Foreshadowing subtly hints at future events, creating suspense and preparing Your mind for plot twists. Writers use this literary device to engage readers by planting clues that add layers of meaning to the narrative. Discover how foreshadowing enhances storytelling throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
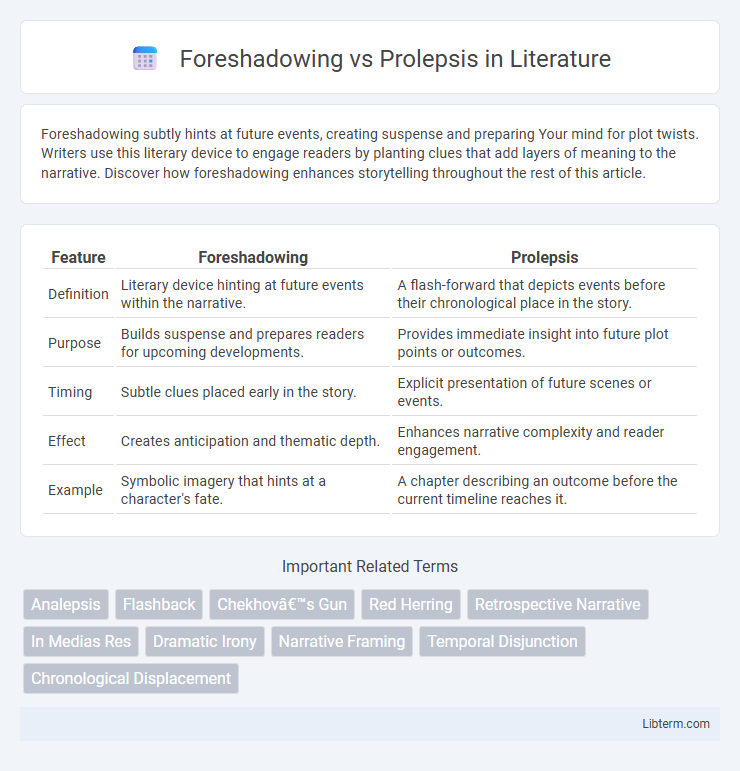
| Feature | Foreshadowing | Prolepsis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary device hinting at future events within the narrative. | A flash-forward that depicts events before their chronological place in the story. |
| Purpose | Builds suspense and prepares readers for upcoming developments. | Provides immediate insight into future plot points or outcomes. |
| Timing | Subtle clues placed early in the story. | Explicit presentation of future scenes or events. |
| Effect | Creates anticipation and thematic depth. | Enhances narrative complexity and reader engagement. |
| Example | Symbolic imagery that hints at a character's fate. | A chapter describing an outcome before the current timeline reaches it. |
Understanding Foreshadowing: A Literary Overview
Foreshadowing in literature involves subtle hints or clues about events that will occur later in the narrative, enriching the reader's anticipation and emotional engagement. This technique contrasts with prolepsis, or flashforward, which explicitly presents future events before returning to the present timeline. Understanding foreshadowing enhances appreciation of thematic depth and narrative structure by revealing how authors seed future developments through symbols, dialogue, or setting.
Defining Prolepsis: Meaning and Usage
Prolepsis is a narrative technique involving the anticipation or representation of events that will occur later in the story, often used to create suspense or provide insight into future outcomes. This literary device differs from foreshadowing by explicitly depicting future events rather than hinting at them subtly. Prolepsis can manifest as flash-forwards, character thoughts, or direct narrative interruption, enhancing plot complexity and reader engagement.
Historical Origins of Foreshadowing and Prolepsis
Foreshadowing originated in classical Greek literature, where playwrights used subtle hints to prepare audiences for future plot twists, enhancing dramatic tension. Prolepsis, derived from the Greek term meaning "anticipation," found its roots in rhetoric and narrative techniques as a way to introduce and address future events or counterarguments ahead of time. Both concepts evolved through Roman and medieval storytelling, influencing modern narrative structures in literature and film.
Key Differences Between Foreshadowing and Prolepsis
Foreshadowing hints at future events through subtle clues embedded in the narrative, creating anticipation without revealing specific details. Prolepsis, or flash-forward, directly presents future scenes or information, disrupting chronological order to provide immediate insight into upcoming plot developments. The key difference lies in foreshadowing's indirect suggestion versus prolepsis's explicit depiction of future events.
Techniques for Effective Foreshadowing
Effective foreshadowing employs subtle clues, symbolic imagery, and strategic dialogue to hint at future events without revealing too much, maintaining reader intrigue. Techniques such as planting objects, using metaphorical references, and crafting character behavior that alludes to upcoming plot twists enhance narrative cohesion and suspense. Mastering the balance between foreshadowing and prolepsis creates a seamless temporal flow, enriching storytelling depth and audience engagement.
Techniques for Skillful Prolepsis
Skillful prolepsis employs techniques such as flash-forwards, character anticipation, and narrative time shifts to reveal future events without disrupting story cohesion. This method creates suspense and deepens thematic resonance by strategically placing future information within the present timeline. Mastery of prolepsis enhances narrative complexity and engages audiences through layered storytelling.
Impact of Foreshadowing on Reader Expectations
Foreshadowing subtly hints at future events, shaping reader expectations by creating suspense and anticipation, which enhances engagement with the narrative. This technique primes readers to look for clues, influencing their interpretation of unfolding events and increasing emotional investment. In contrast, prolepsis, or flash-forward, explicitly reveals future occurrences, potentially diminishing suspense but providing dramatic irony and complex narrative layers.
How Prolepsis Shapes Narrative Structure
Prolepsis shapes narrative structure by presenting future events or outcomes before their chronological occurrence, creating anticipation and complex temporal layers within the story. This technique allows authors to manipulate reader expectations and deepen engagement by revealing key plot points ahead of time, thereby influencing the interpretive framework of the narrative. By juxtaposing present moments with glimpses of the future, prolepsis enhances tension and thematic resonance throughout the text.
Common Examples in Classic and Modern Literature
Foreshadowing in classic literature often appears as subtle hints or symbols, such as the storm in Shakespeare's "Macbeth" signaling chaos to come, while in modern works like "The Great Gatsby," the recurring eyes of Dr. T.J. Eckleburg suggest impending doom. Prolepsis, or flashforward, frequently surfaces in Sophocles' "Oedipus Rex," where the audience foresees Oedipus's tragic fate, and in contemporary novels like "Slaughterhouse-Five," where the nonlinear narrative reveals future events out of sequence. Both devices enrich storytelling by creating anticipation and deepening thematic complexity across eras.
Choosing the Right Device: Foreshadowing or Prolepsis?
Choosing the right narrative device between foreshadowing and prolepsis depends on the intended impact on the audience's anticipation and understanding. Foreshadowing subtly hints at future events, creating suspense and preparing readers emotionally, whereas prolepsis involves a direct leap forward in the timeline, revealing future events to increase dramatic irony or thematic depth. Writers should consider pacing and narrative clarity when deciding whether to plant indirect clues or provide explicit glimpses of the future to enhance storytelling effectiveness.
Foreshadowing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com