Incorporate strategies that enhance productivity and foster collaboration within your team to achieve better results. Leveraging modern tools and clear communication channels can significantly improve efficiency. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical tips for successful incorporation in your projects.
Table of Comparison
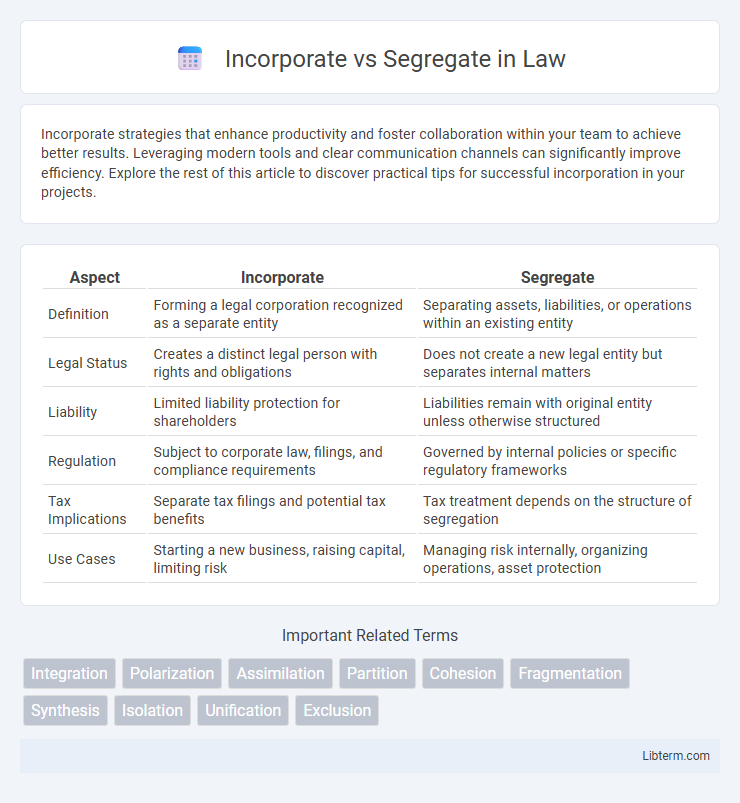
| Aspect | Incorporate | Segregate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forming a legal corporation recognized as a separate entity | Separating assets, liabilities, or operations within an existing entity |
| Legal Status | Creates a distinct legal person with rights and obligations | Does not create a new legal entity but separates internal matters |
| Liability | Limited liability protection for shareholders | Liabilities remain with original entity unless otherwise structured |
| Regulation | Subject to corporate law, filings, and compliance requirements | Governed by internal policies or specific regulatory frameworks |
| Tax Implications | Separate tax filings and potential tax benefits | Tax treatment depends on the structure of segregation |
| Use Cases | Starting a new business, raising capital, limiting risk | Managing risk internally, organizing operations, asset protection |
Understanding Incorporate and Segregate: Key Definitions
Incorporate means combining or blending distinct elements into a unified whole, enhancing integration and synergy within systems or organizations. Segregate refers to separating or isolating components based on specific criteria such as function, category, or characteristics to maintain clarity and organization. Understanding these definitions allows businesses to strategically manage resources, optimize workflows, and improve operational efficiency through either integration or separation.
Historical Perspective: How Incorporation and Segregation Emerged
In the historical context, incorporation emerged as a strategy to integrate diverse populations and expanding urban areas into a unified administrative framework, fostering political cohesion and economic development. Segregation arose from social, economic, and legal policies aimed at separating communities based on race, ethnicity, or class, often institutionalized through laws and zoning practices. The contrasting emergence of incorporation and segregation reflects shifting power dynamics and ideologies influencing urban planning and social structures over time.
Core Differences Between Incorporate and Segregate
Incorporate refers to combining or integrating elements into a single unified whole, while segregate means to separate or set apart distinct components based on differences or criteria. The core difference lies in the intent: incorporation aims for inclusion and cohesion, whereas segregation emphasizes division and isolation. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in contexts such as organizational management, data handling, and social dynamics.
Benefits of Incorporating Systems or Groups
Incorporating systems or groups enhances collaboration, promotes resource sharing, and drives innovation by unifying diverse expertise and perspectives. Integrated systems improve efficiency through streamlined processes and reduced redundancies, leading to cost savings and faster decision-making. Incorporation also fosters a cohesive organizational culture, increasing employee engagement and adaptability in dynamic environments.
Advantages and Limitations of Segregation
Segregation in business offers advantages such as enhanced risk management by isolating liabilities and clearer financial tracking for separate units, which simplifies regulatory compliance. Limitations of segregation include increased administrative complexity and potentially higher operational costs due to duplicated resources and management structures. This approach may also lead to reduced synergy and communication challenges between segregated entities, impacting overall efficiency.
Sector Applications: Incorporate vs Segregate in Business
In business sectors such as manufacturing and IT, incorporating diverse systems and processes enhances operational efficiency, enabling seamless integration of technologies and resources. Segregation is vital in finance and healthcare industries to maintain data privacy, comply with regulatory standards like GDPR and HIPAA, and reduce risks of security breaches. This strategic choice impacts overall organizational agility, cost management, and compliance adherence across various business verticals.
Educational Context: Inclusive vs Separate Approaches
In educational contexts, incorporating students with diverse needs into mainstream classrooms promotes inclusivity, social integration, and equal access to learning resources. Segregating learners in separate special education settings can provide tailored instruction but may limit social interactions and reinforce stigmatization. Research on inclusive education highlights improved academic outcomes and social skills for students in integrated environments compared to segregated settings.
Social Impacts: Incorporation vs Segregation in Communities
Incorporation fosters social cohesion by integrating diverse groups into unified communities, enhancing access to shared resources and collective decision-making. Segregation often leads to social isolation, economic disparities, and limited opportunities, perpetuating systemic inequalities. Communities that emphasize incorporation experience stronger social networks and improved quality of life for all residents.
Legal and Policy Considerations
In legal and policy contexts, incorporating diverse elements promotes inclusion and compliance with anti-discrimination laws, whereas segregation can lead to violations of equal opportunity statutes and foster systemic inequities. Policies favoring incorporation align with international human rights frameworks and aim to create unified, equitable environments, minimizing legal risks associated with segregationist practices. Legal precedents often emphasize the benefits of integrated approaches, highlighting the importance of cohesive policy design in reducing conflict and promoting social cohesion.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between incorporate and segregate strategies depends on factors such as data sensitivity, compliance requirements, and operational efficiency. Incorporation enables unified management and streamlined processes, ideal for organizations prioritizing integration and real-time access. Segregation enhances security and reduces risk by isolating data or functions, preferred in highly regulated industries or when protecting critical assets.
Incorporate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com