A ballad is a narrative poem or song that tells a story, often focusing on themes of love, tragedy, or adventure. Its simple language, rhythmic structure, and repetition make it memorable and engaging. Discover how ballads have shaped literature and music by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
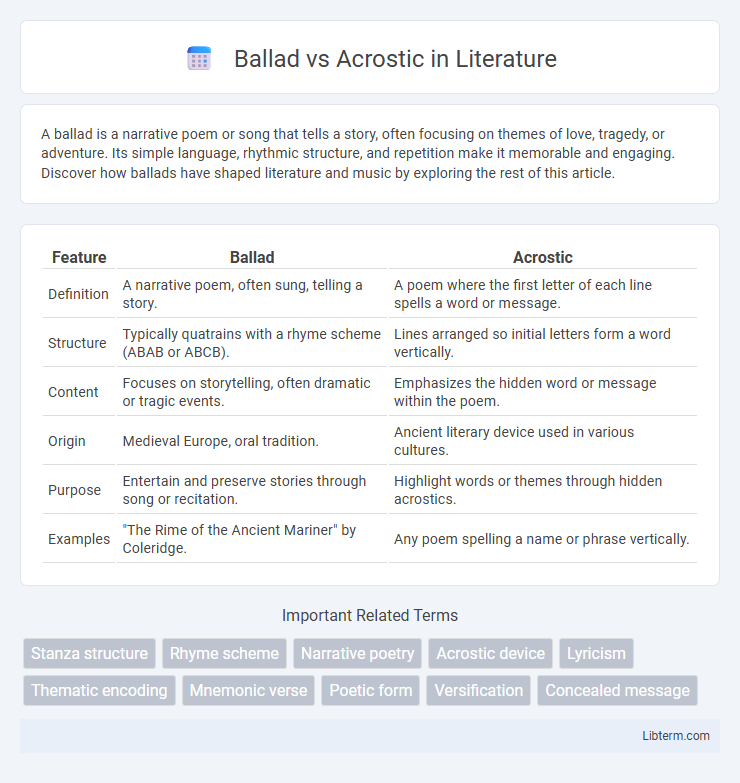
| Feature | Ballad | Acrostic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A narrative poem, often sung, telling a story. | A poem where the first letter of each line spells a word or message. |
| Structure | Typically quatrains with a rhyme scheme (ABAB or ABCB). | Lines arranged so initial letters form a word vertically. |
| Content | Focuses on storytelling, often dramatic or tragic events. | Emphasizes the hidden word or message within the poem. |
| Origin | Medieval Europe, oral tradition. | Ancient literary device used in various cultures. |
| Purpose | Entertain and preserve stories through song or recitation. | Highlight words or themes through hidden acrostics. |
| Examples | "The Rime of the Ancient Mariner" by Coleridge. | Any poem spelling a name or phrase vertically. |
Understanding Ballads: Definition and Origins
Ballads are narrative poems that traditionally recount stories of love, tragedy, or adventure, often composed in quatrains with a regular rhyme scheme and meter, originating from oral folk traditions in medieval Europe. Their roots trace back to medieval minstrel songs and balladry, evolving through centuries as a means of storytelling and cultural expression. The enduring popularity of ballads lies in their rhythmic structure and emotive language that facilitate memorization and communal sharing.
What is an Acrostic Poem?
An acrostic poem is a literary form where the first letter of each line spells out a word or message vertically, often related to the poem's theme. This structure emphasizes creativity in wordplay and can convey hidden meanings or personalize content. Unlike ballads, which focus on narrative storytelling with a specific rhyme and meter, acrostic poems prioritize the visual arrangement of letters to enhance semantic impact.
Structural Differences: Ballad vs Acrostic
Ballads feature a narrative structure with quatrains following an ABAB or ABCB rhyme scheme, often emphasizing rhythm and repetition to tell a story. Acrostics uniquely arrange the first letters of each line or stanza to spell out a word or message vertically, focusing on visual and thematic alignment rather than rhyme or meter. The structural difference lies in ballads prioritizing storytelling through consistent rhyme and meter, while acrostics prioritize hidden textual patterns embedded within the poem's layout.
Themes Commonly Explored in Ballads
Ballads commonly explore themes of love, tragedy, adventure, and heroism, often telling stories of emotional intensity and dramatic events. In contrast, acrostic poems focus on spelling out words or messages vertically, with thematic content driven by the chosen word rather than narrative depth. The emotional and narrative richness in ballads offers a distinct storytelling experience compared to the structured, letter-based format of acrostics.
Popular Themes in Acrostic Poetry
Popular themes in acrostic poetry often revolve around personal names, holidays, and motivational messages, making the form ideal for celebrations and reminders. Unlike ballads, which typically convey dramatic stories or tragic events using a narrative structure, acrostic poems emphasize creativity through wordplay and symbolic significance embedded in initial letters. This focus on thematic versatility allows acrostics to resonate in educational settings and occasions emphasizing individuality or values.
Rhyme Scheme and Meter: A Comparative Analysis
Ballads typically feature a consistent rhyme scheme such as ABAB or ABCB and maintain a regular meter, often iambic tetrameter or trimeter, to create a rhythmic and musical quality. Acrostic poems, however, do not adhere strictly to rhyme schemes or meter, as their primary focus lies in the initial letters of each line forming a word or message. This distinction highlights ballads' structured rhythmic patterns compared to the flexible and message-driven format of acrostic poetry.
Creativity and Purpose: Expressing Meaning
Ballads creatively narrate stories or emotions through structured verses and rhythmic patterns, emphasizing storytelling and emotional engagement. Acrostics prioritize purposeful expression by aligning the first letters of each line to spell words or messages, enhancing the thematic depth and memorability. Both forms channel creativity uniquely: ballads evoke vivid imagery and mood, while acrostics embed hidden meanings to enrich the overall impact.
Famous Examples of Ballads and Acrostics
Famous ballads include "The Rime of the Ancient Mariner" by Samuel Taylor Coleridge and "La Belle Dame sans Merci" by John Keats, both known for their narrative storytelling and lyrical rhythm. Notable acrostics feature works like Lewis Carroll's "A Boat Beneath a Sunny Sky," where the first letters of each line spell out a hidden message or name. These forms highlight the blend of literary creativity and structural ingenuity in poetry.
Writing Tips: Crafting Your Own Ballad
When crafting your own ballad, focus on narrative storytelling with a clear emotional arc, using quatrains and a consistent rhyme scheme like ABAB or ABCB to maintain rhythm and flow. Incorporate repetition and dialogue to enhance the oral tradition feel, emphasizing memorable characters and dramatic events. Unlike acrostics, which prioritize the hidden word or phrase, ballads demand vivid imagery and a strong sense of pace to engage readers through lyrical storytelling.
How to Write a Compelling Acrostic Poem
Writing a compelling acrostic poem involves selecting a meaningful word as the poem's spine, with each letter beginning a line that relates to the central theme. Emphasize vivid imagery and emotional language to create an engaging narrative within the constrained structure. Unlike ballads, which rely on rhyme and meter, acrostics prioritize clarity and creativity with word placement to deliver impactful messages or sentiments.
Ballad Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com