An eponym is a word derived from the name of a person, often reflecting their influence or association with a specific invention, discovery, or concept. Understanding eponyms can enhance your appreciation of language and history by revealing the stories behind common terms. Explore the full article to learn fascinating examples and the role eponyms play in everyday communication.
Table of Comparison
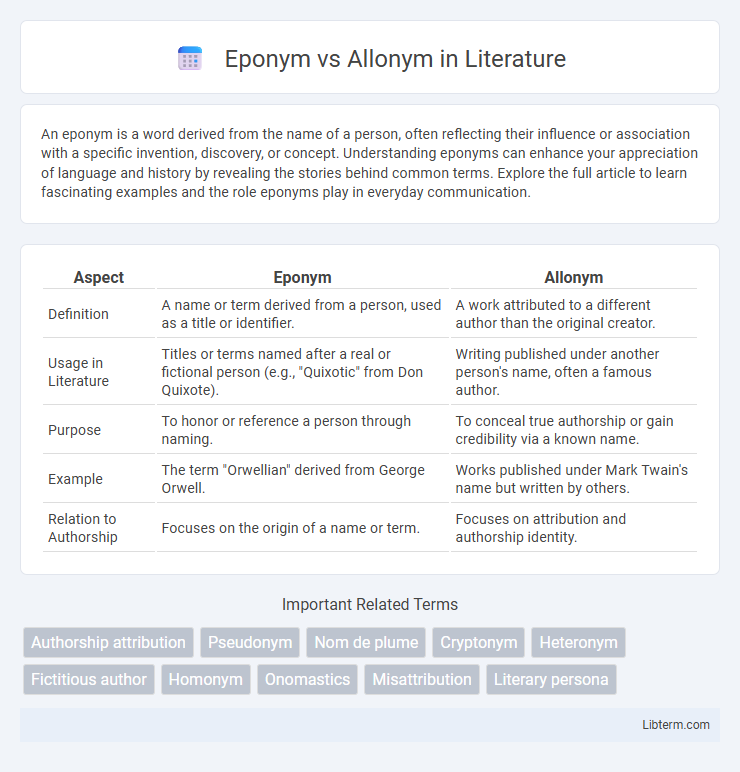
| Aspect | Eponym | Allonym |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A name or term derived from a person, used as a title or identifier. | A work attributed to a different author than the original creator. |
| Usage in Literature | Titles or terms named after a real or fictional person (e.g., "Quixotic" from Don Quixote). | Writing published under another person's name, often a famous author. |
| Purpose | To honor or reference a person through naming. | To conceal true authorship or gain credibility via a known name. |
| Example | The term "Orwellian" derived from George Orwell. | Works published under Mark Twain's name but written by others. |
| Relation to Authorship | Focuses on the origin of a name or term. | Focuses on attribution and authorship identity. |
Definition of Eponym
An eponym is a person whose name is given to a particular place, invention, discovery, or phenomenon, serving as a source for its designation. Unlike an allonym, which involves attributing a work to another person's name, an eponym specifically denotes the originator whose name becomes synonymous with the entity in question. Examples of eponyms include "Newton" for the unit of force and "Alzheimer" for the disease.
Definition of Allonym
An allonym is a type of pseudonym where a writer attributes their work to another real person, often a famous author, rather than using their own name or an invented one. Unlike an eponym, which is a name derived from a real person's name used to identify a discovery or invention, an allonym involves deliberate misattribution of authorship. Understanding allonyms is crucial in literary studies and authorship analysis, revealing dynamics of anonymity, influence, and intellectual property.
Key Differences Between Eponym and Allonym
Eponyms are terms derived from the name of a person or figure directly associated with the concept, invention, or discovery, such as "Alzheimer's disease" named after Alois Alzheimer. Allonyms, on the other hand, refer to works or ideas attributed to an author's name used as a pseudonym or another person's name, often for anonymity or stylistic reasons. The key difference lies in eponyms being actual names that honor originators, while allonyms involve the use of false or borrowed names for attribution.
Historical Origins of Eponyms
Eponyms originate from ancient practices where names of prominent individuals, such as gods, royalty, or heroes, became attached to places, inventions, or concepts, solidifying their legacy in language. The term derives from the Greek "eponymos," meaning "giving name," with examples like Alexandria named after Alexander the Great. These historical origins illustrate how eponyms serve as linguistic monuments, preserving cultural memory and societal values through naming conventions.
Historical Origins of Allonyms
Allonyms originated historically as a literary device where authors attributed their work to well-known or fictitious figures, often to gain credibility or avoid persecution, with notable examples traced back to ancient Greece and the Renaissance period. This practice contrasts with eponyms, which derive from the names of individuals who directly coined or inspired a term, concept, or invention. Historical allonyms reveal cultural dynamics in authorship attribution, reflecting social, political, and intellectual contexts influencing literary production.
Common Examples of Eponyms
Common examples of eponyms include "Sandwich," derived from the Earl of Sandwich, and "Fahrenheit," named after physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit. Brand names like "Kleenex" for tissues and "Google" as a verb for online searching have also become eponyms. These terms originate from people's names but evolve into generic words widely used in everyday language.
Notable Uses of Allonyms
Allonyms are names or works attributed to one person but actually created by another, often used to honor or conceal the true author's identity. Notable uses of allonyms include the writings published under the name of J.K. Rowling's pseudonym "Robert Galbraith," which allowed her to explore new genres while maintaining anonymity. Another example is the philosophical works attributed to Socrates, written by Plato, illustrating how allonyms preserve legacy and influence across disciplines.
Significance in Literature and Culture
An eponym represents a person or character after whom a particular literary work, place, or invention is named, serving as a powerful symbol linking identity and narrative significance. Allonyms, in contrast, involve the attribution of a text or idea to a different author, often reflecting cultural or ideological shifts and influencing the reception and authority of literary works. Understanding the roles of eponyms and allonyms reveals deep insights into cultural memory, authorship legitimacy, and the dynamics of literary influence.
Eponyms and Allonyms in Modern Usage
Eponyms are terms derived from the names of people, often used to identify products, concepts, or discoveries, such as "Sandwich" from the Earl of Sandwich or "Alzheimer's disease" from Alois Alzheimer. Allonyms refer to works or ideas attributed to a different author than the original creator, commonly seen in literature and academia to maintain anonymity or lend authority. In modern usage, eponyms serve as tools for branding and scientific classification, while allonyms highlight issues of authorship, intellectual property, and cultural context.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Eponym and Allonym
Choosing between an eponym and an allonym depends on the context of attribution and intent behind name usage. Eponyms, derived from real individuals' names, create direct associations with achievements or discoveries, enhancing credibility and recognition. Allonyms, using names of other authors or fictional creators, offer anonymity or stylistic effect, often employed to evoke certain literary traditions or avoid personal exposure.
Eponym Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com