An executive plays a crucial role in driving strategic decisions and managing organizational performance to achieve business goals. Effective leadership, communication skills, and the ability to inspire teams are essential traits for success in executive positions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how you can excel in executive roles and advance your career.
Table of Comparison
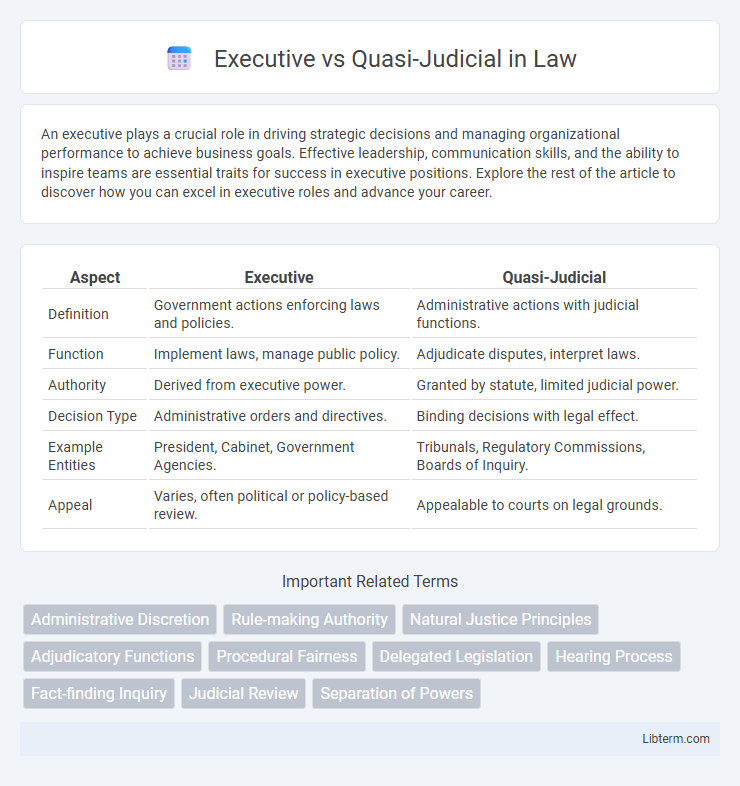
| Aspect | Executive | Quasi-Judicial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government actions enforcing laws and policies. | Administrative actions with judicial functions. |
| Function | Implement laws, manage public policy. | Adjudicate disputes, interpret laws. |
| Authority | Derived from executive power. | Granted by statute, limited judicial power. |
| Decision Type | Administrative orders and directives. | Binding decisions with legal effect. |
| Example Entities | President, Cabinet, Government Agencies. | Tribunals, Regulatory Commissions, Boards of Inquiry. |
| Appeal | Varies, often political or policy-based review. | Appealable to courts on legal grounds. |
Introduction to Executive and Quasi-Judicial Authorities
Executive authorities implement and enforce laws through administrative agencies, carrying out government policies in sectors such as health, education, and public safety. Quasi-judicial authorities possess decision-making powers similar to courts, resolving disputes and interpreting regulations within specialized areas like labor boards or zoning commissions. Understanding the distinct roles of executive and quasi-judicial bodies is crucial for comprehending government functions and administrative law frameworks.
Defining Executive Functions
Executive functions involve the implementation and enforcement of laws through administrative agencies, focusing on policy-making, regulation, and service delivery. These functions are distinct from quasi-judicial roles, which require adjudicating disputes and making decisions based on legal evidence and procedures. The executive branch exercises its authority primarily by managing government operations and ensuring compliance with legislative mandates.
Understanding Quasi-Judicial Roles
Quasi-judicial roles involve administrative or executive agencies performing functions similar to courts, such as making decisions on disputes, interpreting regulations, and applying legal standards. These roles require adherence to due process, including hearings, evidence evaluation, and impartial decision-making, bridging the gap between purely administrative actions and judicial proceedings. Understanding quasi-judicial functions is essential for recognizing how non-judicial bodies exercise legal authority while maintaining fairness and accountability.
Key Differences Between Executive and Quasi-Judicial Bodies
Executive bodies implement laws and policies, focusing on administrative functions and decision-making within government agencies. Quasi-judicial bodies possess the authority to interpret laws, conduct hearings, and issue rulings or orders similar to courts, particularly in regulatory or disciplinary matters. Key differences include their scope of authority, procedural formalities, and the nature of decisions made, with executive bodies emphasizing administration and quasi-judicial bodies ensuring due process and legal adjudication.
Legal Framework Governing Both Authorities
The legal framework governing executive authorities is primarily based on administrative law, which grants these bodies the power to enforce laws, implement policies, and oversee public administration. Quasi-judicial authorities operate under a distinct legal framework that combines elements of judicial procedure and administrative oversight, enabling them to adjudicate disputes, issue rulings, and enforce compliance within specific sectors. Statutes, regulations, and enabling acts define the scope, powers, and procedural safeguards guiding both executive and quasi-judicial bodies to ensure legality, fairness, and accountability in their functions.
Powers and Limitations of Executive Agencies
Executive agencies possess broad administrative powers to enforce laws, implement policies, and manage public programs, often with direct control over regulatory actions and day-to-day operations. Their limitations include restrictions on adjudicatory functions, as they generally lack the authority to conduct formal hearings or issue binding legal judgments, which are reserved for quasi-judicial bodies. Quasi-judicial agencies, by contrast, exercise limited adjudicative powers allowing them to resolve disputes and impose penalties within their jurisdiction, subject to procedural due process and judicial review.
Powers and Scope of Quasi-Judicial Bodies
Quasi-judicial bodies possess the authority to adjudicate disputes, interpret laws, and make binding decisions within a limited jurisdiction, bridging the gap between administrative agencies and courts. Their powers include conducting hearings, examining evidence, and rendering judgments that have legal consequences, often subject to judicial review to ensure fairness and legality. Unlike executive bodies that primarily enforce laws, quasi-judicial agencies operate with procedural safeguards similar to courts, enabling them to resolve conflicts in specialized areas such as labor, taxation, and consumer protection.
Decision-Making Process: Executive vs Quasi-Judicial
The decision-making process in executive functions revolves around policy implementation and administrative discretion, often guided by legislative frameworks but without strict procedural formalities. In contrast, quasi-judicial decision-making involves formal procedures, evidence evaluation, and impartial adjudication similar to courts, ensuring fairness and due process. Executive decisions emphasize flexibility and efficiency, whereas quasi-judicial decisions prioritize legal correctness and transparency.
Impact on Administrative Justice and Governance
Executive actions directly influence administrative justice by implementing policies and decisions that shape governance frameworks, often emphasizing efficiency and policy goals. Quasi-judicial bodies ensure administrative justice by providing fair hearings and impartial decisions, reinforcing accountability and legal compliance within governance. The balance between executive discretion and quasi-judicial oversight enhances transparency, protects rights, and upholds the rule of law in administrative governance.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Executive and Quasi-Judicial Mechanisms
Choosing between executive and quasi-judicial mechanisms depends on the nature of the issue and the desired outcome. Executive actions offer flexibility and swift decision-making, ideal for administrative tasks and policy enforcement, while quasi-judicial processes provide formal procedures and legal safeguards necessary for disputes requiring impartial adjudication. Careful evaluation of the context ensures the selection of the mechanism that best balances efficiency, fairness, and legal authority.
Executive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com