An agreement is a legally binding arrangement between two or more parties outlining their rights, responsibilities, and obligations. Understanding the key elements, such as offer, acceptance, and consideration, ensures that your contracts are enforceable and protect your interests. Continue reading to explore the essential components and types of agreements you need to know.
Table of Comparison
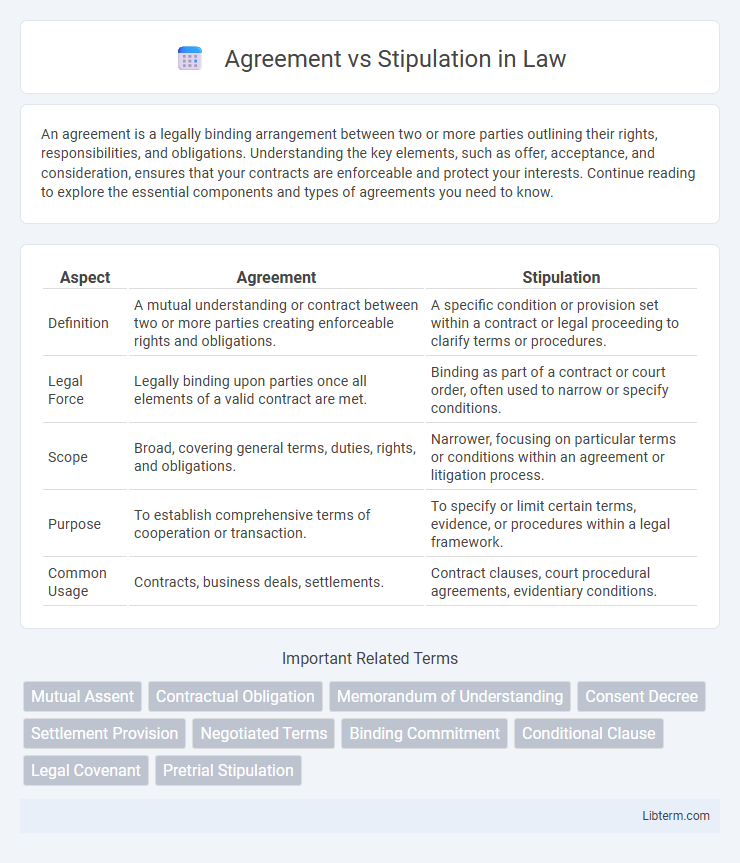
| Aspect | Agreement | Stipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A mutual understanding or contract between two or more parties creating enforceable rights and obligations. | A specific condition or provision set within a contract or legal proceeding to clarify terms or procedures. |
| Legal Force | Legally binding upon parties once all elements of a valid contract are met. | Binding as part of a contract or court order, often used to narrow or specify conditions. |
| Scope | Broad, covering general terms, duties, rights, and obligations. | Narrower, focusing on particular terms or conditions within an agreement or litigation process. |
| Purpose | To establish comprehensive terms of cooperation or transaction. | To specify or limit certain terms, evidence, or procedures within a legal framework. |
| Common Usage | Contracts, business deals, settlements. | Contract clauses, court procedural agreements, evidentiary conditions. |
Understanding Agreement: Definition and Key Elements
An agreement is a mutual understanding between two or more parties outlining their rights and obligations, often characterized by essential elements such as offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual intent to be legally bound. It forms the foundation of contract law, requiring clarity, legality, and the capacity of parties involved. Understanding these key elements ensures the agreement is enforceable and reflects the true intention of the parties.
What Is a Stipulation? Core Concepts Explained
A stipulation is a formal agreement between parties in a legal case that outlines specific facts or procedures agreed upon to avoid dispute during trial. It streamlines court proceedings by establishing mutually accepted terms, reducing the need for proof or argument on those points. Unlike a general agreement, a stipulation is binding within the context of litigation and often recorded in court documents to ensure clarity and enforceability.
Legal Distinctions: Agreement vs Stipulation
An agreement is a mutual understanding between two or more parties about their rights and obligations, which may or may not be legally binding depending on its nature and intent. A stipulation is a specific type of agreement primarily used in legal proceedings where parties voluntarily declare certain facts or conditions to avoid proving them at trial. Unlike general agreements, stipulations have binding legal effect within the context of litigation and are often incorporated into court records or judgments to streamline the legal process.
Types of Agreements in Law
Types of agreements in law encompass contracts, bilateral and unilateral agreements, express and implied agreements, and executed or executory agreements. Stipulations are specific conditions or terms agreed upon within a broader contract or legal proceeding, often narrowing the scope or details of the agreement. Understanding the distinctions and classifications helps in drafting precise legal documents and ensuring enforceability under relevant jurisdictional statutes.
Types of Stipulations and Their Uses
Stipulations, unlike general agreements, are specific provisions or conditions agreed upon during legal proceedings to simplify issues and expedite the process. Common types of stipulations include stipulations of fact, where parties agree on certain facts to avoid proving them in court, and stipulations of evidence, which allow the admission of documents or testimony without formal introduction. These stipulations are widely used in civil litigation, criminal cases, and administrative hearings to streamline trial preparation and reduce litigation costs.
Enforceability: Agreements Compared to Stipulations
Agreements generally require offer, acceptance, and consideration to be enforceable, reflecting mutual obligations between parties. Stipulations are specific agreements made within legal proceedings, often accepted by the court without formal trial evidence and thus carry enforceability based on procedural rules. Courts typically enforce stipulations strictly since they streamline litigation and reduce disputes, whereas agreements may face challenges if lacking essential contractual elements.
Common Scenarios: When to Use Each Term
Agreements are typically used in broader contexts involving mutual consent between two or more parties, such as business contracts, partnerships, or service arrangements where terms are negotiated and documented. Stipulations arise more frequently in legal or formal settings, often specifying precise conditions or requirements within court cases, settlements, or regulatory compliance. Choosing between agreement and stipulation depends on whether the context involves general mutual understanding or legally binding, narrowly defined conditions.
Real-World Examples: Agreement vs Stipulation
In contract law, an agreement represents a mutual understanding between parties on their respective rights and obligations, often exemplified by business contracts or employment terms. Stipulations typically appear in legal proceedings, where parties agree on specific facts or conditions to streamline the trial process, such as stipulating the authenticity of documents. Real-world examples include a rental lease agreement outlining tenant responsibilities, contrasted with court stipulations where both sides accept certain evidence without dispute.
How Courts Interpret Agreements and Stipulations
Courts interpret agreements by examining the explicit terms and the parties' intent, emphasizing clear, mutual consent documented within the contract. Stipulations are viewed as formal concessions or admissions made during litigation, binding the parties to specific facts or procedural matters without the need for further proof. Judicial interpretation prioritizes the precise language and context of agreements and stipulations to ensure enforceability and fairness in legal proceedings.
Choosing the Right Legal Tool: Agreement or Stipulation?
Choosing the right legal tool between an agreement and a stipulation depends on the context and enforceability needed. Agreements are broader contracts involving mutual obligations and rights between parties, commonly used in business and personal arrangements. Stipulations are specific legal conditions or concessions, often used in litigation or court proceedings to streamline issues and avoid disputes.
Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com