Analepsis, commonly known as a flashback, is a narrative technique used to provide background or context by returning to earlier events within a story. This method enriches character development and plot by revealing motivations and past experiences that influence current actions. Explore the article to understand how analepsis enhances storytelling and engages your audience effectively.
Table of Comparison
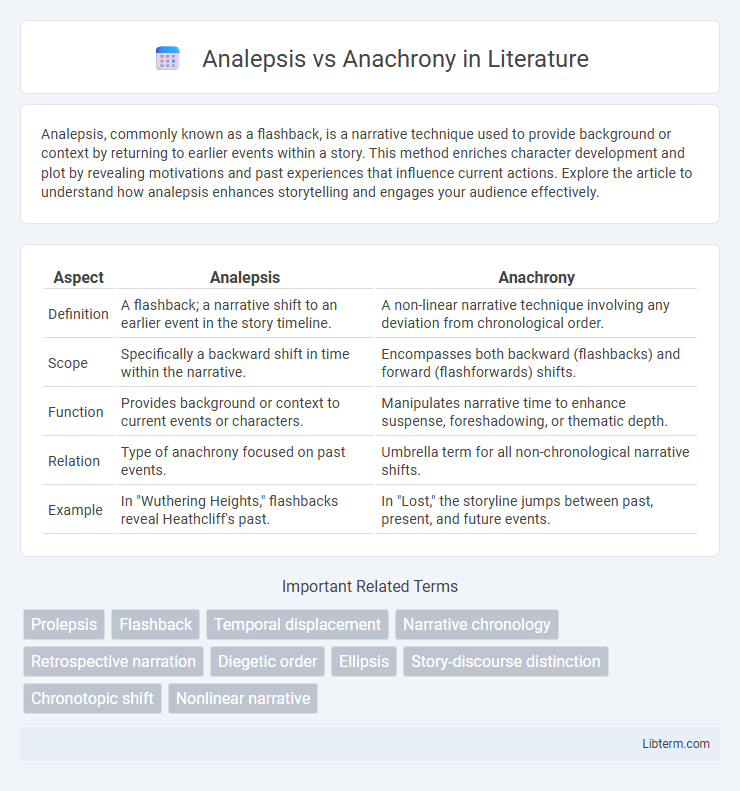
| Aspect | Analepsis | Anachrony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A flashback; a narrative shift to an earlier event in the story timeline. | A non-linear narrative technique involving any deviation from chronological order. |
| Scope | Specifically a backward shift in time within the narrative. | Encompasses both backward (flashbacks) and forward (flashforwards) shifts. |
| Function | Provides background or context to current events or characters. | Manipulates narrative time to enhance suspense, foreshadowing, or thematic depth. |
| Relation | Type of anachrony focused on past events. | Umbrella term for all non-chronological narrative shifts. |
| Example | In "Wuthering Heights," flashbacks reveal Heathcliff's past. | In "Lost," the storyline jumps between past, present, and future events. |
Understanding Analepsis and Anachrony
Analepsis is a narrative technique involving a flashback that interrupts the chronological flow to revisit earlier events, enhancing story depth and character motivation. Anachrony refers to any disruption in the chronological sequence of events, encompassing both analepsis (flashbacks) and prolepsis (flash-forwards), which creators use to enrich narrative complexity and audience engagement. Understanding analepsis within anachrony allows for better analysis of temporal structures in literature, film, and storytelling media.
Defining Key Terms: Analepsis Explained
Analepsis, a narrative technique commonly known as a flashback, involves a return to an earlier point in the storyline to provide background or context. It enhances storytelling by revealing crucial information about characters or events that influence the current plot, distinguishing it from anachrony, which broadly refers to any temporal disruption in narrative order. Understanding analepsis as a specific form of anachrony is essential for analyzing complex narrative structures in literature and film.
What is Anachrony in Narrative Structure?
Anachrony in narrative structure refers to the displacement of events from their chronological order within a story, encompassing both analepsis (flashbacks) and prolepsis (flashforwards). This temporal manipulation enables complex storytelling by altering the sequence in which the plot unfolds, enhancing suspense and thematic depth. Unlike simple linear narratives, anachrony disrupts the timeline to provide background information or foreshadow future events, enriching the reader's understanding of character motivations and plot development.
Types of Temporal Distortions in Literature
Analepsis and anachrony are key types of temporal distortions in narrative literature that manipulate the chronological sequence of events. Analepsis, commonly known as a flashback, provides a backward shift to reveal past events that inform the present narrative context. Anachrony broadly encompasses all temporal disruptions, including analepsis and prolepsis, the latter being a flash-forward that anticipates future events.
Analepsis: Functions and Examples
Analepsis, a key narrative technique in literary theory, functions as a flashback that enriches the story by revealing past events crucial for character development and plot understanding. It interrupts the chronological flow, providing readers with essential background information or hidden motives, often enhancing emotional depth and thematic complexity within works like Marcel Proust's "In Search of Lost Time" or Faulkner's "The Sound and the Fury." This narrative device contrasts with anachrony, which broadly denotes any chronological disruption, while analepsis specifically refers to retrospection that anticipates or explains current narrative contexts.
Exploring the Scope of Anachrony
Anachrony encompasses all narrative time shifts, including analepsis (flashbacks) and prolepsis (flash-forwards), enabling complex temporal structures in storytelling. Exploring the scope of anachrony reveals its capacity to manipulate chronological order, enrich plot development, and deepen thematic resonance by juxtaposing past, present, and future events. This temporal flexibility enhances narrative engagement and allows for multifaceted character exploration and thematic layering.
Comparing Analepsis and Other Forms of Anachrony
Analepsis, a subtype of anachrony, specifically refers to a flashback that interrupts the chronological sequence of events to provide background information or context. In contrast, other forms of anachrony include prolepsis, which projects future events ahead of the current narrative timeline, creating anticipation or foreshadowing. Comparing analepsis and prolepsis reveals their opposite temporal orientations within the broader category of anachrony, both essential for complex narrative structures in literature and film.
Narrative Impact: Why Authors Use Analepsis
Analepsis, a form of anachrony, serves to enrich narrative impact by providing critical background information that shapes character motivations and plot developments, enhancing reader engagement through deeper understanding. Authors use analepsis to create suspense or emotional resonance by revealing past events strategically, allowing audiences to piece together the story non-linearly and appreciate the complexity of characters. This technique fosters a multidimensional narrative, making the storytelling more immersive and intellectually stimulating by linking past and present events meaningfully.
Anachrony Across Literary Genres
Anachrony, the non-linear sequencing of events, appears across literary genres such as novels, drama, and film to disrupt chronological order and enhance narrative depth. In novels, anachrony often manifests as flashbacks or flashforwards that reveal crucial backstory or foreshadow events, while in drama, it can create tension through temporal shifts within scenes. Film utilizes anachrony visually and temporally to manipulate viewer perception, often blending multiple timelines for complex storytelling.
Enhancing Storytelling: Choosing Between Analepsis and Anachrony
Analepsis, a specific form of anachrony, refers to flashbacks that reveal past events to deepen character development and plot complexity, enhancing storytelling by providing crucial context. Anachrony broadly encompasses all narrative disruptions of chronological order, including both analepsis (flashbacks) and prolepsis (flash-forwards), allowing authors to manipulate time for dramatic tension and thematic layering. Selecting between analepsis and broader anachrony techniques depends on the desired narrative impact, with analepsis ideal for reflective depth and anachrony offering diverse temporal shifts to engage audiences more dynamically.
Analepsis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com