Satire uses humor, irony, and exaggeration to critique social, political, or cultural issues, exposing flaws and prompting reflection. This literary technique engages readers by highlighting absurdities in a way that provokes thought and discussion. Explore the rest of the article to understand how satire influences society and sharpens critical thinking.
Table of Comparison
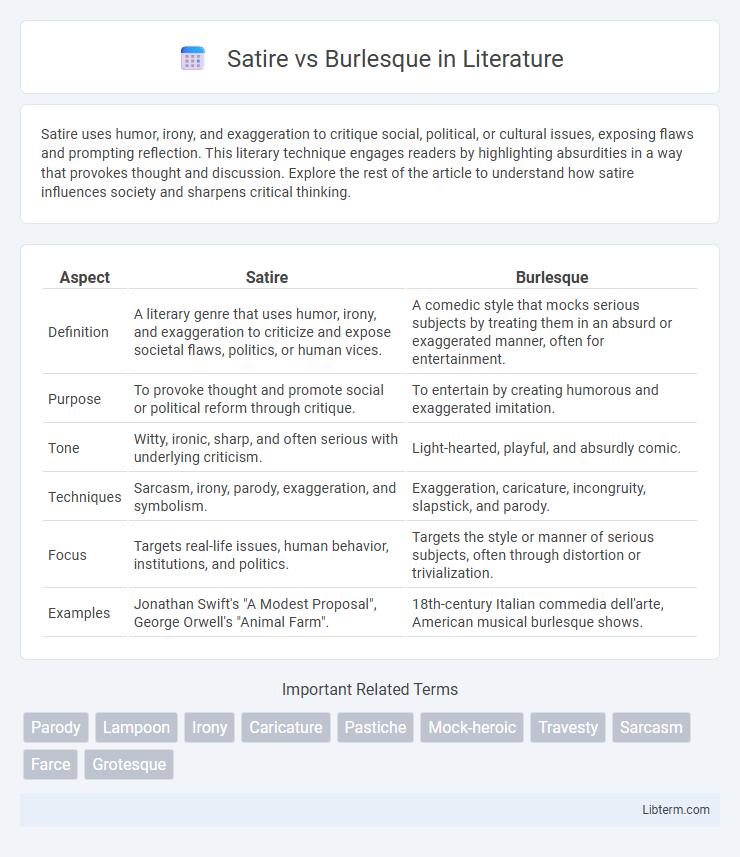
| Aspect | Satire | Burlesque |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A literary genre that uses humor, irony, and exaggeration to criticize and expose societal flaws, politics, or human vices. | A comedic style that mocks serious subjects by treating them in an absurd or exaggerated manner, often for entertainment. |
| Purpose | To provoke thought and promote social or political reform through critique. | To entertain by creating humorous and exaggerated imitation. |
| Tone | Witty, ironic, sharp, and often serious with underlying criticism. | Light-hearted, playful, and absurdly comic. |
| Techniques | Sarcasm, irony, parody, exaggeration, and symbolism. | Exaggeration, caricature, incongruity, slapstick, and parody. |
| Focus | Targets real-life issues, human behavior, institutions, and politics. | Targets the style or manner of serious subjects, often through distortion or trivialization. |
| Examples | Jonathan Swift's "A Modest Proposal", George Orwell's "Animal Farm". | 18th-century Italian commedia dell'arte, American musical burlesque shows. |
Defining Satire and Burlesque
Satire is a literary and artistic form that uses humor, irony, and exaggeration to criticize and expose the flaws or vices of individuals, society, or institutions, aiming to provoke thought and reform. Burlesque, on the other hand, is a comedic genre that ridicules serious subjects by treating them in a ludicrous or exaggeratedly trivial manner, often relying on parody and over-the-top performances. While satire targets underlying social or political issues through pointed critique, burlesque prioritizes entertainment and exaggeration without necessarily engaging in moral or intellectual commentary.
Historical Origins of Satire and Burlesque
Satire originated in ancient Rome with writers like Horace and Juvenal using humor and irony to criticize social and political issues, embedding moral lessons through sharp wit. Burlesque emerged in the 17th century as a theatrical form that exaggerated and mocked serious subjects by using parody and ludicrous imitation, evolving into popular variety shows by the 19th century. Both genres historically served as cultural tools to challenge authority and entertain audiences, but satire often aimed for intellectual critique while burlesque emphasized broad physical humor and spectacle.
Key Characteristics of Satire
Satire employs irony, wit, and exaggeration to expose and criticize human vices or societal flaws, aiming to provoke thought and reform. It often uses humor with a serious purpose, targeting politics, culture, or behavior through sharp social commentary. Classic examples include Jonathan Swift's "A Modest Proposal" and George Orwell's "Animal Farm," which highlight satire's ability to blend entertainment with moral critique.
Essential Elements of Burlesque
Burlesque is characterized by its exaggerated imitation of serious subjects using humor, parody, and caricature to entertain and provoke laughter. Essential elements include over-the-top costumes, physical comedy, exaggerated gestures, and playful mockery of social norms or literary works. This form relies heavily on visual spectacle and comedic timing to create an amusing distortion of its source material, distinguishing it from the more intellectually driven critique found in satire.
Satire vs Burlesque: Main Differences
Satire and burlesque both use humor to critique, but satire targets societal flaws with irony and wit to provoke thought and change, while burlesque amplifies and exaggerates subjects for comedic or ludicrous effect. Satire often conveys deeper moral or political messages, employing subtlety and nuance, whereas burlesque tends to be overt, theatrical, and focused on entertainment through parody or caricature. The main differences lie in satire's intent to inspire reflection and burlesque's goal of eliciting laughter through exaggeration and absurdity.
Literary Techniques in Satire and Burlesque
Satire employs literary techniques such as irony, sarcasm, exaggeration, and parody to criticize human follies and societal issues, often with a moral or political motive. Burlesque utilizes exaggeration, caricature, and ludicrous imitation to create humorous or grotesque effects, frequently targeting specific genres or serious subjects to provoke laughter rather than reflection. Both forms use parody and irony, but satire aims to provoke thought and reform, while burlesque primarily seeks entertainment through ridiculous distortion.
Famous Examples in Literature and Media
Satire is exemplified by Jonathan Swift's "A Modest Proposal," which uses irony and exaggeration to criticize social issues, while burlesque is represented by Miguel de Cervantes' "Don Quixote," parodying chivalric romances with comedic imitation. In media, satirical shows like "The Daily Show" expose political absurdities, whereas burlesque-style performances in variety shows emphasize exaggerated humor and parody of popular culture. These genres differ in intent, with satire aiming for social critique and burlesque focusing on entertainment through caricature.
Purpose and Audience Engagement
Satire aims to expose and criticize societal flaws or human vices through humor, provoking critical reflection and societal change, often appealing to an intellectually engaged audience. Burlesque focuses on exaggeration and parody for entertainment, using ludicrous imitation to elicit laughter without necessarily promoting deeper analysis, targeting a broader, entertainment-seeking crowd. Both techniques engage audiences via humor, but satire stimulates thought while burlesque prioritizes amusement through absurdity.
Impact on Society and Culture
Satire critiques social and political issues through humor, fostering critical thinking and promoting awareness that can inspire reform and cultural reflection. Burlesque uses exaggerated performance and parody to entertain, often challenging norms and social conventions by highlighting absurdities in a more theatrical and less direct manner. Both forms influence society by shaping perceptions, but satire tends to drive intellectual engagement, while burlesque emphasizes spectacle and emotional response.
Choosing the Right Form: Satire or Burlesque
Choosing between satire and burlesque depends on the intended impact and audience engagement; satire employs irony and exaggeration to criticize social or political issues with wit and insight. Burlesque uses parody and grotesque exaggeration to entertain by mocking subjects in a more exaggerated and often comedic manner. Understanding the nuanced tone and purpose behind each form ensures effective communication and audience resonance.
Satire Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com