Joint tenancy is a form of property co-ownership where two or more individuals hold equal shares with rights of survivorship, meaning when one tenant dies, their interest automatically passes to the surviving tenants. This arrangement simplifies inheritance but requires all owners to agree on actions regarding the property, ensuring shared control and responsibility. Explore the rest of this article to understand how joint tenancy could impact your property ownership and estate planning.
Table of Comparison
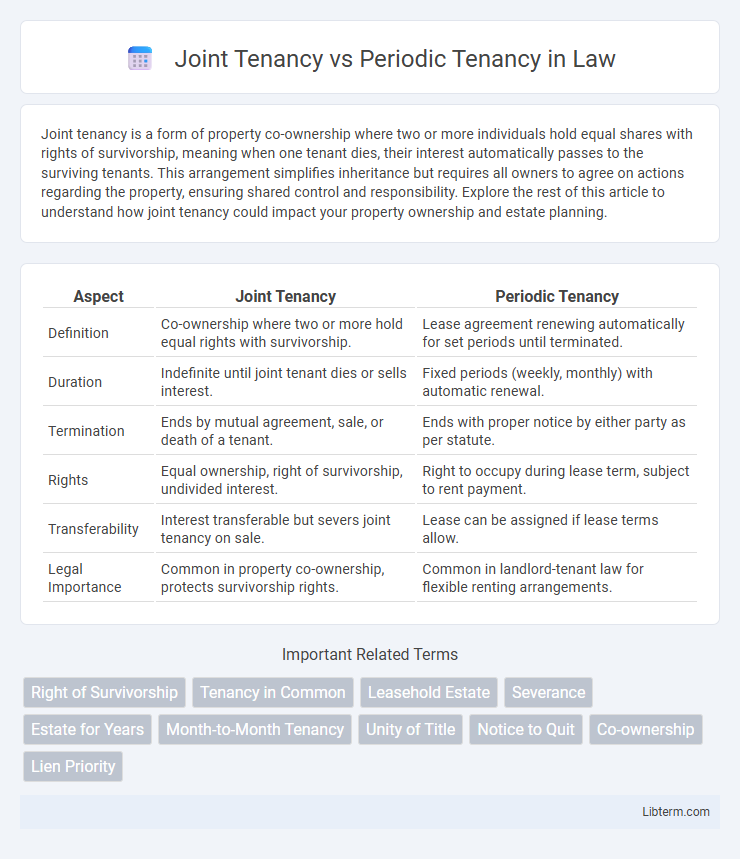
| Aspect | Joint Tenancy | Periodic Tenancy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Co-ownership where two or more hold equal rights with survivorship. | Lease agreement renewing automatically for set periods until terminated. |
| Duration | Indefinite until joint tenant dies or sells interest. | Fixed periods (weekly, monthly) with automatic renewal. |
| Termination | Ends by mutual agreement, sale, or death of a tenant. | Ends with proper notice by either party as per statute. |
| Rights | Equal ownership, right of survivorship, undivided interest. | Right to occupy during lease term, subject to rent payment. |
| Transferability | Interest transferable but severs joint tenancy on sale. | Lease can be assigned if lease terms allow. |
| Legal Importance | Common in property co-ownership, protects survivorship rights. | Common in landlord-tenant law for flexible renting arrangements. |
Understanding Joint Tenancy
Joint tenancy is a legal form of property ownership where two or more individuals hold equal shares with rights of survivorship, meaning that upon the death of one tenant, their interest automatically passes to the surviving joint tenants. This type of tenancy requires the four unities of time, title, interest, and possession to be valid. It is commonly used in real estate to ensure seamless transfer of ownership without probate, contrasting with periodic tenancy, which pertains to rental agreements with recurring lease periods.
Key Features of Periodic Tenancy
Periodic tenancy is a lease arrangement that automatically renews at the end of each period, such as weekly or monthly, offering flexibility for both landlords and tenants. Key features include the lack of a fixed end date, the requirement for proper notice to terminate, and the ability to adjust rent at renewal intervals. This tenancy type provides ongoing occupancy rights until either party decides to end the agreement according to the specified notice period.
Legal Differences Between Joint and Periodic Tenancy
Joint tenancy involves co-owners holding equal shares with rights of survivorship, meaning when one tenant dies, their interest automatically passes to the remaining tenants. Periodic tenancy is a lease agreement that renews automatically at the end of each rental period, such as monthly or weekly, without a fixed end date. Unlike joint tenancy, periodic tenancy does not grant ownership rights but rather establishes a landlord-tenant relationship governed by lease terms and state laws.
Rights and Responsibilities of Tenants
Joint tenancy grants tenants equal rights to possess and use the entire property, with each having a shared responsibility for rent and maintenance obligations; importantly, it includes the right of survivorship, where ownership passes automatically to remaining tenants upon a tenant's death. Periodic tenancy offers tenants the right to occupy property for successive periods, such as month-to-month, with responsibilities including timely rent payment and proper notice for termination, but does not provide rights of survivorship. Both tenancy types require tenants to uphold lease terms, maintain the property in good condition, and communicate effectively with landlords to avoid breaches.
Duration and Termination Conditions
Joint tenancy involves co-owners holding equal shares with a right of survivorship, typically lasting indefinitely until one owner dies, sells, or terminates their interest. Periodic tenancy automatically renews at the end of each period--such as month-to-month or year-to-year--and continues until proper notice is given by either party to terminate. Termination of joint tenancy can occur through mutual agreement or court action, while periodic tenancy requires advance written notice based on the rental period, making duration and termination more flexible but less permanent.
Pros and Cons of Joint Tenancy
Joint tenancy allows co-owners to have equal shares with rights of survivorship, ensuring seamless transfer of property ownership upon the death of a tenant. The main advantage is avoiding probate, but it limits flexibility since all decisions require unanimous consent and individual interests cannot be sold or transferred without dissolving the tenancy. A significant drawback includes potential risks if one tenant incurs debt, as creditors may place liens on the entire property.
Pros and Cons of Periodic Tenancy
Periodic tenancy offers flexibility with lease terms that automatically renew, allowing tenants to stay month-to-month without long-term commitment. This arrangement provides ease of termination for both landlords and tenants, but may result in less security due to the potential for sudden eviction with proper notice. Rent increases can occur more frequently, making financial planning more challenging compared to fixed-term leases like joint tenancy.
Impact on Rent and Payments
Joint tenancy typically requires all tenants to share equal responsibility for rent and payments, ensuring collective liability and potentially simplifying rent collection for landlords. Periodic tenancy offers flexibility with rent payments adjusting according to the agreed period, such as monthly or weekly, allowing tenants to renegotiate terms regularly. Rent stability is more predictable in joint tenancy, whereas periodic tenancy may involve variable rent amounts based on market conditions or lease modifications.
Suitability for Different Tenant Needs
Joint Tenancy is ideal for tenants seeking shared ownership with equal rights and survivorship benefits, often used by families or close associates. Periodic Tenancy suits tenants desiring flexible rental terms with automatic renewal periods, ideal for those uncertain about long-term commitments. Choosing between them depends on the tenant's need for stability versus adaptability in lease agreements.
Choosing the Right Tenancy Type
Selecting the appropriate tenancy type depends on the tenant's long-term plans and flexibility needs. Joint Tenancy offers equal ownership interests and survivorship rights, making it ideal for co-tenants seeking shared responsibility and continuity. Periodic Tenancy provides a flexible lease arrangement with automatic renewals, suitable for tenants requiring short-term commitment and adjustable tenancy periods.
Joint Tenancy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com