Quo Warranto is a legal proceeding used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or exercise authority. This writ ensures that public officials or entities act within their legal bounds, preventing unlawful usurpation of power. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Quo Warranto can protect Your rights and maintain governmental accountability.
Table of Comparison
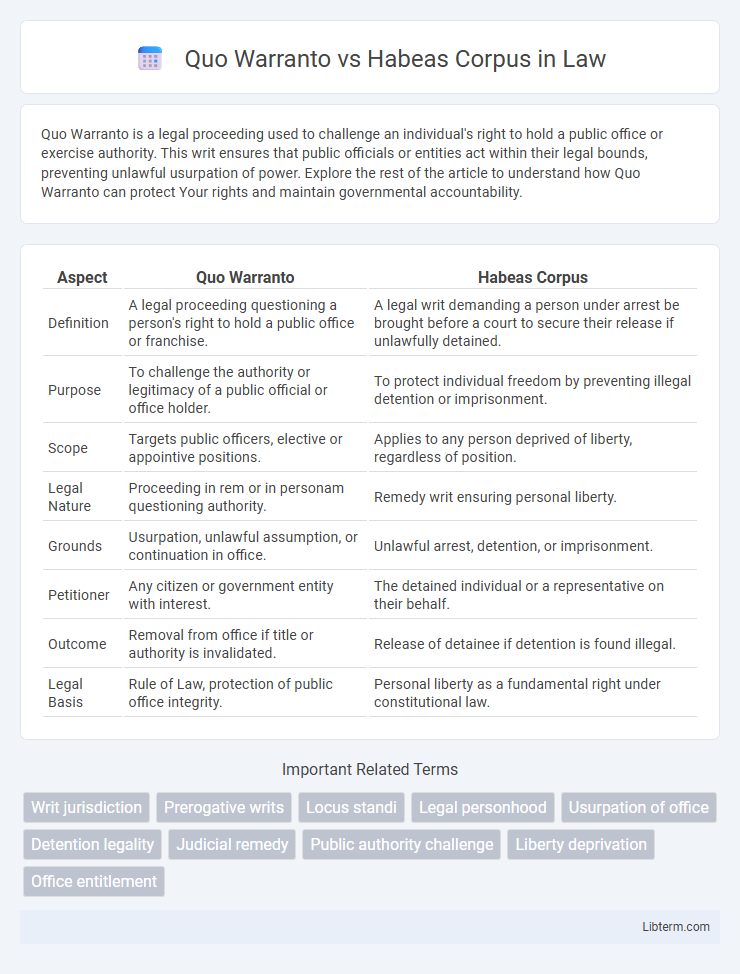
| Aspect | Quo Warranto | Habeas Corpus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal proceeding questioning a person's right to hold a public office or franchise. | A legal writ demanding a person under arrest be brought before a court to secure their release if unlawfully detained. |
| Purpose | To challenge the authority or legitimacy of a public official or office holder. | To protect individual freedom by preventing illegal detention or imprisonment. |
| Scope | Targets public officers, elective or appointive positions. | Applies to any person deprived of liberty, regardless of position. |
| Legal Nature | Proceeding in rem or in personam questioning authority. | Remedy writ ensuring personal liberty. |
| Grounds | Usurpation, unlawful assumption, or continuation in office. | Unlawful arrest, detention, or imprisonment. |
| Petitioner | Any citizen or government entity with interest. | The detained individual or a representative on their behalf. |
| Outcome | Removal from office if title or authority is invalidated. | Release of detainee if detention is found illegal. |
| Legal Basis | Rule of Law, protection of public office integrity. | Personal liberty as a fundamental right under constitutional law. |
Understanding Quo Warranto: Definition and Purpose
Quo Warranto is a legal writ used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or governmental position by requiring them to show by what authority they exercise such power. Its primary purpose is to prevent unlawful usurpation of office and ensure that public officials have legitimate claims based on law or appointment. Unlike Habeas Corpus, which protects personal liberty by contesting unlawful detention, Quo Warranto safeguards the integrity of public offices by verifying the legality of occupancy.
What is Habeas Corpus? Meaning and Importance
Habeas Corpus is a legal writ requiring a person under arrest to be brought before a judge or court, ensuring protection against unlawful detention. Its importance lies in safeguarding individual liberty by preventing illegal imprisonment and maintaining the rule of law. This writ serves as a fundamental check on executive power, upholding constitutional rights and due process.
Historical Origins: Quo Warranto vs Habeas Corpus
Quo Warranto originated in medieval England as a legal procedure to challenge a person's right to hold a public office or governmental authority, emphasizing the legitimacy of power and jurisdiction. Habeas Corpus, dating back to the 13th century Magna Carta, is a fundamental legal safeguard designed to protect individual freedom by preventing unlawful detention or imprisonment. Both writs played crucial roles in shaping constitutional law by balancing state authority with individual rights through distinct historical functions.
Legal Provisions Governing Quo Warranto
Quo Warranto is governed by specific legal provisions, primarily under the Rules of Court, which outline procedures for questioning a person's authority to hold public office or exercise a franchise. The petition must clearly allege illegality or usurpation of authority, supported by substantial evidence to warrant a court-issued writ. Unlike Habeas Corpus, which protects individual liberty against unlawful detention, Quo Warranto serves as a legal remedy to ensure lawful exercise of public authority.
Constitutional Basis for Habeas Corpus
Habeas Corpus is constitutionally enshrined to protect individual liberty by ensuring that a person cannot be detained unlawfully, as stipulated in Article I, Section 15 of the Philippine Constitution. It serves as a legal remedy to challenge unlawful detention, compelling authorities to justify the legality of a person's imprisonment before the court. Quo Warranto, on the other hand, is used to question a person's right to hold a public office or position, but Habeas Corpus specifically safeguards personal freedom against arbitrary detention under constitutional law.
Key Differences Between Quo Warranto and Habeas Corpus
Quo Warranto challenges an individual's right to hold a public office by questioning the legal authority behind their claim, whereas Habeas Corpus protects personal liberty by ensuring a person is not held unlawfully in custody. Quo Warranto is typically used to address public office disputes and is initiated by the government or an interested party, while Habeas Corpus is a fundamental safeguard against illegal detention and can be filed by the detainee or any person on their behalf. The main difference lies in their purpose: Quo Warranto seeks to prevent unauthorized occupation of public positions, whereas Habeas Corpus secures individual freedom from unlawful imprisonment.
Procedures for Filing Quo Warranto Petitions
Filing a Quo Warranto petition involves submitting a verified complaint to the court challenging a person's right to hold a public office or governmental position, typically supported by evidence questioning the legitimacy of the officeholder's claim. The petitioner must identify the office in question, the grounds for disqualification, and any relevant facts showing usurpation or unlawful occupancy. Courts require adherence to specific procedural requirements, such as jurisdictional rules and timing constraints, before issuance of a writ to compel the respondent to show by what authority they hold the office.
Steps in Habeas Corpus Proceedings
Habeas Corpus proceedings begin with the filing of a petition by the detained individual or their representative, challenging the legality of the detention. The court issues a writ commanding the custodian to produce the detainee and justify the detention. A prompt hearing follows where the court examines the evidence to determine if the detention violates constitutional or legal rights, leading to either release or continuation of custody.
Landmark Cases: Quo Warranto and Habeas Corpus in Jurisprudence
Quo Warranto and Habeas Corpus represent critical writs in jurisprudence with landmark cases shaping their application. The Quo Warranto case of *Republic v. Sandiganbayan* underscored authority challenges, questioning official legitimacy under Philippine law. Landmark Habeas Corpus rulings, such as *Javier v. Executive Secretary*, reinforced protection against unlawful detention, affirming fundamental constitutional rights.
Practical Implications and Contemporary Relevance
Quo Warranto challenges an individual's right to hold public office by questioning the legality of their claim, serving as a critical tool for maintaining the integrity of government positions. Habeas Corpus provides immediate protection against unlawful detention by ensuring a person's right to physical liberty, making it essential in upholding human rights and due process. Both remedies remain vital in contemporary legal systems for enforcing accountability and protecting individual freedoms within the framework of constitutional law.
Quo Warranto Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com