Prolepsis, a rhetorical device, involves anticipating and addressing potential objections or future events within a narrative or argument, enhancing persuasive impact. It creates a sense of immediacy by projecting future outcomes into the present moment, enriching storytelling and communication. Discover how mastering prolepsis can elevate your writing and speaking skills throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
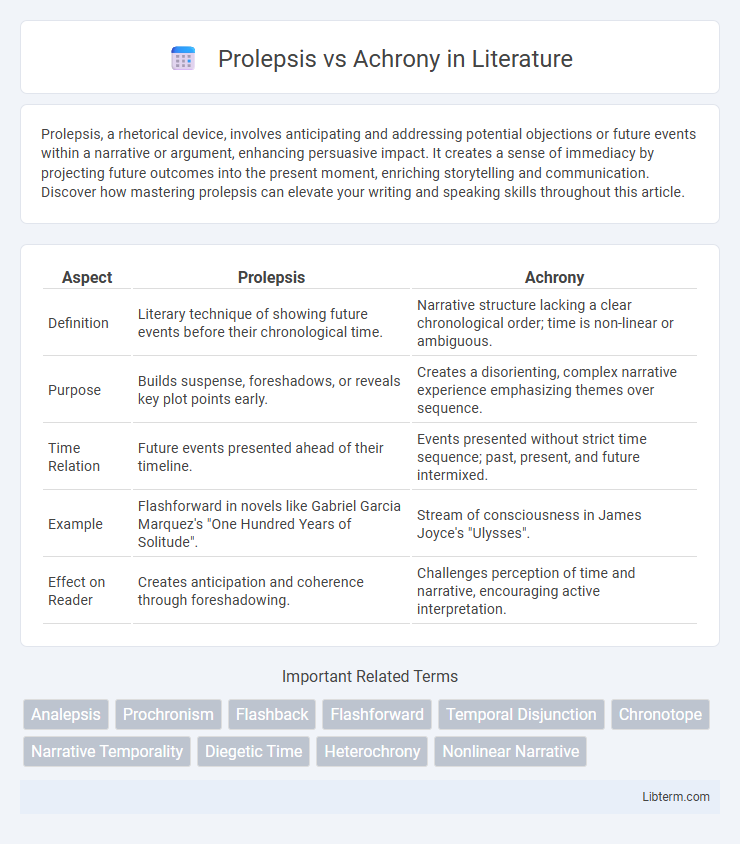
| Aspect | Prolepsis | Achrony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary technique of showing future events before their chronological time. | Narrative structure lacking a clear chronological order; time is non-linear or ambiguous. |
| Purpose | Builds suspense, foreshadows, or reveals key plot points early. | Creates a disorienting, complex narrative experience emphasizing themes over sequence. |
| Time Relation | Future events presented ahead of their timeline. | Events presented without strict time sequence; past, present, and future intermixed. |
| Example | Flashforward in novels like Gabriel Garcia Marquez's "One Hundred Years of Solitude". | Stream of consciousness in James Joyce's "Ulysses". |
| Effect on Reader | Creates anticipation and coherence through foreshadowing. | Challenges perception of time and narrative, encouraging active interpretation. |
Introduction to Prolepsis and Achrony
Prolepsis refers to a narrative technique where future events are anticipated or depicted ahead of their chronological occurrence, creating a forward-looking temporal shift in storytelling. Achrony, by contrast, involves the disruption or suspension of linear time within a narrative, presenting events outside the traditional chronological sequence without a clear temporal order. These concepts are essential in understanding non-linear narratives and temporal manipulation in literature and film.
Defining Prolepsis in Narrative Structures
Prolepsis in narrative structures refers to a literary technique where future events are presented out of chronological order, offering a glimpse ahead to enhance suspense or foreshadowing. It contrasts with achrony, which involves a non-linear timeline that disrupts the natural sequence of events without necessarily revealing future occurrences explicitly. Prolepsis effectively creates anticipation by incorporating flash-forwards that influence the reader's understanding of the plot's progression.
Understanding Achrony in Storytelling
Achrony in storytelling disrupts the chronological flow by presenting events out of their temporal order, creating a nonlinear narrative that invites deeper audience engagement and reflection. Unlike prolepsis, which specifically involves flash-forwards or future events, achrony encompasses a broader range of temporal displacements, including flashbacks, parallel timelines, and fragmented sequences. Understanding achrony enhances narrative complexity, allowing storytellers to manipulate time perception and enrich thematic exploration in literature, film, and other media.
Key Differences Between Prolepsis and Achrony
Prolepsis refers to the literary or rhetorical device where future events are anticipated or depicted ahead of their chronological occurrence, creating a forward-looking narrative effect. Achrony denotes the absence of chronological order in narrative structure, often presenting events without adhering to a linear timeline, emphasizing thematic or emotional connections instead. The key difference lies in prolepsis's focus on foreshadowing specific future moments, while achrony involves a broader non-linear approach to time representation within a text.
Historical Origins of Prolepsis and Achrony
Prolepsis, rooted in classical rhetoric and early Greek literature, originated as a technique to anticipate and respond to potential objections within arguments, enhancing persuasive communication. Achrony emerged later in literary theory, particularly within modern narratology, denoting non-linear temporal structures that break chronological sequence for thematic or psychological effect. The historical development of prolepsis highlights its role in ancient dialectics, while achrony reflects evolving narrative experimentation in contemporary storytelling.
Functions of Prolepsis in Literature
Prolepsis in literature serves to foreshadow future events, creating suspense and guiding reader expectations while enriching narrative complexity. It functions as a tool to reveal character motivations and thematic elements before their chronological occurrence, enhancing depth and engagement. By juxtaposing future and present moments, prolepsis enables authors to manipulate time perception, intensify emotional impact, and underscore causality within the plot.
Narrative Effects of Achrony
Achrony, characterized by the disruption of chronological order in narrative, enhances storytelling by creating suspense and engaging readers through fragmented time sequences. The narrative effects of achrony include heightened reader curiosity, prompting active interpretation and deepening emotional impact by revealing critical events out of temporal sequence. This technique contrasts with prolepsis, which specifically anticipates future events, whereas achrony broadly encompasses non-linear temporal manipulation to enrich narrative complexity.
Examples of Prolepsis and Achrony in Fiction
Prolepsis in fiction involves the portrayal of future events ahead of their chronological occurrence, such as the flashforward scenes in "Breaking Bad" that reveal Walter White's fate. Achrony disrupts linear time entirely, as seen in the novel "Slaughterhouse-Five" by Kurt Vonnegut, where the protagonist experiences moments out of chronological order. Both techniques enhance narrative complexity by manipulating temporal structure to influence reader perception and thematic depth.
Impact on Reader Interpretation
Prolepsis propels the narrative by revealing future events, intensifying suspense and shaping reader expectations through anticipation. Achrony disrupts chronological flow, encouraging readers to actively piece together the timeline, which enhances engagement and deepens comprehension. The interplay between these temporal techniques influences how readers interpret character motivations and plot developments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Technique
Selecting the appropriate narrative technique between prolepsis and achrony hinges on the intended impact and clarity of the storyline. Prolepsis, or flash-forward, effectively builds suspense by revealing future events, engaging readers with foreshadowing. Achrony, involving non-linear timelines, enhances thematic depth and character development but requires careful structuring to maintain coherence and reader engagement.
Prolepsis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com