A beneficiary is an individual or entity designated to receive assets, benefits, or proceeds from a will, trust, insurance policy, or retirement account. Understanding the roles and rights of beneficiaries is essential for effective estate planning and ensuring your wishes are carried out after your passing. Explore the rest of this article to learn more about how beneficiary designations impact your financial and legal future.
Table of Comparison
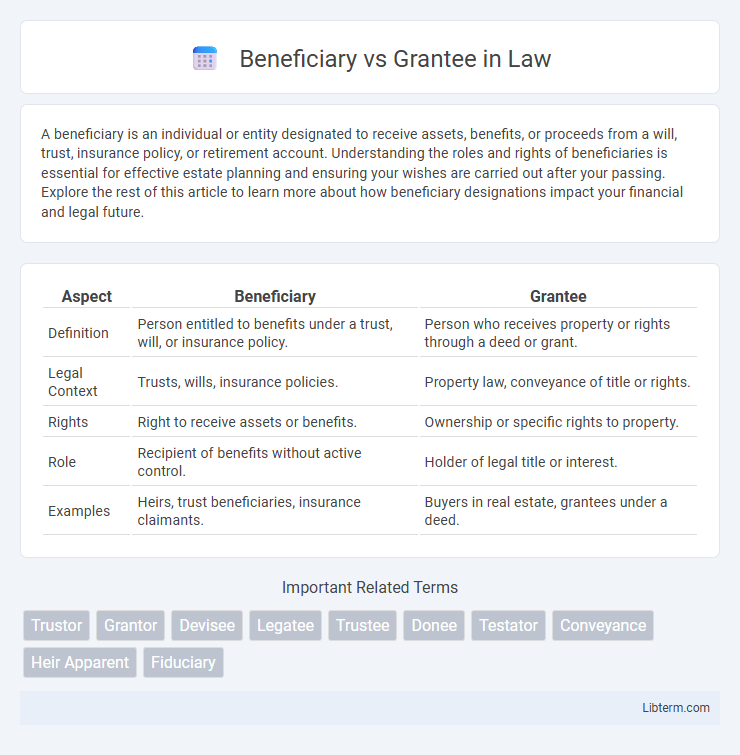
| Aspect | Beneficiary | Grantee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Person entitled to benefits under a trust, will, or insurance policy. | Person who receives property or rights through a deed or grant. |
| Legal Context | Trusts, wills, insurance policies. | Property law, conveyance of title or rights. |
| Rights | Right to receive assets or benefits. | Ownership or specific rights to property. |
| Role | Recipient of benefits without active control. | Holder of legal title or interest. |
| Examples | Heirs, trust beneficiaries, insurance claimants. | Buyers in real estate, grantees under a deed. |
Understanding the Terminology: Beneficiary vs Grantee
A beneficiary is an individual or entity entitled to receive benefits, assets, or rights under a legal arrangement such as a trust, insurance policy, or will. A grantee is a person or party who receives a grant, deed, or conveyance of property, typically through a formal transfer of ownership or rights. Understanding the distinction hinges on the context: beneficiaries gain benefits without necessarily holding title, while grantees acquire legal ownership or interests.
Legal Definitions of Beneficiary and Grantee
A beneficiary is a person or entity entitled to receive benefits, assets, or rights from a trust, will, insurance policy, or contract, often without active involvement in the creation of the legal instrument. A grantee is an individual or entity that receives legal title or ownership of property through a deed or grant in real estate transactions. The legal distinction centers on the beneficiary's passive receipt of benefits versus the grantee's active acquisition of property rights or ownership interests.
Key Differences Between Beneficiary and Grantee
A beneficiary is the individual or entity entitled to receive benefits or assets from a trust, will, insurance policy, or contract, while a grantee is the party who receives property or rights through a legal conveyance such as a deed. Key differences include the nature of rights held: beneficiaries have equitable interests or contingent benefits, whereas grantees gain legal ownership or title. Beneficiaries often have rights contingent on specific conditions, but grantees typically acquire immediate and enforceable property rights upon transfer.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Beneficiary
A beneficiary is the individual or entity entitled to receive benefits, assets, or rights from a trust, will, or contract, with responsibilities centered around accepting and utilizing these benefits as outlined by the terms. Unlike a grantee, who is typically the recipient of property or rights through a grant or deed, a beneficiary's role often involves compliance with fiduciary rules and ensuring proper use of the received assets. Key responsibilities include monitoring the management of the trust or asset, reporting requirements if applicable, and safeguarding the interests specified by the granting document.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Grantee
A grantee is an individual or organization that receives funds or resources from a grantor to carry out specific projects or programs, with explicit responsibilities to manage and utilize the grant according to agreed terms. Their roles include ensuring compliance with grant conditions, maintaining detailed financial records, and providing progress reports to the grantor to demonstrate how resources are allocated and objectives are achieved. Unlike a beneficiary who benefits from the program outcomes, the grantee holds accountability for project execution, budget management, and regulatory adherence.
Common Scenarios Involving Beneficiaries and Grantees
Beneficiaries commonly appear in trust and insurance contexts, receiving assets or benefits without direct control over the property, while grantees are involved in real estate transactions, obtaining title or ownership rights. In estate planning, beneficiaries inherit property or funds designated by the grantor, whereas grantees receive legal ownership through deeds or conveyances. Common scenarios include beneficiaries of a living trust collecting income or principal and grantees acquiring land via warranty deeds or quitclaim deeds.
Beneficiary vs Grantee in Trusts and Estates
In trusts and estates, a beneficiary is an individual or entity entitled to receive benefits or assets from the trust or estate according to its terms, while a grantee is the party who receives legal title or ownership of property through a conveyance or transfer. Beneficiaries hold equitable interests and may have rights to income or principal distributions, whereas grantees hold legal title and control over the property conveyed. Understanding the distinction clarifies roles in estate planning, as beneficiaries benefit from trusts without necessarily holding legal ownership, contrasting with grantees who acquire ownership through instruments like deeds or wills.
Property Transfers: Who Is the Grantee?
The grantee in property transfers is the individual or entity receiving legal title to real estate or property from the grantor. Unlike a beneficiary, who may gain interest through trusts or wills without direct title, a grantee holds formal ownership recognized by the deed. Understanding the distinction ensures clarity in property transactions and legal documentation.
Rights and Protections for Beneficiaries and Grantees
Beneficiaries possess enforceable rights to benefits designated in trusts or wills, ensuring legal protection for receiving assets or income, whereas grantees hold title or ownership rights to property transferred through deeds or grants. Beneficiaries' protections include fiduciary oversight by trustees to prevent mismanagement, while grantees rely on title guarantees and property laws safeguarding their ownership against claims or defects. Both parties have distinct legal remedies: beneficiaries can sue trustees for breach of duty, and grantees can pursue action for title disputes or encroachments.
Choosing the Right Term: Beneficiary or Grantee?
Choosing the right term between beneficiary and grantee depends on the context of the transfer of rights or assets. A beneficiary typically refers to a person or entity designated to receive benefits from a trust, will, insurance policy, or financial account, emphasizing entitlement to funds or benefits. A grantee, on the other hand, specifically denotes the recipient of a property transfer or deed, highlighting legal ownership in real estate or title conveyance.
Beneficiary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com