General provisions establish the foundational rules and guidelines that govern contracts, ensuring clarity and mutual understanding between parties. These provisions define essential terms, responsibilities, and legal frameworks that protect your rights and obligations throughout the agreement. Explore the rest of this article to understand how general provisions safeguard your interests and facilitate smooth contractual relationships.
Table of Comparison
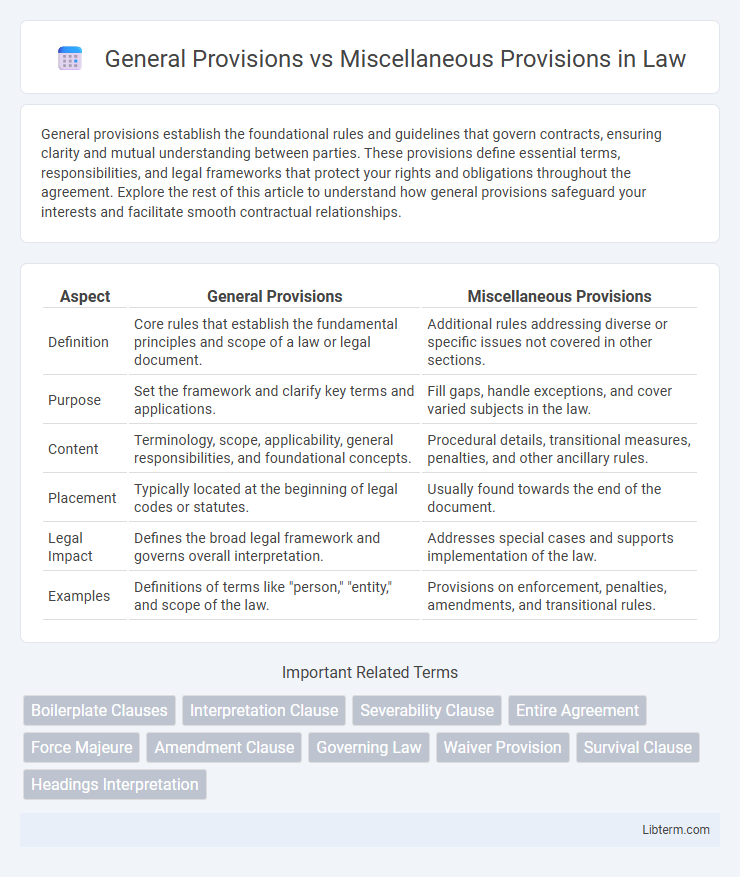
| Aspect | General Provisions | Miscellaneous Provisions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Core rules that establish the fundamental principles and scope of a law or legal document. | Additional rules addressing diverse or specific issues not covered in other sections. |
| Purpose | Set the framework and clarify key terms and applications. | Fill gaps, handle exceptions, and cover varied subjects in the law. |
| Content | Terminology, scope, applicability, general responsibilities, and foundational concepts. | Procedural details, transitional measures, penalties, and other ancillary rules. |
| Placement | Typically located at the beginning of legal codes or statutes. | Usually found towards the end of the document. |
| Legal Impact | Defines the broad legal framework and governs overall interpretation. | Addresses special cases and supports implementation of the law. |
| Examples | Definitions of terms like "person," "entity," and scope of the law. | Provisions on enforcement, penalties, amendments, and transitional rules. |
Understanding General Provisions: Definition and Scope
General Provisions establish the foundational rules and definitions that govern the interpretation and application of a contract, statute, or legal document, outlining the scope, purpose, and key terms crucial for clarity and consistency. These provisions set the framework within which all other specific clauses operate, ensuring uniformity and minimizing ambiguity. Unlike Miscellaneous Provisions, which address ancillary or supplemental aspects, General Provisions are central to understanding the document's overall structure and intent.
What Are Miscellaneous Provisions? Key Characteristics
Miscellaneous Provisions in legal documents encompass a variety of clauses that do not fit neatly into other sections but are crucial for the contract's completeness and enforceability. Key characteristics include their role in addressing administrative details, interpretation rules, severability, governing law, and dispute resolution mechanisms. These provisions ensure clarity, prevent ambiguities, and provide fallback rules that uphold the contract's intent when unforeseen issues arise.
Historical Context: Evolution of Legal Provisions
General Provisions historically established the foundational legal principles and structured the framework for statutes, serving as the backbone of legislative documents since early codifications. Miscellaneous Provisions emerged later to address specific issues, exceptions, or clarifications that do not fit within the main sections, reflecting the increasing complexity and specialization of modern law. This evolution highlights the adaptation of legal drafting to accommodate nuanced regulations and evolving societal needs while maintaining coherence in legal codes.
Primary Functions of General Provisions in Legal Documents
General Provisions in legal documents establish foundational definitions, applicability, and the scope of the agreement, serving as the blueprint for interpreting subsequent clauses. They clarify essential terms, set the framework for rights and obligations, and outline effective dates and governing law, ensuring consistent understanding throughout the contract. Miscellaneous Provisions typically address supplementary matters such as dispute resolution, amendment procedures, and severability, which do not fit into primary contractual sections.
The Role of Miscellaneous Provisions in Agreements
Miscellaneous provisions in agreements serve to address various practical and administrative details that ensure the enforceability and clarity of the contract, such as governing law, dispute resolution, and amendment procedures. These clauses complement the general provisions, which establish the core rights and obligations of the parties involved. By covering contingencies and procedural elements, miscellaneous provisions help prevent disputes and facilitate smooth agreement execution.
Structural Placement: Where Provisions Appear in Contracts
General Provisions typically appear at the beginning of contracts, outlining essential definitions, scope, and core obligations that frame the agreement. Miscellaneous Provisions are usually located towards the end, covering ancillary clauses such as severability, governing law, and notice requirements. This structural placement ensures clarity by establishing fundamental terms upfront and addressing supplementary legal elements separately.
Key Differences Between General and Miscellaneous Provisions
General provisions establish the foundational rules and primary obligations governing the entire contract, setting the scope and framework for interpretation and enforcement. Miscellaneous provisions address ancillary, less central issues such as notice requirements, amendment procedures, severability, and governing law, ensuring smooth contract administration and legal compliance. The key difference lies in their function: general provisions form the core terms, while miscellaneous provisions handle supplementary matters that support contract execution.
Common Examples of General vs Miscellaneous Clauses
General provisions in contracts commonly include definitions, scope of agreement, and effective dates, establishing the foundational terms governing the contract's operation. Miscellaneous provisions typically cover clauses such as severability, force majeure, and notices, addressing ancillary but essential legal safeguards and procedural requirements. Both sections ensure clarity and enforceability, with general clauses defining core contract elements and miscellaneous clauses managing exceptions and administrative details.
Legal Implications and Enforceability of Each Provision Type
General provisions outline fundamental contract terms, establishing the legal framework and primary obligations, thereby holding clear enforceability in court. Miscellaneous provisions address supplementary issues like notices, governing law, and dispute resolution, which can significantly affect contract interpretation and enforcement outcomes. Understanding the legal implications of each provision type is crucial for risk management and ensuring the contract's comprehensive enforceability.
Best Practices for Drafting General and Miscellaneous Provisions
Best practices for drafting general provisions emphasize clarity, consistency, and comprehensive coverage of foundational contract terms such as definitions, governing law, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Miscellaneous provisions should address supplementary elements like amendment procedures, severability, and notice requirements to ensure enforceability and flexibility. Combining precise language with standardized clauses enhances interpretability and reduces potential disputes in contract execution.
General Provisions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com