Fee Simple Absolute represents the most complete ownership interest one can have in real estate, granting unlimited duration, transferability, and hereditary succession. It provides you with full control over the property without conditions or limitations, making it the preferred form of ownership in real estate transactions. Explore the article to understand how Fee Simple Absolute affects your property rights and real estate decisions.
Table of Comparison
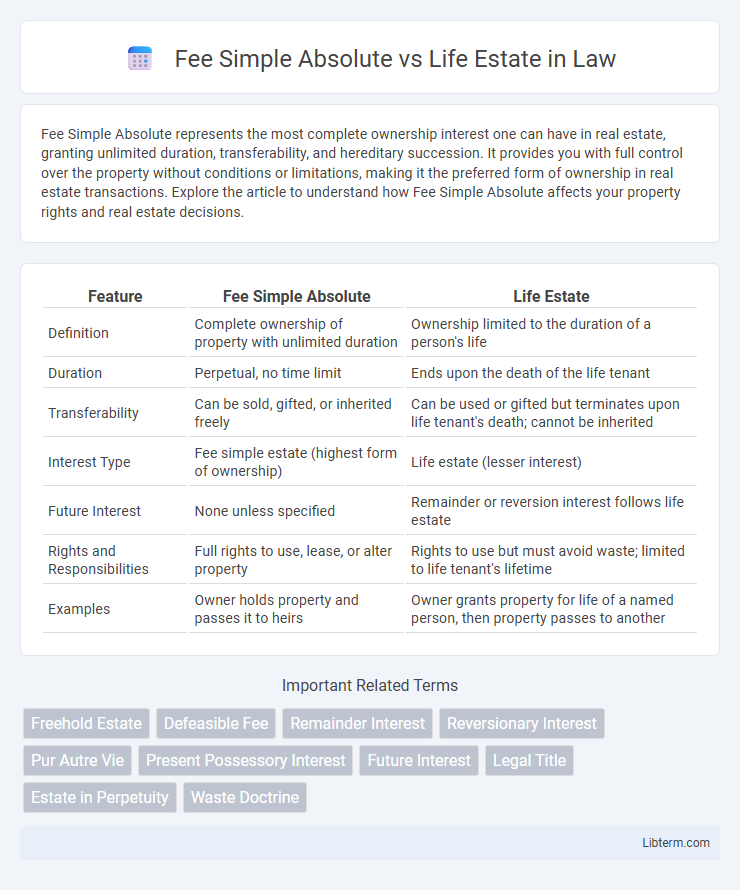
| Feature | Fee Simple Absolute | Life Estate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete ownership of property with unlimited duration | Ownership limited to the duration of a person's life |
| Duration | Perpetual, no time limit | Ends upon the death of the life tenant |
| Transferability | Can be sold, gifted, or inherited freely | Can be used or gifted but terminates upon life tenant's death; cannot be inherited |
| Interest Type | Fee simple estate (highest form of ownership) | Life estate (lesser interest) |
| Future Interest | None unless specified | Remainder or reversion interest follows life estate |
| Rights and Responsibilities | Full rights to use, lease, or alter property | Rights to use but must avoid waste; limited to life tenant's lifetime |
| Examples | Owner holds property and passes it to heirs | Owner grants property for life of a named person, then property passes to another |
Introduction to Fee Simple Absolute and Life Estate
Fee Simple Absolute represents the most complete form of property ownership, granting the owner unlimited rights to use, sell, or transfer the property indefinitely. Life Estate conveys ownership rights for the duration of a specified individual's life, after which the property automatically transfers to a designated remainderman or reverts to the original grantor. Understanding these concepts is crucial in property law to determine possession rights, duration, and future interests involved in real estate transactions.
Definition of Fee Simple Absolute
Fee Simple Absolute represents the most complete ownership interest in real property, providing the owner with unlimited rights to use, transfer, or bequeath the property indefinitely without conditions. It is the highest form of property ownership recognized by law, granting the holder full control over the estate during their lifetime and the ability to convey the property freely to heirs or others. Unlike a Life Estate, which restricts ownership to the duration of an individual's life, Fee Simple Absolute estate persists perpetually unless voluntarily transferred or legally encumbered.
Key Features of Fee Simple Absolute
Fee Simple Absolute represents the most complete ownership interest in real property, granting the owner unlimited duration, transferability, and inheritance rights without conditions or limitations. This estate type provides absolute control over the property, including the right to sell, lease, or bequeath it freely. Unlike Life Estate, which lasts only for the lifetime of a specified individual, Fee Simple Absolute ensures perpetual ownership.
Definition of Life Estate
A Life Estate is a property interest granting ownership rights for the duration of a person's lifetime, after which the property automatically transfers to a designated remainderman or reverts to the original grantor. In contrast, Fee Simple Absolute represents the most complete form of ownership, providing indefinite, unrestricted rights to the property without any conditions or limitations based on someone's lifespan. Understanding Life Estate involves recognizing its temporary nature and conditional transfer of ownership upon the end of the life tenant's life.
Key Features of Life Estate
A life estate grants ownership of property for the duration of an individual's life, with full rights to possess and use the property but without the ability to sell or transfer ownership beyond their lifetime. Upon the life tenant's death, the property automatically passes to a designated remainderman or reverts to the original grantor, ensuring clear succession of ownership. This contrasts with fee simple absolute, which provides indefinite ownership rights and the ability to transfer the property freely.
Major Differences between Fee Simple Absolute and Life Estate
Fee Simple Absolute grants complete ownership of property with unlimited duration, transferrable to heirs or other parties, whereas Life Estate provides ownership rights only for the duration of a specified person's life, after which the property passes to a remainderman or reverts to the original grantor. Fee Simple Absolute owners have the right to use, sell, lease, or bequeath the property without restrictions, while Life Estate holders have limited rights and cannot encumber the estate beyond their lifetime. Unlike Life Estate, Fee Simple Absolute is the most comprehensive form of property ownership recognized in real estate law.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fee Simple Absolute
Fee Simple Absolute offers complete ownership of property with unlimited duration, providing maximum control and the ability to sell, lease, or bequeath the estate without restrictions. Its primary advantage lies in the absolute freedom it grants the owner, but this also means the owner bears full responsibility for property taxes, maintenance, and any legal issues. A key disadvantage is the absence of conditions or limitations, which can result in the estate being subject to creditors or foreclosure without protective restrictions.
Pros and Cons of Life Estate
Life estate grants ownership rights for the duration of an individual's life, allowing the life tenant to use and benefit from the property, while the remainder interest passes to another party upon death. Pros include protection from creditors and control during the tenant's lifetime, along with the avoidance of probate for the remainderman. Cons involve limited transferability, potential difficulty in obtaining financing, and the risk of property deterioration since the life tenant may lack long-term incentives to maintain the estate.
Legal Implications and Use Cases
Fee Simple Absolute grants the owner full and indefinite ownership rights, including the power to sell, lease, or bequeath the property without restrictions, making it the most complete form of property ownership under common law. Life Estate limits ownership duration to the lifetime of the holder, after which the property automatically transfers to a remainderman, often used in estate planning to provide for heirs while retaining control during the grantor's life. Legal implications of Fee Simple Absolute include unrestricted inheritance and alienation, whereas Life Estate carries future interest considerations and potential maintenance responsibilities for the life tenant.
Choosing Between Fee Simple Absolute and Life Estate
Choosing between Fee Simple Absolute and Life Estate depends on the desired level of ownership control and duration. Fee Simple Absolute provides complete ownership with unlimited duration and transferability, making it ideal for those seeking maximum rights and inheritance ability. Life Estate restricts ownership to the lifetime of a designated individual, offering benefits like avoiding probate but limiting control and future transfer options.
Fee Simple Absolute Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com