Authority defines the recognized power or influence someone holds within a specific domain, shaping decisions and guiding actions. Understanding how authority functions can enhance your ability to navigate professional and social environments effectively. Explore the full article to discover the key principles and practical insights about authority.
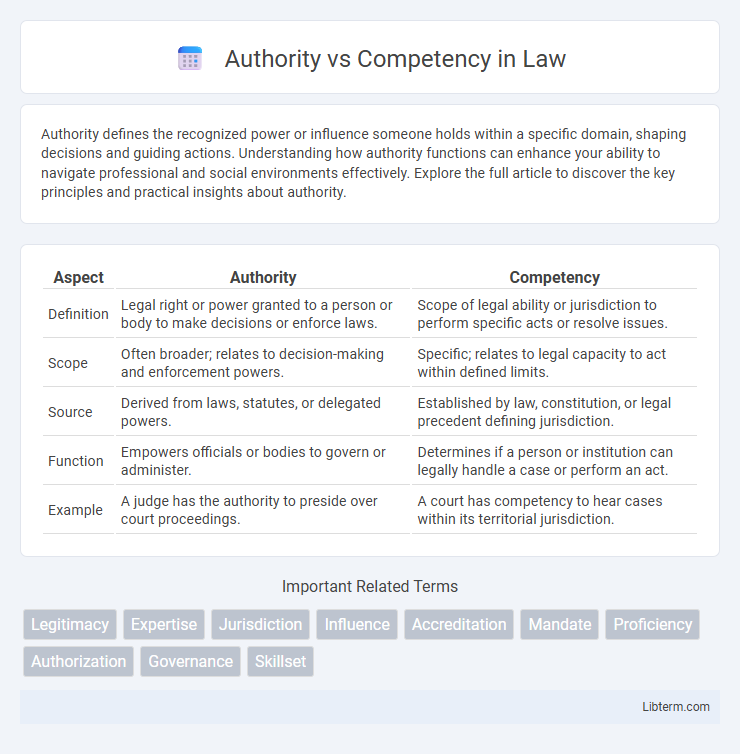
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Authority | Competency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal right or power granted to a person or body to make decisions or enforce laws. | Scope of legal ability or jurisdiction to perform specific acts or resolve issues. |
| Scope | Often broader; relates to decision-making and enforcement powers. | Specific; relates to legal capacity to act within defined limits. |
| Source | Derived from laws, statutes, or delegated powers. | Established by law, constitution, or legal precedent defining jurisdiction. |
| Function | Empowers officials or bodies to govern or administer. | Determines if a person or institution can legally handle a case or perform an act. |
| Example | A judge has the authority to preside over court proceedings. | A court has competency to hear cases within its territorial jurisdiction. |
Understanding Authority and Competency
Authority defines the formal right to make decisions and enforce rules within an organizational hierarchy, often granted through position or role. Competency encompasses the skills, knowledge, and abilities required to perform tasks effectively and achieve desired outcomes. Understanding authority and competency clarifies the balance between positional power and individual capability, essential for organizational success.
Defining Authority: Power and Position
Authority refers to the formal power granted to an individual or role based on their position within an organizational hierarchy, enabling them to make decisions, allocate resources, and enforce rules. It derives from the official capacity recognized by the organization's structure and legal framework, providing legitimacy to command and control functions. Unlike competency, which centers on skills and expertise, authority originates from the designated status and responsibilities assigned to a role.
What is Competency? Skills and Expertise
Competency encompasses the specific skills, knowledge, and expertise that enable an individual to perform tasks effectively and meet job requirements. It includes both technical abilities and behavioral attributes that contribute to consistent, high-quality performance in a professional environment. Developing competency involves continuous learning and practical application of skills relevant to one's field or role.
The Interplay Between Authority and Competency
The interplay between authority and competency shapes organizational effectiveness, where authority provides the formal power to make decisions, while competency ensures those decisions are informed by expertise and skill. Leaders with high competency leverage their authority to implement strategies successfully, fostering trust and commitment among team members. Balancing authority with competency prevents misuse of power and enhances decision-making quality, driving sustainable performance and innovation.
Authority Without Competency: Risks and Consequences
Authority without competency often leads to poor decision-making, decreased team morale, and operational inefficiencies. Leaders lacking the necessary skills and knowledge may impose ineffective policies, resulting in project failures and lost organizational credibility. This gap undermines trust and stifles innovation, threatening long-term business stability and growth.
Competency Without Authority: Missed Opportunities
Competency without authority often leads to missed opportunities as skilled individuals cannot fully apply their expertise or implement decisions effectively. Organizations risk stagnation when competent employees lack the power to influence outcomes, resulting in underutilized talent and decreased innovation. Empowering employees with both competency and authority enhances productivity, drives strategic initiatives, and fosters a culture of accountability.
Building Competency in Positions of Authority
Building competency in positions of authority enhances leadership effectiveness by integrating specialized skills and knowledge with decision-making power. Organizations that invest in continuous training and professional development for their leaders foster adaptive and informed authority, improving team performance and strategic outcomes. Competency-driven authority promotes credibility and trust, ensuring leaders can navigate complex challenges while inspiring confidence among stakeholders.
Recognizing Competency Regardless of Rank
Competency should be recognized based on skills, knowledge, and performance rather than formal rank or title. Empowering employees by valuing expertise fosters innovation and improves decision-making across organizational levels. Organizations that prioritize competency build resilient teams capable of adapting to evolving challenges effectively.
Strategies for Aligning Authority with Competency
Aligning authority with competency enhances organizational efficiency by ensuring decision-making power resides with qualified individuals. Strategies include implementing competency-based assessments to match roles with skills, fostering continuous professional development to elevate capabilities, and designing clear delegation frameworks that reflect expertise areas. Regular performance reviews and feedback loops help to recalibrate authority boundaries, promoting accountability and optimal resource utilization.
Cultivating Effective Leadership Through Balance
Effective leadership thrives on balancing authority and competency, where authority grants the power to make decisions and enforce rules, while competency ensures leaders possess the skills and knowledge to guide teams effectively. Cultivating this balance enhances trust, promotes accountability, and drives organizational success by empowering leaders to inspire and manage diverse talents. Organizations that invest in developing both authority and competency create resilient leadership capable of navigating complex challenges and fostering sustainable growth.
Authority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com