Foreclosure occurs when a homeowner fails to make mortgage payments, leading the lender to seize the property to recover the loan balance. This process can result in significant financial and emotional stress, often affecting credit scores and future borrowing capacity. Explore the full article to understand foreclosure causes, consequences, and prevention strategies tailored to protect your home.
Table of Comparison
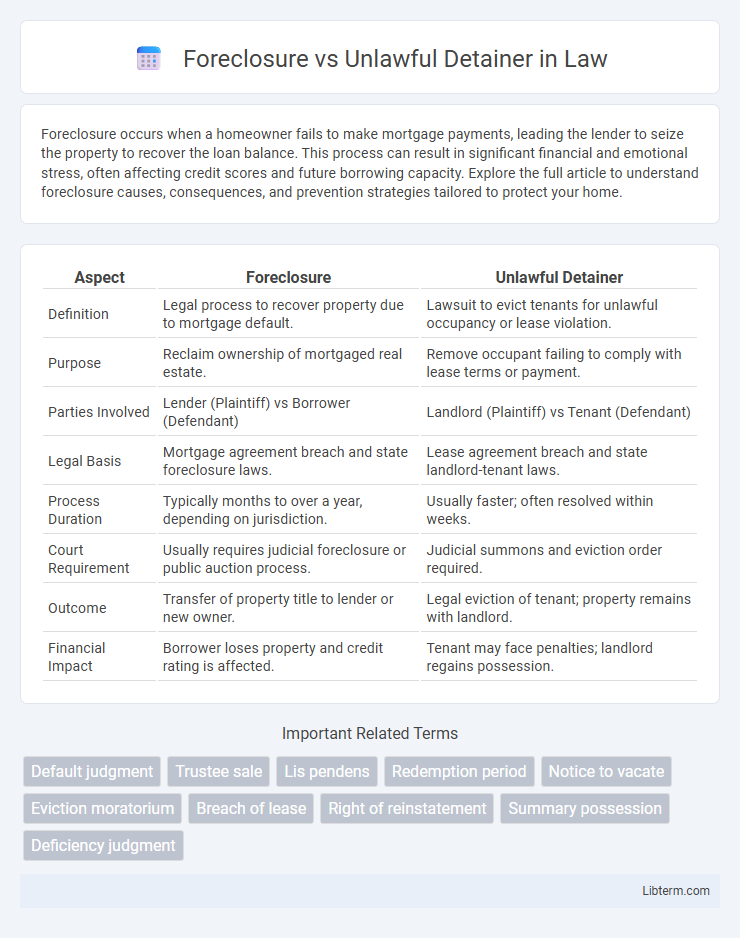
| Aspect | Foreclosure | Unlawful Detainer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process to recover property due to mortgage default. | Lawsuit to evict tenants for unlawful occupancy or lease violation. |
| Purpose | Reclaim ownership of mortgaged real estate. | Remove occupant failing to comply with lease terms or payment. |
| Parties Involved | Lender (Plaintiff) vs Borrower (Defendant) | Landlord (Plaintiff) vs Tenant (Defendant) |
| Legal Basis | Mortgage agreement breach and state foreclosure laws. | Lease agreement breach and state landlord-tenant laws. |
| Process Duration | Typically months to over a year, depending on jurisdiction. | Usually faster; often resolved within weeks. |
| Court Requirement | Usually requires judicial foreclosure or public auction process. | Judicial summons and eviction order required. |
| Outcome | Transfer of property title to lender or new owner. | Legal eviction of tenant; property remains with landlord. |
| Financial Impact | Borrower loses property and credit rating is affected. | Tenant may face penalties; landlord regains possession. |
Understanding Foreclosure: Definition and Process
Foreclosure is a legal process where a lender attempts to recover the balance of a loan from a borrower who has defaulted on mortgage payments by forcing the sale of the property used as collateral. This process begins with a notice of default, followed by a period for the borrower to cure the default or negotiate alternatives such as loan modification. If the borrower fails to resolve the debt, the property is sold through a public auction to satisfy the outstanding mortgage balance.
What is an Unlawful Detainer?
An unlawful detainer is a legal action initiated by a landlord to regain possession of a property when a tenant refuses to vacate after the lease has expired or after eviction has been lawfully ordered. This process is separate from foreclosure, which involves the lender attempting to reclaim ownership due to mortgage default. Unlawful detainer specifically addresses tenant eviction, focusing on leading to a court order for removal from the premises.
Key Differences Between Foreclosure and Unlawful Detainer
Foreclosure is a legal process where a lender seeks to recover the balance owed on a defaulted loan by forcing the sale of the debtor's property, while an unlawful detainer is a lawsuit filed by a landlord to evict a tenant who refuses to vacate the rental property. Foreclosure primarily addresses the mortgage holder's rights and ownership transfer, whereas unlawful detainer focuses on tenants' possession and eviction procedures. The timelines, legal grounds, and remedies differ significantly: foreclosure involves complex lien priority and public auction, whereas unlawful detainer deals with possession and rent issues in tenant-landlord disputes.
Legal Grounds for Foreclosure
Legal grounds for foreclosure primarily arise when a borrower defaults on their mortgage payments, violating the terms of the loan agreement. Foreclosure processes vary by jurisdiction but generally require proving the borrower's failure to fulfill payment obligations, often supported by a recorded deed of trust or mortgage lien. Unlike unlawful detainer actions, which address possession disputes post-foreclosure, foreclosure litigation focuses on the enforceability of the lender's security interest in the property.
Legal Grounds for Unlawful Detainer
Legal grounds for unlawful detainer primarily involve the tenant's failure to comply with the terms of the lease agreement, such as nonpayment of rent, violation of property rules, or expiration of the lease term without renewal. Unlike foreclosure, which involves a lender's legal process to repossess property due to mortgage default, unlawful detainer actions focus on regaining possession from tenants who refuse to vacate after lease termination or breach. Courts require landlords to demonstrate valid notice and specific legal breaches to succeed in unlawful detainer claims.
Timeline Comparison: Foreclosure vs Unlawful Detainer
Foreclosure timelines typically span several months to over a year, starting with the notice of default, followed by the auction or trustee sale and potential redemption period. Unlawful detainer cases move much faster, often resolved within 30 to 45 days, focusing on regaining possession after eviction notices are served. Understanding these timelines helps homeowners and landlords strategize responses to financial distress or tenant disputes effectively.
Rights of Homeowners and Tenants in Each Process
Homeowners facing foreclosure retain the right to receive proper legal notice and an opportunity to cure the default before the lender initiates the sale of the property. Tenants in unlawful detainer proceedings have the right to a court hearing where they can present defenses before eviction occurs. Both processes require adherence to strict legal timelines to protect homeowners' and tenants' rights under state and federal laws.
Impact on Credit and Future Housing Options
Foreclosure significantly damages credit scores, often dropping them by 100 to 160 points, which can make obtaining new loans or mortgages difficult for up to seven years. Unlawful detainer actions, while they may not directly affect credit scores, can result in eviction records that landlords review during rental applications, limiting future housing opportunities. Both situations pose severe risks to financial stability and housing prospects, emphasizing the importance of addressing these legal issues promptly.
Defenses Against Foreclosure and Unlawful Detainer
Defenses against foreclosure include proving lender misconduct, such as failure to follow proper notice requirements or improper assignment of the mortgage. In unlawful detainer actions, defendants can argue procedural errors, lack of proper service, or show that the foreclosure was invalid to challenge eviction. Understanding state-specific laws on foreclosure and eviction timelines is crucial for mounting effective defenses.
How to Avoid Foreclosure and Unlawful Detainer
To avoid foreclosure and unlawful detainer, homeowners should prioritize proactive communication with lenders to negotiate loan modifications, forbearance plans, or repayment schedules. Engaging legal counsel early can provide valuable guidance on rights and options, including bankruptcy or mediation programs designed to prevent eviction. Maintaining documentation of all communications and payments strengthens defense against unlawful detainer actions and supports a more favorable resolution.
Foreclosure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com