Accord and satisfaction is a legal concept where parties agree to settle a contract dispute by accepting different performance than originally agreed upon, resolving the claim without further litigation. This process involves an "accord," which is the agreement to the new terms, and "satisfaction," the execution of those terms. Explore the article to understand how accord and satisfaction can protect your interests and prevent costly legal battles.
Table of Comparison
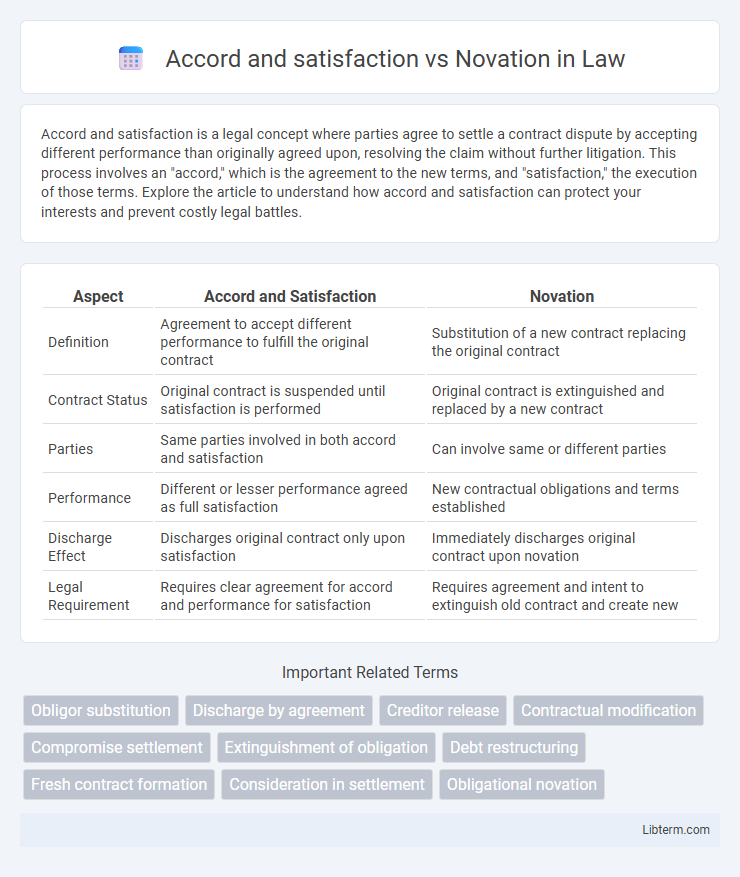
| Aspect | Accord and Satisfaction | Novation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreement to accept different performance to fulfill the original contract | Substitution of a new contract replacing the original contract |
| Contract Status | Original contract is suspended until satisfaction is performed | Original contract is extinguished and replaced by a new contract |
| Parties | Same parties involved in both accord and satisfaction | Can involve same or different parties |
| Performance | Different or lesser performance agreed as full satisfaction | New contractual obligations and terms established |
| Discharge Effect | Discharges original contract only upon satisfaction | Immediately discharges original contract upon novation |
| Legal Requirement | Requires clear agreement for accord and performance for satisfaction | Requires agreement and intent to extinguish old contract and create new |
Understanding Accord and Satisfaction
Accord and satisfaction refers to an agreement between parties where an original contractual obligation is replaced by a new one, with the new agreement settling the dispute. It requires an accord, which is the agreement to accept a different performance, and satisfaction, which is the execution of that agreed performance, thus discharging the original contract. This concept differs from novation, which involves substituting a new contract or party, effectively extinguishing the old contract entirely.
Defining Novation in Contract Law
Novation in contract law refers to the substitution of a new contract or party in place of an original contract or party, creating fresh obligations and extinguishing the original ones. It requires the consent of all parties involved, effectively replacing old agreements with new terms or parties. Accord and satisfaction, by contrast, involves agreeing to accept different performance than originally owed, resolving the existing contract without creating a new one.
Key Differences Between Accord and Satisfaction vs Novation
Accord and satisfaction involve an agreement to accept a different performance than originally contracted, where the original contract remains but is discharged upon fulfillment of the accord. Novation replaces the original contract with a new one, extinguishing the original obligations by creating new parties or terms. The key difference lies in the continuation of the original debt in accord and satisfaction versus the complete substitution of the contract and parties in novation.
Legal Principles Governing Accord and Satisfaction
Accord and satisfaction involves a debtor offering a lesser performance than originally owed, with the creditor agreeing to accept it as full satisfaction, thus extinguishing the original obligation upon performance. The legal principle requires a valid agreement (accord) followed by execution (satisfaction) to discharge the initial contract. Novation, distinct from accord and satisfaction, creates a new contract replacing the old one, requiring agreement by all parties and extinguishing the previous obligations entirely.
Essential Elements of Novation Agreements
Novation agreements require three essential elements: the consent of all original parties, the substitution of a new contract or obligation, and the extinguishment of the original contract. Unlike accord and satisfaction, which modify the terms of an existing obligation without replacing it, novation completely replaces one party or contract with a new one, creating a new legal relationship. Effective novation ensures that previous liabilities are discharged and the new agreement is enforceable.
Practical Applications in Business Transactions
Accord and satisfaction resolves disputes by agreeing to a new performance different from the original contract, effectively discharging the initial obligation once the new agreement is executed. Novation replaces an existing contract with a new one, transferring contractual rights and obligations to a third party, which is crucial in business transactions involving change of parties or refinancing. Both mechanisms streamline debt settlement and contract modifications, minimizing litigation risks and enhancing operational flexibility.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Accord and Satisfaction
Accord and satisfaction offer the advantage of resolving disputes by agreeing on a new contract with modified terms, providing flexibility and preventing litigation costs. However, this approach may lead to uncertainties if the satisfaction is not fully performed, potentially causing further disputes. Unlike novation, which completely replaces the original contract and parties involved, accord and satisfaction only modifies the obligations, maintaining the original contract's existence until performance is fulfilled.
Benefits and Risks of Novation
Novation offers the benefit of completely replacing the original contract, ensuring clear release of prior obligations and reducing liability risks for all parties involved. It allows parties to substitute a new contract with new terms and obligations, enabling flexibility in managing and restructuring agreements. However, novation carries risks such as potential misunderstandings if not all parties consent or if the new contract terms are ambiguous, which can lead to disputes or unintended liabilities.
Common Scenarios: When to Use Each Principle
Accord and satisfaction commonly applies in disputes where parties agree to a new performance to settle an existing claim, such as accepting a lower payment to resolve a debt. Novation is used when replacing an original contract or party with a new one, often seen in business mergers or when transferring contractual obligations to a third party. Understanding these scenarios helps choose accord and satisfaction for dispute resolution, while novation suits restructuring or transferring contracts.
Case Law Highlights: Accord and Satisfaction vs Novation
Accord and satisfaction involves an agreement to accept different performance from the original obligation, effectively discharging the initial duty once completed, as established in Foakes v Beer [1884] UKHL 1 where the court emphasized consideration in accord scenarios. Novation replaces the original contract entirely with a new one, extinguishing prior obligations, illustrated by the case of London and South Western Railway Co v Wright (1882) 8 QBD 192, which clarified the necessity of mutual consent for novation. Courts differentiate these based on whether the original contract remains enforceable; in accord and satisfaction, it is suspended pending performance, whereas in novation, it is terminated and replaced.
Accord and satisfaction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com