, addressing violations of constitutional rights beyond personal liberty, while Habeas Corpus specifically safeguards against unlawful detention or imprisonment. Both mechanisms serve as vital tools in upholding human rights and ensuring judicial review in constitutional law.
Historical Background of Amparo
The Amparo remedy originated in Mexico's 1847 Constitution as a legal mechanism to protect individual constitutional rights against state violations, serving as a pivotal tool for human rights defense in Latin America. Unlike Habeas Corpus, which exclusively addresses unlawful detention, Amparo provides broader protection encompassing civil, political, and constitutional rights. This historical development established Amparo as a foundational legal instrument in numerous countries for safeguarding fundamental freedoms.
Historical Overview of Habeas Corpus
Habeas corpus, originating in 12th-century England under the Magna Carta, serves as a legal safeguard against unlawful detention by requiring authorities to justify the imprisonment before a court. This writ evolved into a fundamental human rights mechanism, influencing legal systems worldwide by ensuring personal liberty and protection against arbitrary arrest. Its historical development underscores its enduring role in upholding the rule of law and preventing abuses of power.
Legal Definitions and Scope
Amparo is a legal remedy in Latin American jurisdictions designed to protect constitutional rights broadly against acts by authorities or individuals, covering a wide range of civil liberties and fundamental rights. Habeas Corpus specifically addresses unlawful detention or imprisonment, ensuring a person's right to liberty by requiring authorities to justify the legality of the individual's confinement. While Amparo offers a comprehensive protection framework for various rights, Habeas Corpus is narrowly focused on protection against arbitrary detention and guarantees personal freedom.
Key Differences Between Amparo and Habeas Corpus
Amparo is a broader legal remedy in Mexico designed to protect constitutional rights against laws, acts, or omissions by authorities, while Habeas Corpus specifically addresses unlawful detentions or restraints of personal liberty. Amparo can challenge any public authority action violating constitutional rights, including laws, judicial decisions, or administrative acts, whereas Habeas Corpus is limited to securing immediate release from illegal imprisonment. The procedural scope of Amparo encompasses both preventive and corrective relief, contrasting with Habeas Corpus, which primarily seeks prompt liberation from unlawful detention.
Grounds for Filing Amparo Petitions
Amparo petitions are filed primarily to protect constitutional rights against violations by authorities, including threats to life, liberty, and security, while Habeas Corpus specifically addresses unlawful detention or imprisonment. Grounds for filing an Amparo petition include acts or omissions by public officials that result in rights infringements, threats to personal liberty beyond detention, and violations affecting property or privacy rights. The Amparo serves as a broader remedy compared to Habeas Corpus, which is strictly limited to unlawful restraint cases.
Circumstances Warranting Habeas Corpus
Habeas Corpus is warranted in situations where an individual is unlawfully detained or imprisoned without proper legal authority, serving as a prompt remedy against illegal restraint of liberty. It is especially applicable when there is no due process, such as arbitrary arrest, detention without charges, or violation of the right to bail. Unlike Amparo, which addresses a broader range of constitutional rights, Habeas Corpus specifically protects personal freedom against unlawful confinement.
Legal Procedures and Process
Amparo and Habeas Corpus are legal remedies designed to protect constitutional rights but differ significantly in procedures. Amparo involves a comprehensive judicial review addressing any violation of constitutional rights, allowing broader claims beyond unlawful detention. Habeas Corpus specifically targets illegal detention or imprisonment, requiring the immediate presentation of the detainee before the court to assess the lawfulness of their confinement.
Landmark Cases Involving Amparo and Habeas Corpus
The landmark case Ex parte Quirin (1942) clarified the scope of habeas corpus by addressing the detention of enemy combatants and affirming limited rights under military tribunals. In contrast, the Mexican Supreme Court's ruling in the Amparo case, Citizens United v. Federal Electoral Institute (2010), expanded protections against government actions violating constitutional rights, reinforcing individual legal recourse. These pivotal cases highlight habeas corpus's role in safeguarding personal liberty from unlawful detention, while amparo broadly defends constitutional rights against diverse governmental abuses.
Comparative Importance in Human Rights Protection
Amparo and Habeas Corpus serve distinct yet complementary roles in human rights protection, with Amparo offering a broad mechanism to challenge violations of constitutional rights beyond just personal liberty. Habeas Corpus specifically safeguards individuals against unlawful detention, ensuring prompt judicial review to prevent arbitrary imprisonment. The comparative importance lies in Amparo's wider scope for defending a range of fundamental rights, while Habeas Corpus remains crucial for protecting freedom from illegal confinement.
Amparo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com