Detinue is a legal claim used to recover personal property wrongfully withheld by another party despite your rightful ownership. This action seeks the return of an item rather than monetary compensation, distinguishing it from other property disputes. Explore the full article to understand how detinue can protect your rights and the steps involved in making a claim.
Table of Comparison
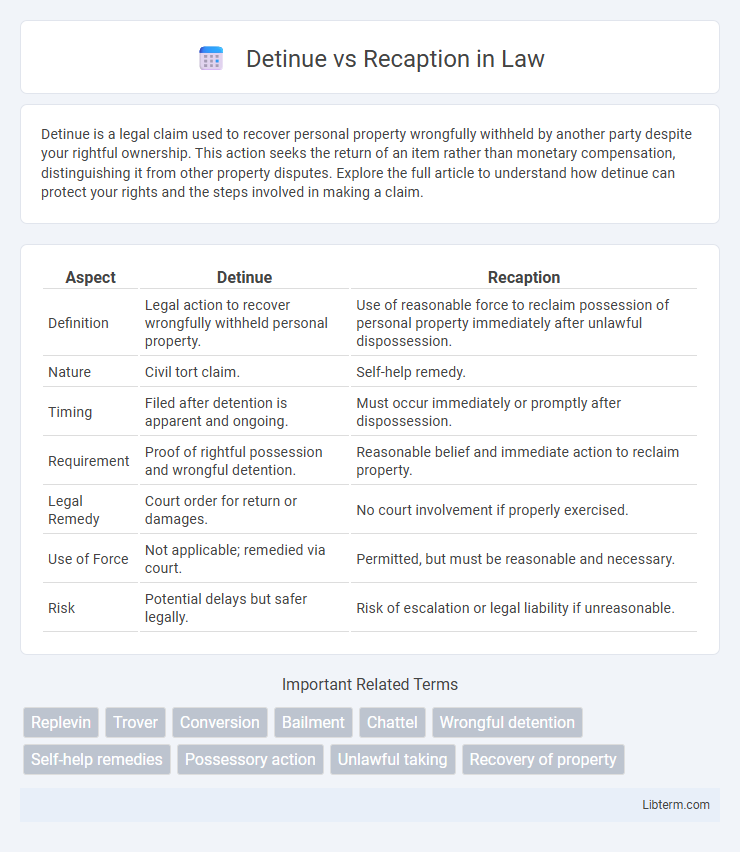
| Aspect | Detinue | Recaption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action to recover wrongfully withheld personal property. | Use of reasonable force to reclaim possession of personal property immediately after unlawful dispossession. |
| Nature | Civil tort claim. | Self-help remedy. |
| Timing | Filed after detention is apparent and ongoing. | Must occur immediately or promptly after dispossession. |
| Requirement | Proof of rightful possession and wrongful detention. | Reasonable belief and immediate action to reclaim property. |
| Legal Remedy | Court order for return or damages. | No court involvement if properly exercised. |
| Use of Force | Not applicable; remedied via court. | Permitted, but must be reasonable and necessary. |
| Risk | Potential delays but safer legally. | Risk of escalation or legal liability if unreasonable. |
Introduction to Detinue and Recaption
Detinue is a common law action used to recover personal property wrongfully detained by another, emphasizing the rightful owner's inherent right to possession rather than ownership disputes. Recaption, historically rooted in feudal law, allows the immediate repossession of goods taken unlawfully, often without formal legal proceedings, as a self-help remedy. Understanding the distinctions between detinue and recaption clarifies the legal processes involved in reclaiming unlawfully withheld possessions.
Legal Definitions: Detinue Explained
Detinue is a common law tort that involves the wrongful detention of someone else's personal property, demanding the return of the specific item rather than monetary compensation. Legal definitions of detinue emphasize the plaintiff's right to immediate possession and the defendant's unlawful retention or refusal to deliver the chattel upon demand. Unlike recaption, which concerns the peaceful retrieval of goods taken wrongfully, detinue requires a legal action to recover possession and addresses the unlawful detention after the initial possession has been transferred.
Legal Definitions: Recaption Explained
Recaption refers to the legal doctrine allowing a person to reclaim goods wrongfully taken or held by another, often seen as a defense in trespass cases. Unlike detinue, which seeks the recovery of specific personal property through a civil action demanding return or compensation for wrongful detention, recaption emphasizes the immediate recovery or repossession of goods taken unlawfully. The key legal distinction lies in recaption's basis on the right to reclaim possession directly, without resorting to a formal lawsuit for damages or return.
Historical Evolution of Detinue and Recaption
Detinue originated in medieval English common law as a remedy for wrongful detention of personal property, emphasizing the return of specific goods rather than monetary compensation. Recaption evolved from Anglo-Saxon legal practices, allowing a person to reclaim goods taken unlawfully without a formal court process, often by the original possessor's immediate retrieval. The historical evolution of detinue and recaption reflects the transition from self-help remedies to more structured legal procedures in property law.
Key Differences Between Detinue and Recaption
Detinue involves the unlawful retention of goods after rightful possession has been transferred, whereas recaption pertains to the lawful reclaiming of goods that were taken unlawfully. Detinue requires proof of original rightful possession and continuous demand for return, while recaption emphasizes immediate recovery of goods within a reasonable time from wrongful taking. The legal remedies differ as detinue leads to compensation or return through court action, whereas recaption allows for self-help recovery without breaching peace.
Legal Procedures in Detinue Cases
Detinue involves a legal action to recover personal property wrongfully detained by another party, requiring the plaintiff to prove rightful ownership and demand for return before filing. The legal procedure in detinue cases focuses on establishing possession and continuous refusal to relinquish the property, often entailing the issuance of summons, pleadings, and an eventual trial for recovery or damages. Recaption, by contrast, refers to the self-help remedy of retaking goods without judicial intervention, which is limited by law to specific circumstances to avoid breach of peace.
Legal Procedures in Recaption Cases
Recaption involves the lawful recovery of goods wrongfully taken, requiring precise adherence to legal procedures such as filing a claim under replevin statutes and providing proof of ownership or right to possession. Courts often mandate prompt action through a verified affidavit, notice to the opposing party, and sometimes a bond to secure potential damages during the recaption process. Failure to comply with these procedural requirements can result in dismissal or delay, emphasizing the importance of detailed legal knowledge in recaption cases.
Remedies and Outcomes for Detinue
Detinue is a legal remedy aimed at recovering specific personal property wrongfully withheld by another party, focusing on returning the exact item rather than monetary compensation. The primary outcomes for detinue include the court ordering the defendant to return the detained goods or, if the goods are unavailable, awarding damages equivalent to their value. This remedy ensures protection of possession rights and provides a direct resolution to possession disputes, differing from recaption where the focus is on reclaiming goods through self-help measures.
Remedies and Outcomes for Recaption
Recaption serves as a self-help remedy allowing a person to regain possession of goods wrongfully taken without court intervention, typically limited to peaceful and immediate recovery. Remedies for recaption emphasize restoring possession rather than awarding damages, ensuring that the possessor's rights are promptly enforced to prevent unlawful detention. Outcomes favor swift restitution of property, minimizing protracted legal disputes while maintaining the principle that possession should not be wrongfully withheld.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
Detinue and recaption are legal remedies primarily used in property disputes to recover possession of goods wrongfully withheld or taken. Detinue often applies when the plaintiff seeks the return of specific personal property unlawfully detained by the defendant, with case studies highlighting its use in recovering unique or irreplaceable items such as heirlooms or leased equipment. Recaption focuses on reclaiming property through self-help, usually requiring immediate repossession upon unlawful taking, illustrated in cases involving theft or unauthorized removal where swift recovery prevents further loss or damage.
Detinue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com