Arbitration offers a private and efficient alternative to traditional court litigation by resolving disputes through a neutral third party. It often results in faster decisions and reduced legal costs, making it an attractive option for businesses and individuals alike. Explore the rest of the article to understand how arbitration can benefit your specific situation.
Table of Comparison
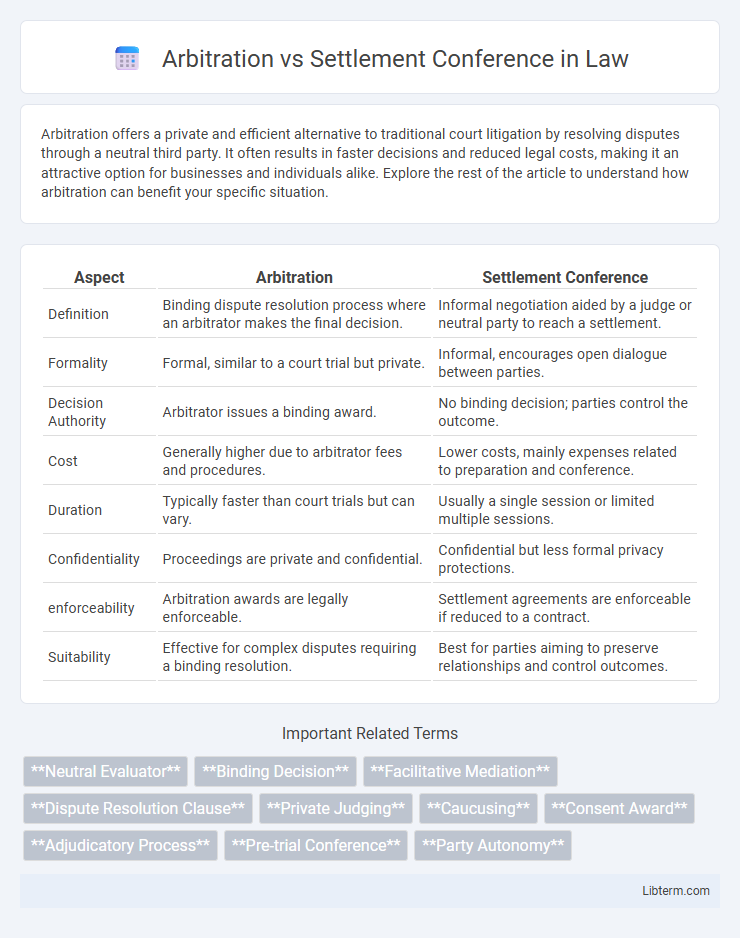
| Aspect | Arbitration | Settlement Conference |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Binding dispute resolution process where an arbitrator makes the final decision. | Informal negotiation aided by a judge or neutral party to reach a settlement. |
| Formality | Formal, similar to a court trial but private. | Informal, encourages open dialogue between parties. |
| Decision Authority | Arbitrator issues a binding award. | No binding decision; parties control the outcome. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to arbitrator fees and procedures. | Lower costs, mainly expenses related to preparation and conference. |
| Duration | Typically faster than court trials but can vary. | Usually a single session or limited multiple sessions. |
| Confidentiality | Proceedings are private and confidential. | Confidential but less formal privacy protections. |
| enforceability | Arbitration awards are legally enforceable. | Settlement agreements are enforceable if reduced to a contract. |
| Suitability | Effective for complex disputes requiring a binding resolution. | Best for parties aiming to preserve relationships and control outcomes. |
Introduction to Arbitration and Settlement Conference
Arbitration is a private dispute resolution process where a neutral arbitrator renders a binding decision after reviewing evidence and hearing arguments, often used to avoid lengthy court trials. A Settlement Conference involves the parties and a judge or neutral facilitator attempting to negotiate a mutually agreeable resolution before trial, promoting dispute resolution without a formal judgment. Both methods aim to reduce litigation costs and time while offering alternative paths to conflict resolution.
Definition and Key Differences
Arbitration is a formal dispute resolution process where an impartial arbitrator renders a binding decision after evaluating evidence and legal arguments. A settlement conference is an informal negotiation session overseen by a judge or neutral facilitator aiming to help parties agree on a voluntary resolution without a binding outcome. Key differences include arbitration's binding nature and evidentiary procedures versus the settlement conference's focus on collaborative negotiation and non-binding agreement.
Process Overview: Arbitration
Arbitration involves a formal process where parties present evidence and arguments before a neutral arbitrator who renders a binding decision, resembling a court trial but typically less formal and faster. The arbitrator is selected by the parties or appointing authority, and the process includes discovery, witness testimonies, and submission of legal briefs. Arbitration agreements often mandate this method to resolve disputes confidentially and conclusively, with limited grounds for appeal.
Process Overview: Settlement Conference
A settlement conference is a structured negotiation facilitated by a neutral third party, often a judge or experienced attorney, aimed at resolving disputes without trial. The process involves confidential discussions where parties exchange information and explore settlement options to reach a mutually agreeable resolution. This approach reduces litigation costs and time by encouraging cooperation and compromise early in the dispute resolution timeline.
Role of the Neutral Party
In arbitration, the neutral party acts as a private judge, making binding decisions after evaluating evidence and legal arguments presented by both sides. During a settlement conference, the neutral party serves as a facilitator, guiding discussions to help the disputing parties reach a voluntary agreement without imposing a decision. The neutral's role in arbitration is adjudicative, while in a settlement conference, it is conciliatory and focused on negotiation.
Confidentiality and Privacy Concerns
Arbitration sessions are typically private and confidential, with strict rules preventing the disclosure of proceedings, protecting sensitive information from public exposure. Settlement conferences also emphasize confidentiality, but the level of privacy can vary depending on jurisdiction and whether parties agree to specific confidentiality terms. Both processes aim to safeguard parties' privacy, yet arbitration's formal settings often provide stronger legal protections against external disclosure.
Timeframe and Efficiency
Arbitration typically resolves disputes faster than traditional court trials, with hearings scheduled within weeks to a few months, making it a time-efficient alternative. Settlement conferences are generally even quicker, often occurring within weeks of case filing, facilitating early resolution by encouraging negotiation and mediation. Both processes aim to reduce litigation time, but settlement conferences prioritize collaborative outcomes, while arbitration offers a binding decision within a defined timeframe.
Costs and Expenses Comparison
Arbitration typically involves higher costs due to arbitrator fees, administrative expenses, and potential charges for hearing facilities, often exceeding several thousand dollars. Settlement conferences are generally less expensive as they usually require only a mediator or judge's time with minimal administrative fees, reducing overall expenses significantly. Choosing a settlement conference can lead to substantial cost savings compared to arbitration, especially in cases with straightforward disputes or limited financial stakes.
Enforceability of Outcomes
Arbitration outcomes result in a legally binding award enforceable in courts, providing a definitive resolution to disputes. In contrast, settlement conference outcomes depend on mutual agreement, and while settlements are generally enforceable as contracts, the process itself lacks binding authority. The enforceability of arbitration awards is governed by statutes like the Federal Arbitration Act, whereas settlement agreements require voluntary compliance or court approval for enforcement.
Choosing the Right Dispute Resolution Method
Choosing the right dispute resolution method depends on factors like case complexity, confidentiality needs, and desired formality. Arbitration offers a binding decision from an impartial arbitrator, ideal for parties seeking a definitive outcome without court involvement. Settlement conferences encourage negotiation and mutual agreement, providing a flexible, cost-effective way to resolve disputes before trial.
Arbitration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com